IDkit HP ONE
Package Insert IDkit:Hp™ for the Exalenz BreathID® System BREATH TEST FOR DETECTION of H. pylori
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- PACKAGE INSERT 005569
- INTENDED USE
- SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION
- PRINCIPLES OF THE EXALENZ BREATHID® BREATH TEST
- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- SHELF LIFE AND STORAGE
- PATIENT PREPARATION
- PROCEDURE
- QUALITY CONTROL
- CALIBRATION
- TEST RESULTS
- LIMITATIONS OF THE TEST
- INTERFERING SUBSTANCES
- EXPECTED VALUES
- PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
- REFERENCES
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
PACKAGE INSERT 005569
This package insert includes information for conducting the BreathID® H. pylori test for two modes of analysis with two Breath Test Kits:
| Breath Test Kit |
BreathID® Mode |
| IDkit: HpTM ONE |
H. pylori PATIENT MODE |
| IDkit: HpTM TWO |
H. pylori BAG MODE |
The following are trademarks of Exalenz Bioscience Ltd.: Exalenz™ , MCS™, IDcircuit™, IDcheck™, IDkit: Hp™, and BreathID®
All reference to Exalenz in this document refers to the company Exalenz Bioscience Ltd.
Note: No license, expressed or implied, is granted under any patents of Exalenz Bioscience Ltd.
INTENDED USE
The Exalenz BreathID® Breath Test System is intended for use in the qualitative detection of urease associated with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) in the human stomach and as an aid in the initial diagnosis and post treatment monitoring of H. pylori infection in adult patients. This test should be used after at least four weeks of H. pylori eradication therapy. For these purposes, the system utilizes Molecular Correlation Spectrometry (MCS™) for the measurement of the ratio of 13CO2 to 12CO2 in breath samples.
The Exalenz BreathID® System is used to detect and monitor H. pylori infection by measuring changes in the 13CO2 to 12CO2 ratio in a patient’s breath following the ingestion of 13C-urea.The Exalenz BreathID® Breath Test System consists of the IDkit: Hp™ kits containing 13C-urea tablet, 75 mg for oral solution and 4.3 g Citrica Powder (4g citric acid) for oral solution; the BreathID® device and the IDcheck™ system quality control accessory.The device is for use by trained healthcare professionals and the test kit is to be administered under a physician’s supervision.
SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION
Since the initial identification of H. pylori in the early 1980s [1], the management of upper gastrointestinal disease has changed dramatically. “Helicobacter pylori is now recognized as an important pathogen and a casual relationship between H. pylori and chronic active gastritis, duodenal ulcer, and gastric ulcer is well documented” [2]. Currently there are numerous H. pylori detection technologies for upper gastrointestinal disease including biopsy and serum analysis. These technologies depend on two general approaches for obtaining a sample for testing: invasive and non-invasive.The first invasive test method requires an endoscopic gastric biopsy. The tissue collected from the biopsy is then examined in a laboratory by microbiological culture of the organism, direct detection of urease activity in the tissue (for example, the CLOtest®), or by histological examination of stained tissue. Biopsy-based methods present an element of patient risk and discomfort and may provide false negative results due to sampling errors.The second invasive test is a serological test; this requires a blood sample which is used to detect serum antibodies to H. pylori. The disadvantage of this test is that it is difficult to distinguish between positive active infections and past exposure to infection, and therefore it is not a conclusive indicator of current H. pylori infection. 13C-urea breath tests provide a non-invasive and non-hazardous analysis of the exhaled breath. The BreathID® test (described in the next section) measures the 12CO2 and 13CO2 components of the exhaled breath before and after the oral ingestion of 13C-enriched urea. This establishes the baseline ratio of 13CO2 / 12CO2 and the post ingestion ratio of 13CO2 / 12CO2 in order to determine the Delta Over Baseline (change in the 13CO2 / 12CO2 ratio). (Delta Over Baseline is defined as: {(13CO2
(N)/12CO2
(N) - 13CO2
(0)/12CO2
(0))*1000}/(13CO2
(PDB)/12CO2
(PDB)) where PDB is the standard 13C/12C isotope ratio (=1.1273%). (0) is the base line measurement and (N) is the measurement of interest.)
