Prednisone
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- PREDNISONE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
- PREDNISONE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- PREDNISONE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- STORAGE AND HANDLING
- REFERENCES
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
PREDNISONE DESCRIPTION
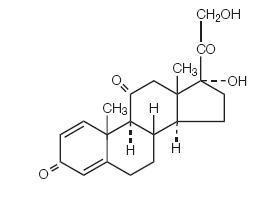
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
INDICATIONS & USAGE
Endocrine disorders: primary or secondary adrenocortical insufficiency (hydrocortisone or cortisone is the first choice; synthetic anaogs may be used in conjunction with mineralocorticoids where applicable; in infancy mineralocorticoid supplementation is of particular importance); congenital adrenal hyperplasia; hypercalcemia associated with cancer; nonsuppurative thyroiditis.
Rheumatic disorders:as adjunctive therapy for short-term administration (to tide the patient over an acute episode or exacerbation) in: psoriatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, including juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (selected cases may require low-dose maintenance therapy), ankylosing spondylitis, acute and subacute bursitis, acute nonspecific tenosynovitis, acute gouty arthritis, post-traumatic osteoarthritis, synovitis of osteoarthritis, epicondylitis.
Collagen diseases:during an exacerbation or as maintenance therapy in selected cases of: systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic dermatomyositis (polymyositis), acute rheumatic carditis.
Dermatologic diseases: pemphigus; bullous dermatitis herpetiformis; severe erythema multiforme (Stevens-Johnson syndrome); exfoliative dermatitis; mycosis fungoides; severe psoriasis; severe seborrheic dermatitis.
Allergic states: control of severe or incapacitating allergic conditions intractable to adequate trials of conventional treatment: seasonal or perennial allergic rhinitis; bronchial asthma; contact dermatitis; atopic dermatitis; serum sickness; drug hypersensitivity reactions.
Ophthalmic diseases:severe acute and chronic allergic and inflammatory processes involving the eye and its adnexa such as: allergic corneal marginal ulcers, herpes zoster ophthalmicus, anterior segment inflammation, diffuse posterior uveitis and choroiditis, sympathetic ophthalmia, allergic conjunctivitis, keratitis, chorioretinitis, optic neuritis, iritis and iridocyclitis.
Respiratory diseases: symptomatic sarcoidosis; Loeffler's syndrome not manageable by other means; berylliosis; fulminating or disseminated pulmonary tuberculosis when used concurrently with appropriate antituberculous chemotherapy; aspiration pneumonitis.
Hematologic disorders: idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in adults; secondary thrombocytopenia in adults; acquired (autoimmune) hemolytic anemia; erythroblastopenia (RBC anemia); cogenital (erythroid) hypoplastic anemia.
Neoplastic diseases:for palliative management of: leukemias and lymphomas in adults, acute leukemia of childhood.
Edematous states:to induce a diuresis or remission of proteinuria in the nephrotic syndrome, without uremia, of the idiopathic type or that due to lupus erythematosus.
Gastrointestinal diseases:to tide the patient over a critical period of the disease in: ulcerative colitis, regional enteritis.
Nervous system:acute exacerbations of multiple sclerosis.
Miscellaneous: tuberculous meningitis with subarachnoid block or impending block when used concurrently with appropriate antituberculous chemotherapy; trichinosis with neurologic or myocardial involvement.
PREDNISONE CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS
Usage in pregnancy
PRECAUTIONS
General PrecautionsDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
Drug Interactions
Information for Patients
PREDNISONE ADVERSE REACTIONS
Fluid and electrolyte disturbances: sodium retnetion; fluid retention; congestive heart failure in susceptible patients; potassium loss; hypokaleic alkalosis; hypertension.Musculoskeletal: muscle weakness; steroid myopathy; loss of muscle mass; osteoporosis; tendon rupture, particularly of the Achiles tendon; vertebral compression fractures; aseptic necrosis of femoral and humeral heads; pathologic fracture of long bones.
Gastrointestinal: peptic ulcer with possible perforation and hemorrhage; pancreatitis; abdominal distention; ulcerative esophagitis; increases in alanine transaminase (ALT, SGPT), aspartate transaminase (AST, SGOT) and alkaline phosphatase have been observed following corticosteroid treatment. These changes are usually small, not associated with any clinical syndrome and are reversible upon discontinuation.
Dermatologic: impaired wound healing; thin fragile skin; petechiae and ecchymoses; facial erythema; increased sweating; may suppress reactions to skin tests.
Metabolic:negative nitrogen balance due to protein catabolism.
Neurological: increased intracranial pressure with papilledema (pseudo-tumor cerebri) usually after treatment; convulsions; vertigo; headache.
Endocrine: menstrual irregularities; development of cushingoid state; secondary adrenocortical and pituitary unresponsiveness, particularly in times of stress, as in trauma, surgery or illness; suppression of growth in children; decreased carbohydrate tolerance; manifestations of latent diabetes mellitus; increased requirements for insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents in diabetics.
Ophthalmic: posterior subcapsular cataracts; increased intraocular pressure; glaucoma; exophthalmos.
Additional Reactions:urticaria and other allergic, anaphylactic or hypersensitivity reactions.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
IT SHOULD BE EMPHASIZED THAT DOSAGE REQUIREMENTS ARE VARIABLE AND MUST BE INDIVIDUALIZED ON THE BASIS OF THE DISEASE UNDER TREATMENT AND THE RESPONSE OF THE PATIENT.After a favorable response is noted, the proper maintenance dosage should be determined by decreasing the initial drug dosage in small decrements at appropriate time intervals until the lowest dosage which will maintain an adequate clinical response is reached. It should be kept in mind that constant monitoring is needed in regard to drug dosage. Included in the situations which may make dosage adjustments necessary are changes in clinical status secondary to remissions or exacerbations in the disease process, the patientcondition. If after long-term therapy the drug is to be stopped, it is recommended that it be withdrawn gradually rather than abruptly.Multiple Sclerosis
Alternate Day Therapy
HOW SUPPLIED
DAN DANand5052supplied in bottles of 100 and 1000.DAN DANand5442supplied in bottles of 100, 500 and 1000.
DAN DANand5443supplied in bottles of 100, 500 and 1000.
STORAGE AND HANDLING
REFERENCES
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION

PrednisonePREDNISONE TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!