Valproic Acid
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- BOXED WARNING
- VALPROIC ACID DESCRIPTION
- INACTIVE INGREDIENT
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- PHARMACODYNAMICS
- PHARMACOKINETICS
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
- VALPROIC ACID CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
- PREGNANCY
- NURSING MOTHERS
- PEDIATRIC USE
- GERIATRIC USE
- VALPROIC ACID ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- STORAGE AND HANDLING
- SPL PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
VALPROIC ACID DESCRIPTION
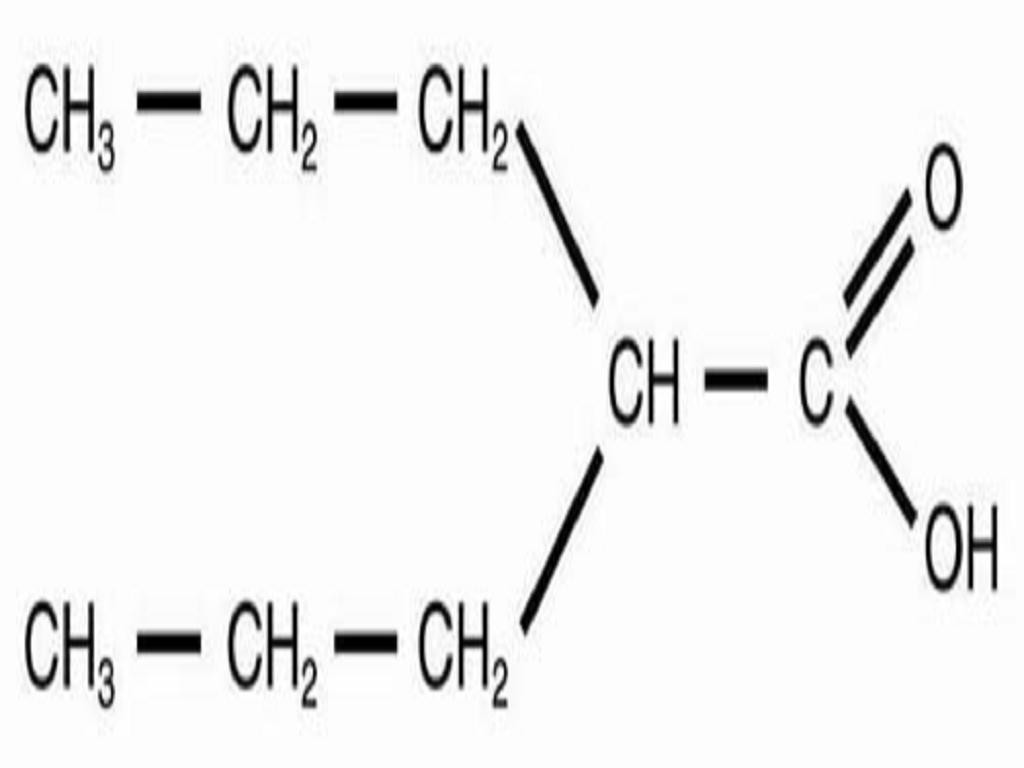
INACTIVE INGREDIENT
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
PHARMACODYNAMICS
PHARMACOKINETICS
Absorption/BioavailabilityDistribution
Protein Binding:
CNS Distribution:
Metabolism
Elimination
Special Populations
Effect of Age:
Neonates
Children
Elderly
Effect of Gender:
Effect of Race:
Effect of Disease:
Liver Disease
Renal Disease
Plasma Levels and Clinical Effect
Epilepsy:
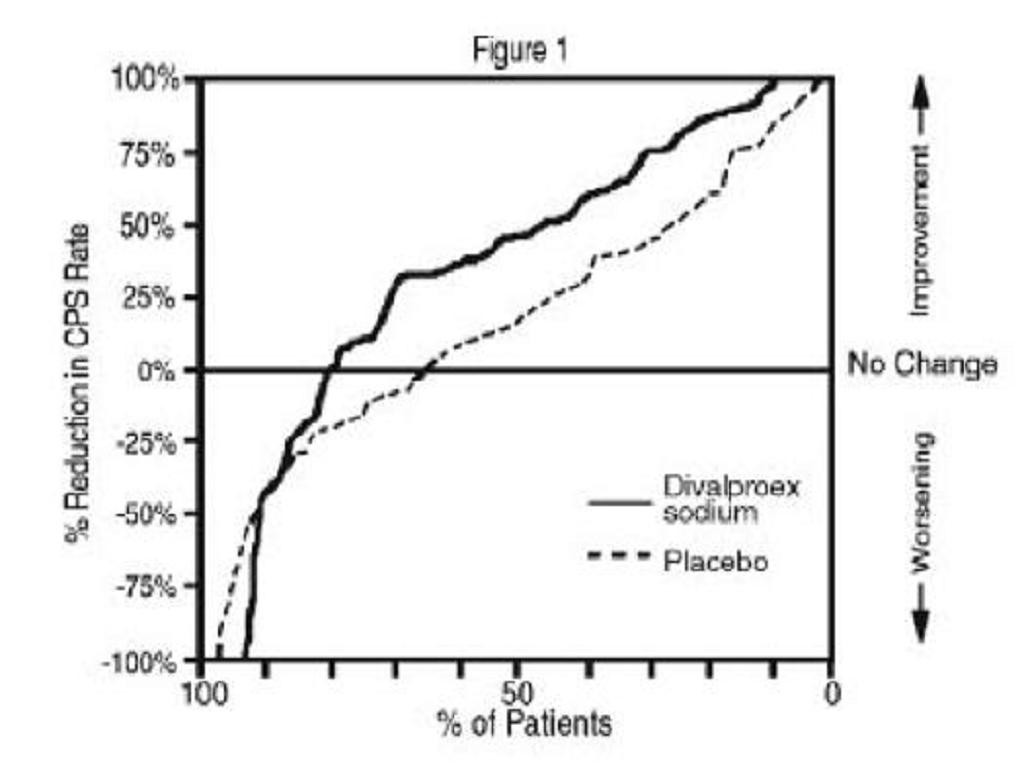
Clinical Trials
Epilepsy

INDICATIONS & USAGE
VALPROIC ACID CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS
HepatotoxicityPancreatitis
Urea Cycle Disorders (UCD)
Somnolence in the Elderly
Thrombocytopenia
Usage in Pregnancy
Human Data
Congenital Malformations
THE STRONGEST ASSOCIATION OF MATERNAL VALPROATE USAGE WITH CONGENITAL MALFORMATIONS IS WITH NEURAL TUBE DEFECTS (AS DISCUSSED UNDER THE NEXT SUBHEADING). HOWEVER, OTHER CONGENITAL ANOMALIES (E.G. CRANIOFACIAL DEFECTS, CARDIOVASCULAR MALFORMATIONS AND ANOMALIES INVOLVING VARIOUS BODY SYSTEMS), COMPATIBLE AND INCOMPATIBLE WITH LIFE, HAVE BEEN REPORTED. SUFFICIENT DATA TO DETERMINE THE INCIDENCE OF THESE CONGENITAL ANOMALIES IS NOT AVAILABLE.
Neural Tube Defects