PRINCIPLES OF THE EXALENZ BREATHID® BREATH TEST
The Exalenz BreathID® non-invasive breath test is a diagnostic test that analyzes a breath sample before and after ingestion of 13C-enriched urea; it is used to identify those patients with H. pylori infection.The Exalenz BreathID® breath test is performed as follows: a 75 mg 13C-urea tablet and 4.3 g Citrica Powder are dissolved in water, and the resulting solution is ingested by the patient. The presence of the Citrica creates an acidic environment in the stomach and also delays the transfer of the ingested solution to the duodenum. These two characteristics facilitate the decomposition of the urea by H. pylori, if present. Thus, in the presence of urease associated with gastric H. pylori, 13C-urea is decomposed to 13CO2 and NH3 according to the following equation:
2 13C-urea + 2 H2O ----------> H. pylori urease----------> 2 13CO2+ 2 NH3
The 13CO2 is absorbed into the blood and then exhaled in the breath. Absorption and distribution of 13CO2 is fast. Therefore, the cleavage of urea by the H. pylori urease that produces the 13CO2 occurs immediately after the solution is ingested and enables immediate detection of increased 13CO2 in the exhaled breath of H. pylori-positive patients.In the case of H. pylori-negative patients, the 13C-urea does not produce 13CO2 in the stomach because there are no human enzymes that can decompose the urea in the stomach.
DESCRIPTION OF THE 13C-UREA DIAGNOSTIC COMPONENT
The diagnostic drug component of the kits is 13C-enriched urea prepared as a tablet. The tablet should be dissolved with Citrica Powder in a glass of water, providing a clear, colorless solution for oral administration.
The 75 mg 13C-urea component is supplied as a tablet in a sealed pouch. The 4.3 g of Citrica Powder (4 g citric acid [3,4,5], aspartame, and Tutti Frutti flavoring) is supplied in a separate sealed pouch.
An average adult body normally contains about 9.0 grams of urea, which is a product of protein metabolism. Urea in the body is referred to as a natural isotopic abundance urea since it is composed of 98.9% 12C-urea and 1.1% 13C-urea.
Greater than or equal to 99% of the carbon molecules in the supplied tablet are in the form of 13C; a stable, naturally occurring, non-radioactive isotope of carbon. 13C-urea is the diamide of 13C carbonic acid and is highly soluble in water (1 gram per ml at 25OC). It has the following chemical formula: 13CH4N2O.
DESCRIPTION OF THE MODE OF OPERATION OF THE BREATHID® DEVICE
The BreathID® device can be operated in two pre-selected modes of testing. These are the PATIENT MODE and the BAG MODE as described below.
PATIENT MODE
The test begins with the selection of the PATIENT MODE and with the collection of a baseline breath sample. The patient breathes normally while the BreathID® device collects samples through the IDcircuit™ nasal cannula. The IDcircuit™ extracts moisture and patient secretions from the breath samples to provide accurate CO2 readings, and the device measures the 13CO2 / 12CO2 ratio of the baseline measurement. The patient then ingests a test drink consisting of 13C-urea tablet 75 mg and 4.3 g of citric Powder (4g citric acid).
While the patient continues to breathe normally, the BreathID® device continually and non-invasively samples the patient’s breath (via the cannula) and measures the changes in the 13CO2 / 12CO2 ratio versus the original baseline sample. These changes are displayed as a graph on the large display screen while the test continues. The graph shows multiple points that allow the physician to identify the change in the DOB of the 13CO2 / 12CO2 ratio in response to the administered 13C-urea. Once the BreathID® device has collected enough data to determine whether or not a patient is H. pylori-positive, (i.e. the graph passes the threshold unambiguously), it automatically ends the test and prints out the results.
BAG MODE
The test begins with the collection of normally exhaled breath of the patient into a baseline breath collection bag, which is then sealed. This sample provides the baseline isotope ratio reading. Next, the patient ingests the test drink consisting of dissolved of 13C-urea tablet, 75 mg and 4.3 g of Citrica Powder (4g citric acid), as in the PATIENT MODE. After 20 minutes, the patient exhales into a post-ingestion breath collection bag, which is subsequently sealed.
The test is performed on the BreathID® device. After selecting BAG MODE, the baseline and then the post-ingestion breath collection bags are connected to the BreathID® device, one after the other. Each bag is separately sampled by the BreathID® device to determine the 13CO2 / 12CO2 ratio. The values of the ratios obtained are compared in order to determine the Delta Over Baseline (change in the 13CO2 / 12CO2 ratio between the baseline and the post-ingestion measurements). Once the BreathID® completes measuring the bags, it automatically displays and prints the results. This enables the physician to determine whether a patient is positive or negative for H. pylori, based on whether or not the graph passed the threshold line.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- For in vitro diagnostic use only. The 13C-urea tablet and Citrica Powder are dissolved in a glass of water and the resulting solution is taken orally as part of the diagnostic procedure.
- Phenylketonurics: Contains Phenylalanine, 84 mg per dosage unit of Citrica Powder.
- In the case of accidental overdose – drink water and call the physician.
- A negative result does not rule out the possibility of H. pylori infection. False negative results can occur with this procedure. If clinical signs suggest H. pylori infection, retest with a new sample or an alternate method.
- A false positive test may (rarely) occur due to urease associated with other gastric spiral organisms observed in humans such as Helicobacter heilmanni.
- A false positive test could occur in patients who have achlorhydria.
- Antimicrobials, proton pump inhibitors, and bismuth preparations are known to suppress H. pylori. Ingesting these medications within two weeks prior to performing the breath test may produce false negative test results.
- Tiny particles may remain visible in the reconstituted 13 C-urea and Citrica solution after thorough mixing for up to five minutes. However, if more substantial particulate matter is still present after five minutes of mixing, the solution should not be used, and a new kit should be opened.
SHELF LIFE AND STORAGE
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. The following components of the test kits have expiration dates: the 13C-urea tablet and the Citrica Powder. Do not use either of these components beyond the expiration date stated on the respective labels.
PATIENT PREPARATION
Remind the patient that the Citrica contains 84 mg of phenylalanine per packet of Citrica. Phenylketonurics restrict dietary phenylalanine.The patient should have fasted at least one hour before administering the solution.The patient should not have taken antimicrobials, proton pump inhibitors or bismuth preparations within two weeks prior to administering the test.
PROCEDURE
PATIENT MODE
Materials
A single BreathID® IDkit: Hp™ ONE is provided to perform the Breath Test in the PATIENT MODE.
Each IDkit: Hp™ ONE for the Exalenz BreathID® Breath Test System contains:
- One Tablet of 13C-enriched urea, 75 mg.
- One Packet of 4.3 g (4 g citric acid, aspartame, Tutti Frutti flavoring) of Citrica Powder.
- One IDcircuit™ nasal cannula.
- One straw for stirring and drinking.
SystemCheck
One SystemCheck accessory is supplied for every 25 units of BreathID® kits, IDkit: Hp™ ONE. The SystemCheck accessory supplied with the BreathID® kits provides quality control for the BreathID® system as described in the Quality Control section. The SystemCheck has an expiration date and shouldn't be used beyond this date as stated on the label.
Materials Needed But Not Provided:
- A drinking cup with a capacity of eight ounces (236 ml) or greater.
- Tap water.
Step-by-Step Procedure for the PATIENT MODE
For more detailed information regarding the step-by-step procedure, on screen instructions, and device operation, refer to the BreathID® Operator’s Manual.
For performing the BreathID® H. pylori test in PATIENT MODE, use the IDkit: Hp™ ONE single-use kit.
Administer the test drink within two hours of preparation, as this is the maximal time for maintaining solution stability.
Tiny particles may remain visible after thorough mixing. However, if more substantial particulate matter is still present after five minutes of stirring, discard the solution and repeat the procedure with a new kit.
Do not administer the drink until prompted by the screen instructions on the device (this makes certain that the baseline sample has been collected properly).
BAG MODE
Materials
A single BreathID® IDkit: Hp™ TWO is provided to perform the Breath Test in the BAG MODE. Each Exalenz IDkit: Hp™ TWO for the Exalenz BreathID® Breath Test System contains:
- One Tablet of 13C-enriched urea, 75 mg
- One Packet with 4.3 g (4 g citric acid, aspartame, Tutti Frutti flavoring) of Citrica Powder
- Two differently colored Breath Collection Bags. One bag is silver and marked as BASELINE (T-0) while the other is blue and marked as POST-INGESTION (T-20).
- One mouthpiece.
- Two caps, one for sealing each of the collection bags after the breath collections.