THE INCIDENCE OF NEURAL TUBE DEFECTS IN THE FETUS IS INCREASED IN MOTHERS RECEIVING VALPROATE DURING THE FIRST TRIMESTER OF PREGNANCY. THE CENTERS FOR DISEASE CONTROL (CDC) HAS ESTIMATED THE RISK OF VALPROIC ACID EXPOSED WOMEN HAVING CHILDREN WITH SPINA BIFIDA TO BE APPROXIMATELY 1 TO 2%. THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF OBSTETRICIANS AND GYNECOLOGISTS (ACOG) ESTIMATES THE GENERAL POPULATION RISK FOR CONGENITAL NEURAL TUBE DEFECTS AS 0.14% TO 0.2%.
Tests to detect neural tube and other defects using current accepted procedures should be considered a part of routine prenatal care in pregnant women receiving valproate.
Evidence suggests that pregnant women who receive folic acid supplementation may be at decreased risk for congenital neural tube defects in their offspring compared to pregnant women not receiving folic acid. Whether the risk of neural tube defects in the offspring of women receiving valproate specifically is reduced by folic acid supplementation is unknown. DIETARY FOLIC ACID SUPPLEMENTATION BOTH PRIOR TO AND DURING PREGNANCY SHOULD BE ROUTINELY RECOMMENDED TO PATIENTS CONTEMPLATING PREGNANCY.
Other Adverse Pregnancy Effects
PATIENTS TAKING VALPROATE MAY DEVELOP CLOTTING ABNORMALITIES (SEE PRECAUTIONS - GENERAL AND WARNINGS). A PATIENT WHO HAD LOW FIBRINOGEN WHEN TAKING MULTIPLE ANTICONVULSANTS INCLUDING VALPROATE GAVE BIRTH TO AN INFANT WITH AFIBRINOGENEMIA WHO SUBSEQUENTLY DIED OF HEMORRHAGE. IF VALPROATE IS USED IN PREGNANCY, THE CLOTTING PARAMETERS SHOULD BE MONITORED CAREFULLY.
PATIENTS TAKING VALPROATE MAY DEVELOP HEPATIC FAILURE (SEE WARNINGS - HEPATOTOXICITY AND BOX WARNING). FATAL HEPATIC FAILURES, IN A NEWBORN AND IN AN INFANT, HAVE BEEN REPORTED FOLLOWING THE MATERNAL USE OF VALPROATE DURING PREGNANCY.