- One straw for stirring and drinking.
- One abridged User Guide (Instruction for Use - IFU).
- One patient requisition form.
- Two labels (stickers) to be completed with patient and clinical institution information.
- One plastic bag for the filled breath collection bags and the patient requisition form.
SystemCheck
One SystemCheck accessory is supplied for every 25 units of BreathID® IDkit: Hp™ TWO. The SystemCheck accessory supplied with IDkit: Hp™ TWO provides quality control for the BreathID® System, as described in the Quality Control section. The SystemCheck has an expiration date and shouldn't be used beyond this date as stated on the label.
Materials Needed But Not Provided:
- A drinking cup with a capacity of 8 oz (236 ml) or greater.
- Tap water.
Step-by-Step Procedure of the BAG MODE
For detailed information regarding the step-by-step procedure, on screen instructions, and device operation, refer to the BreathID® Operator’s Manual.
For performing the BreathID® H. pylori test in the BAG MODE, use the IDkit: Hp™ TWO single-use kit.
Administer the test drink within two hours of preparation, as this is the maximal time for maintaining solution stability.
Tiny particles may remain visible after thorough mixing. However, if more substantial particulate matter is still present after five minutes, discard the solution and repeat the procedure with a new kit.
H. pylori
IDkit: Hp™ TWO
QUALITY CONTROL
The BreathID® device is an instrument for measuring changes in the ratio of 13CO2 to 12CO2 in the patient’s exhalation. Since the BreathID®is not a laboratory device, no field laboratory quality control procedures are required. The BreathID® device undergoes rigorous quality assurance procedures before leaving the manufacturer.However, to ensure correct functioning of the BreathID® in the field, an accessory labeled SystemCheck is provided for every 25 units of IDkit: Hp™. The BreathID® will automatically display a request to perform a SystemCheck™ after 25 tests are completed. The BreathID® device will not continue to function unless the SystemCheck accessory is used as directed.The SystemCheck quality control is accomplished by introducing a single-use cartridge that contains a known concentration of CO2 into the device after every 25 breath tests. This procedure confirms that the BreathID® System is functional and is performing within specifications.Complete operating information including appropriate quality control activities is provided in the BreathID® Operator’s Manual.
CALIBRATION
The calibration stability of the BreathID® system is ensured by the Exalenz proprietary 12CO2 and 13CO2 Isotope Specific InfraRed (ISIR) lamps. The physical process underlying gas discharge emissions supports this stability. The emissions are caused by molecular rotation-vibration transitions, each generating a spectral line at a specific wavelength, uniquely defined to an accuracy of better than 0.01 Å (Angstrom). Five gas samples of known concentration and isotope ratio are used to adjust the absorption cell calibration curves, aiming to attain identical isotope ratios over the collection range of CO2 concentrations. This will ensure accurate readings in both negative and positive samples.In addition, quality checks as described above in the Quality Control section are performed by the BreathID® device after every 25 tests in order to ensure that the BreathID® System performs within established limits, and calibration is performed if required. Refer to the BreathID® Operator’s Manual for a complete description of the SystemCheck and calibration procedure.
TEST RESULTS
THE TEST METHOD
The ratio of 13CO2 to 12CO2 in breath samples is determined by Molecular Correlation Spectrometry (MCS™), which is utilized by the BreathID® device software.
CALCULATION OF RESULTS
The results of the BreathID® test are provided as Delta Over Baseline. Delta Over Baseline is the difference between the Delta value (based on a ratio of 13CO2 / 12CO2) in the test specimen and the corresponding baseline sample. There are no calculations required by the user.
DETERMINATION OF THE CUTOFF POINT
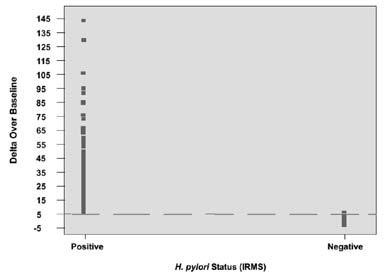
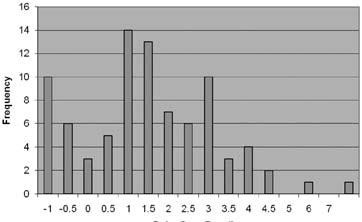
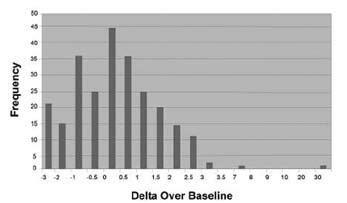
The cutoff point is the level (threshold) used to discriminate betweeny H. pylori-infected and uninfected individuals.The Delta Over Baseline cutoff point was determined to be five in a controlled study of 186 adult asymptomatic and symptomatic patients (101 infected and 85 uninfected). The study was conducted in Israel using a local reference standard called the Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometer (IRMS). The cutoff point was evaluated by determining the BreathID® test result (DOB) threshold at which positive and negative patients, as determined by the Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometer, were best distinguished. Figure 3 shows the BreathID® cutoff point graphically, which distinguishes H. pylori-positive and negative patients.
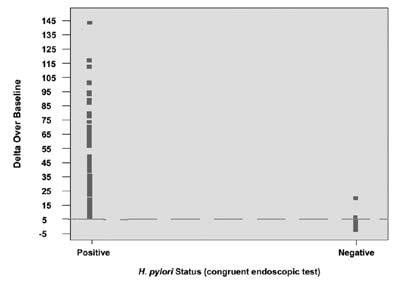
The cutoff point was confirmed in a controlled pivotal clinical study where 300 subjects were enrolled. The study consisted of a pre-therapy and post-therapy phase. Patients enrolled in the pre-therapy phase had dyspeptic symptoms, active peptic ulcer disease, or a past history of peptic ulcer disease. To be eligible for the post therapy phase, H. pylori-positive patients had to be treated for infection four weeks prior to enrollment (some patients participated in both the pre-therapy and post-therapy phases). In the pre-therapy phase, 47 patients were found to be infected and 253 were found to be uninfected. Congruent results obtained by rapid urease test and histological examination of biopsy tissue were used as the reference standard. In the post-therapy phase, 22 patients were infected and 50 were uninfected. The reference standard was a positive finding by endoscopic test (rapid urease or histology) or Meretek UBT®. For more details, refer to the Performance Characteristics section. Figure 4 shows the BreathID® Delta Over Baseline results.
Interpretation of Results
A BreathID® test result of greater than 5 Delta Over Baseline is interpreted as diagnostically positive, indicating the presence of urease associated with H. pylori. A BreathID® test result of less than or equal to 5 Delta Over Baseline is interpreted as diagnostically negative, indicating the absence of urease associated with H. pylori.The 5 Delta Over Baseline cutoff point applies to both initial diagnosis and post treatment monitoring of H. pylori infection.For more details, refer to the Performance Characteristics section.
LIMITATIONS OF THE TEST
- Post treatment monitoring of H. pylori should be performed after at least four weeks of treatment for H. pylori infection. Earlier assessment may give false results.
- Safety and effectiveness in patients under the age of 18 years have not yet been established.
- Data is insufficient for recommending the use of this test on patients with total or partial gastrectomy.
- Data is insufficient to recommend the use of this test on pregnant and lactating women.
- A correlation between the number of H. pylori organisms in the stomach and the BreathID® results has not been established.
INTERFERING SUBSTANCES
Potentially interfering substances typically found in a patient’s breath were tested using the BreathID® System to determine their effect on the test results. The potential sources tested were:
- Mouthwash
- Chewing gum
- Carbonated beverages
- Cigarette smoke
- Acetone (to simulate the effect of ketone production that may result from some diets)
- Alcohol
There was no observation that these substances had any significant influence on the outcome of the test.
EXPECTED VALUES
The following values were obtained for the data from the pivotal study:
PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
REPRODUCIBILITY AND REPEATABILITY RESULTS
Tests were conducted to evaluate the reproducibility and repeatability of results when measurements are made by different technicians and/or using different BreathID® devices, or when testing is done on different days.
REPRODUCIBILITY (BENCH STUDY)
Four different accurate gas isotope mixtures were prepared with Delta Over Baseline values of 0, 2.5, 6.5, and 24 in a bench study. Three operators were asked to operate each of three BreathID® devices, in order to measure the Delta Over Baseline values for samples from each of the four batches. The results demonstrated that the standard deviation and overall reproducibility were stable over different batches for both the operator and the devices. The overall reproducibility standard deviation was 0.77, which is less than the natural variability of the Delta Over Baseline measurement.