Animal Data
Animal studies have demonstrated valproate-induced teratogenicity. Increased frequencies of malformations, as well as intrauterine growth retardation and death, have been observed in mice, rats, rabbits, and monkeys following prenatal exposure to valproate. Malformations of the skeletal system are the most common structural abnormalities produced in experimental animals, but neural tube closure defects have been seen in mice exposed to maternal plasma valproate concentrations exceeding 230(2.3 times the upper limit of the human therapeutic range) during susceptible periods of embryonic development. Administration of an oral dose of 200 mg/kg/day or greater (50% of the maximum human daily dose or greater on a mg/m2 basis) to pregnant rats during organogenesis produced malformations (skeletal, cardiac, and urogenital) and growth retardation in the offspring. These doses resulted in peak maternal plasma valproate levels of approximately 340or greater (3.4 times the upper limit of the human therapeutic range or greater). Behavioral deficits have been reported in the offspring of rats given a dose of 200 mg/kg/day throughout most of pregnancy. An oral dose of 350 mg/kg/day (approximately 2 times the maximum human daily dose on a mg/m2 basis) produced skeletal and visceral malformations in rabbits exposed during organogenesis. Skeletal malformations, growth retardation, and death were observed in rhesus monkeys following administration of an oral dose of 200 mg/kg/day (equal to the maximum human daily dose on a mg/m2 basis) during organogenesis. This dose resulted in peak maternal plasma valproate levels of approximately 280(2.8 times the upper limit of the human therapeutic range).
PRECAUTIONS
Hepatic DysfunctionPancreatitis
Hyperammonemia
Hyperammonemia and Encephalopathy Associated with Concomitant Topiramate Use
General
Multi-organ Hypersensitivity Reaction
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Effects of Co-Administered Drugs on Valproate ClearanceDrugs for Which a Potentially Important Interaction Has Been Observed
Aspirin
Felbamate
Rifampin
Drugs for Which Either No Interaction or a Likely Clinically Unimportant Interaction Has Been Observed
Antacids
Chlorpromazine
Haloperidol
Cimetidine and Ranitidine
Effects of Valproate on Other Drugs
Drugs for Which a Potentially Important Valproate Interaction Has Been Observed
Amitriptyline/Nortriptyline
Carbamazepine/carbamazepine-10,11-Epoxide
Clonazepam
Diazepam
Ethosuximide
Lamotrigine
Phenobarbital
Phenytoin
Tolbutamide
Topiramate
Warfarin
Zidovudine
Drugs for Which Either No Interaction or a Likely Clinically Unimportant Interaction Has Been Observed
Acetaminophen
Valproate had no effect on any of the pharmacokinetic parameters of acetaminophen when it was concurrently administered to three epileptic patients.
Clozapine
In psychotic patients (n = 11), no interaction was observed when valproate was co-administered with clozapine.
Lithium
Co-administration of valproate (500 mg BID) and lithium carbonate (300 mg TID) to normal male volunteers (n = 16) had no effect on the steady-state kinetics of lithium.
Lorazepam
Concomitant administration of valproate (500 mg BID) and lorazepam (1 mg BID) in normal male volunteers (n = 9) was accompanied by a 17% decrease in the plasma clearance of lorazepam.
Oral Contraceptive Steroids
Administration of a single-dose of ethinyloestradiol (50(250to 6 women on valproate (200 mg BID) therapy for 2 months did not reveal any pharmacokinetic interaction.
CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
CarcinogenesisMutagenesis
Fertility
PREGNANCY
NURSING MOTHERS
PEDIATRIC USE
GERIATRIC USE
VALPROIC ACID ADVERSE REACTIONS
EpilepsyBody as a Whole:
Cardiovascular System:
Digestive System:
Hemic and Lymphatic System:
Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders:
Musculoskeletal System:
Nervous System:
Respiratory System:
Skin and Appendages:
Special Senses:
Urogenital System:
Other Patient Populations:
Gastrointestinal
CNS Effects
Dermatologic:
Psychiatric:
Musculoskeletal:
Hematologic:
Hepatic:
Endocrine:
Pancreatic:
Metabolic:
Genitourinary:
Special Senses:
Other:
Mania
Body as a Whole:
Cardiovascular System:
Digestive System:
Musculoskeletal System:
Nervous System:
Skin and Appendages:
Special Senses:
Urogenital System:
Migraine
Body as a Whole:
Digestive System:
Urogenital System:
OVERDOSAGE
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
Complex Partial Seizures
Monotherapy (Initial Therapy)
Conversion to Monotherapy
Adjunctive Therapy
Simple and Complex Absence Seizures
General Dosing Advice
Dosing in Elderly Patients
Dose-Related Adverse Events
G.I. Irritation
HOW SUPPLIED
STORAGE AND HANDLING
SPL PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
-
● Women taking any of this medication who are planning to get pregnant should discuss the treatment options with their doctor.
-
● If you become pregnant while taking any of this medication you should contact your doctor immediately.
-
● Your medication should be taken exactly as prescribed by your doctor to get the most benefit from your medication and reduce the risk of side effects.
-
● If you have taken more than the prescribed dose of your medication, contact your hospital emergency room or local poison center immediately.
-
● Your medication was prescribed for your particular condition. Do not use it for another condition or give the drug to others.
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION


Valproic AcidValproic Acid TABLET
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!