REPEATABILITY
Three patients (one H. pylori-negative and two H. pylori-positive) were measured on three different days. From this limited observation, it was assumed that positive and negative subjects maintained their classification with no ambiguity when measured on different occasions. Based on this observed trend and in combination with the reproducibility results, it was concluded that the system is very consistent.
PATIENT RESULTS
The relationship between pre- and post-therapy BreathID® test results in patients enrolled in the clinical study was examined. Of the 13 patients who were positive pre-therapy and negative post-therapy and the three patients who were positive pre- and post-therapy, none had a borderline result post-therapy. The post-therapy negative patients were close to 0 Delta Over Baseline and the post-therapy positive patients were well above the 5 Delta Over Baseline threshold, again supporting the system coherency.
DIAGNOSTIC METHODS COMPARISON IN CLINICAL TRIAL
Experimental Design
The data presented here was collected from a prospective, open-label clinical trial, designed to assess the sensitivity and specificity of the BreathID® test compared to other methods in determining the status of gastrointestinal infection with H. pylori (pre-therapy phase). In addition, the clinical trial was designed to evaluate the ability of the BreathID® system to monitor the efficacy of therapy for H. pylori (post-therapy phase).There were 315 adult pre-therapy patients at two United States hospitals in the study. There were 77 post–therapy patients who were positive for infection and who had undergone eradication therapy at least four weeks previously. Nineteen of these post-therapy patients participated in the pre-therapy phase as well.Patients were evaluated by at least two of four diagnostic methods:
- Histopathology: Biopsy specimens, fixed with 10% buffered formalin, were cut into 4 mm sections, stained with Giemsa stain, and examined by an experienced pathologist.
- Rapid Urease Test (CLOtest®): Biopsy specimens were tested for urease activity with the CLOtest® according to the instructions in its package insert.
- Meretek UBT® Breath Test for H. pylori (post-therapy only): The Meretek UBT® was performed according to the instructions in its package insert.
- Exalenz BreathID® test: The Exalenz BreathID® test was performed in accordance with the procedures described in its package insert.
Results
The results are presented in two-way contingency tables.The exact binomial distribution was used to calculate the lower and upper limits of the 95% confidence intervals of the performance statistic.
Pre-Therapy
Table 1 and Table 2 compare the BreathID® to rapid urease tests and histological exams, respectively. In Table 3, the BreathID® outcome is compared to congruent results from the two endoscopy biopsy-based methods (rapid urease test and histological exam).
Table 1: Comparison of BreathID® Test to Rapid Urease Test (Clotest®)
| CLOtest® | Positive |
Negative |
Total |
| Positive |
50 |
0 |
50 |
| Negative |
2 |
259 |
261 |
| Total |
52 |
259 |
311* |
*Four patients out of the 315 were missing either the rapid urease test or BreathID®test results and therefore were not included in the table.
Relative sensitivity: 100% [95% CI (94.2, 100)]
Relative specificity: 99.2% [95% CI (97.3, 99.9)]
Table 2: Comparison of BreathID® Test to Histology Pre-Therapy
| Histology |
Positive |
Negative |
Total |
| Positive |
47 |
2 |
49 |
| Negative |
6 |
251 |
257 |
| Total |
53 |
253 |
306* |
*Nine patients out of the 315 were missing either histology or BreathID® test results and therefore were not included in the table.
Relative sensitivity: 95.9% [95% CI (86.0, 99.5)]
Relative specificity: 97.7% [95% CI (95.0, 99.1]
Table 3: Comparison of BreathID® Test to Congruent Endoscopic Tests (CLOtest® and histological exam) Pre-Therapy
| Congruent Endoscopic Tests* | Positive |
Negative |
Total |
| Positive |
47 |
0 |
47 |
| Negative |
2 |
251 |
253 |
| Total |
49 |
251 |
300 |
*H. pylori positive is defined as positive rapid urea test and positive histology. H. pylori negative is defined as negative rapid urea test and negative histology.
Sensitivity**: 100% [95% CI (92.5, 100)]
Specificity**: 99.2% [95% CI (97.2, 99.9)]
**These calculations of sensitivity and specificity do not include 15 patients. In five of these patients, results obtained from the rapid urease test and histology did not match, and in 10 of these patients, at least one of the three tests was missing.
Post Therapy
Table 4 compares the BreathID® to congruent results from the two biopsy-based methods (rapid urease test and histological exam) or urea breath test (Meretek UBT®).
Table 4: Comparison of BreathID® Test to Endoscopic Tests or Meretek
| Endoscopic Tests of Meretek UBT®* | Positive |
Negative |
Total |
| Positive |
21 |
1 |
22 |
| Negative |
0 |
50 |
50 |
| Total |
21 |
51 |
72 |
*H. pylori positive is defined as at least one positive on either of the endoscopic tests or Meretek UBT®.
Percent agreement with positive patients: 95.5%
Percent agreement with negative patients: 100%
PATIENT MODE AND BAG MODE EQUIVALENCY
The two sampling modes of the BreathID® are PATIENT MODE sampling (using the continuous measuring of patient's breath before and after ingestion of the test solution*) and BAG MODE sampling (using two breath collection bags to sample patient's breath before and after ingestion of the test solution*). These sampling modes are described in the Procedure section of this Package Insert.
The BreathID® outcome capabilities of these two sampling modes were evaluated and compared in a series of bench tests using accurate gases and in one clinical study, as described below.
*Containing 75 mg 13C-urea tablet and 4.3 g Citrica Powder.
Non-clinical validation (bench tests)
Objectives:
- To demonstrate the accuracy and precision of the BAG MODE sampling collection compared to the PATIENT MODE sampling collection ("protocol 1”).
- To demonstrate precision and stability testing of the isotope ratio readings at time 0 and after seven days of storage ("protocol 2").
Methodology:
- Protocol 1: Three different devices were used to assess DOB of the 13CO2 to 12CO2 ratio from samples taken from different predetermined DOB in gas sources. These DOB were 0, 5.92, 9.58, 15.5 and ~50. These DOB were assessed by both modes of the BreathID® device: the previous inherent PATIENT MODE and the new inherent BAG MODE. Each assessment was repeated three times, so there were a total of 45 tests for each mode. The order of the experiments was randomly assigned.
- Protocol 2: One device was used to assess DOB of the 13CO2 to 12CO2 ratio from samples taken from different predetermined DOB in gas sources. These DOB were 0, 9.5, 15.5 and ~50. Nine collection bags were filled from each of the four sources (total of 36) to be tested at time "0." Another set of 36 collection bags were collected at the same time and stored for seven days, after which they were tested and compared to time "0" for repeatability, in order to evaluate stability of the breath sample in the bag.
In addition (in protocol 2), three collection bags were filled from three sources of 0, 9.5 and 15.5 to complete a set of nine bags. This was repeated twice more, so a total of 27 collection bags were collected in time "0." One set of nine collection bags was tested at time "0" and the other two sets were kept at different temperatures for seven days. One set was kept at 2º-8º Celsius and the second set was kept between 40-50º Celsius. After seven days, the collection bags were tested in the same device. This was done to demonstrate reproducibility.
Criteria for evaluation:
The accuracy and precision of the two modes were evaluated. The mean differences between the DOB as obtained by the device and the true values and their standard deviations were calculated. Mean differences should be near zero if the measurement is accurate.
Statistical methods:
Accuracy was assessed by comparing the measurement to its corresponding known value. Mean differences and 95% confidence intervals were calculated. The standard deviation of the mean difference and its 95% confidence interval were presented as an additional measure of accuracy versus the known constants.Repeatability expresses the precision under the same operating conditions over a short interval of time. Reproducibility expresses the precision between different operating conditions. The 95% confidence intervals for repeatability were calculated using a random effects analysis of variance model using the PROC MIXED procedure. The confidence interval of the reproducibility was calculated with bootstrap methodology using 10,000 simulated samples.
Results:
The overall accuracy of the BAG MODE was 0.11 (95% CI: [-0.91 – 1.13]). This value is similar to the overall accuracy of the PATIENT MODE -0.06 (95% CI: [-0.61 – 0.48]). The repeatability and reproducibility of the measurements assessed with the BAG MODE and PATIENT MODE are similar. Repeatability was 1.07 (95% CI: [0.87 - 1.38]) versus 0.97 (95% CI:[ 0.70 - 1.66]) and reproducibility 1.22 (95% CI:[ 0.70 -1.66]) versus 1.05 (95% CI:[ 0.73 -1.38]), respectively. Again, this demonstrates similar results for both modes.Assessment of the BAG MODE measurements has shown that the overall mean change in DOB measured after seven days is 0.02 (SD=1.21), irrespective of DOB of gas samples; subsequently, it can be reproduced after seven days in storage.Also, the results of the BAG MODE were found to be within the system specification.
Conclusion:
The data provided by these non-clinical experiments demonstrates the overall high agreement between the PATIENT MODE and the BAG MODE performances and the accuracy of the BAG MODE values. Furthermore, the non-clinical testing portrays the high level of precision, repeatability, and reproducibility of the BAG MODE results.
Clinical Validation
Objectives:
To show that the BAG MODE results in human subjects are in very high agreement with the results of the PATIENT MODE.
Methodology:
Validation of the BAG MODE included a clinical study comparing the BAG MODE and the PATIENT MODE applied on the same subjects, which were administered with the test solution of 13C-urea and Citrica as per Clinical protocol number# 4B-CV-409. For evaluation of the BAG MODE, 48 subjects were enrolled in this study.
Statistical methods:
The overall percent agreement between the diagnoses was calculated with a 95% exact confidence interval, sensitivity and specificity of the BAG MODE versus the PATIENT MODE, with their respective exact 95%. A Pearson correlation coefficient between measurements of DOB in both modes was calculated. The mean and standard deviation of the difference between the DOB measurements was calculated together with a 95% confidence interval. A linear regression model was fitted to the DOB value obtained by both modes. The slope and intercept together with their respective 95% confidence intervals were calculated. In addition, a Bland-Altman plot of the mean versus the difference were calculated, and the 95% limits of agreement were calculated together with their respective confidence intervals.
Results:
The overall agreement percentage is 100% (48/48) with a 95% exact binomial CI: [92.6%-100%] sensitivity of the BAG MODE versus the PATIENT MODE. Method diagnosis is 100% (95% exact binomial CI:[87.66%-100%]) and specificity is 100% (95% exact binomial CI:[83.16%-100%]).
Conclusion:
The clinical outcome results obtained by the BAG MODE are essentially the same as those obtained by the PATIENT MODE. Therefore, the two collection modes are considered equivalent and can be used interchangeably for assessing the presence of H. pylori infection with the BreathID® System.
SUMMARY
The above sections of the performance validations of all aspects of the BreathID® System show unequivocally that the BreathID® System can be used with its kits and two sampling modes to determine the DOB (change in the 13CO2 / 12CO2 ratio between the baseline and the post-ingestion measurements) and therefore to imply the presence of H. pylori in humans when the DOB is above 5.
REFERENCES
- Marshall BJ, Warren JR. Unidentified curved bacilli on gastric epithelium in active chronic gastritis. Lancet 1983;1:1273–5.
- Suerbaum S, Michetti P. Helicobacter pylori infection. N Engl J Med 2002;347:1175-86.
- Dominguez-Munoz JE, Leodolter A, Sauerbruch T, et al. A citric acid solution is an optimal test drink in the 13C-urea breath test for the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection. Gut 1997;40:459–62.
- Leodolter A, Dominguez-Munoz JE, Von Armim U, et al. 13C-urea breath test for the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection. A further simplification for clinical practice. Scand J Gastroenterol 1998;33:267–70.
- Graham DY, Runke D, Anderson S, et al. Citric acid as the test meal for the 13C-urea breath test. Am J Gastroenterol 1999;94:1214–7.
- Borriello SP, Reed PJ, Dolby JM, et al. Microbial and metabolic profile of achlorhydric stomach: comparison of pernicious anaemia and hypogammaglobulinaemia. J Clin Pathol 1985;38:946-53.
REPRESENTATIVE PACKAGING
See How Supplied section for a complete list of available
packages of the IDkit:Hp™ for the Exalenz BreathID® System.

Case containing 25 kits of IDkit:Hp™ ONE

Kit label for IDkit:Hp™ ONE

Box containing 5 kits of IDkit:Hp™ TWO
Kit label for IDkit:Hp™ TWO

Citrica pouch

Urea blister pack
IDkit HP ONEcitric acid anhydrous and 13C urea KIT
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||