Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- Rx Only
- SULFAMETHOXAZOLE AND TRIMETHOPRIM DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
- SULFAMETHOXAZOLE AND TRIMETHOPRIM CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
- LABORATORY TESTS
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- DRUG & OR LABORATORY TEST INTERACTIONS
- CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
- PREGNANCY
- NURSING MOTHERS
- PEDIATRIC USE
- GERIATRIC USE
- SULFAMETHOXAZOLE AND TRIMETHOPRIM ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- STORAGE AND HANDLING
- REFERENCES
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
SULFAMETHOXAZOLE AND TRIMETHOPRIM DESCRIPTION
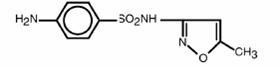
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONsection). Detectable amounts of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim are present in the blood 24 hours after drug administration. During administration of 800 mg sulfamethoxazole and 160 mg trimethoprim b.i.d., the mean steady-state plasma concentration of trimethoprim was 1.72The steady-state mean plasma levels of free and total sulfamethoxazole were 57.4and 68.0respectively. These steady-state levels were achieved after three days of drug administration.1 Excretion of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim is primarily by the kidneys through both glomerular filtration and tubular secretion. Urine concentrations of both sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim are considerably higher than are the concentrations in the blood. The average percentage of the dose recovered in urine from 0 to 72 hours after a single oral dose of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim is 84.5% for total sulfonamide and 66.8% for free trimethoprim. Thirty percent of the total sulfonamide is excreted as free sulfamethoxazole, with the remaining as N4-acetylated metabolite.2 When administered together as sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim, neither sulfamethoxazole nor trimethoprim affects the urinary excretion pattern of the other.
Geriatric Pharmacokinetics
Microbiology
INDICATIONS AND USAGEsection.
Aerobic Gram-Positive Microorganisms:
Aerobic Gram-Negative Microorganisms:
Other Organisms:
Susceptibility Testing Methods
Quality Control
Quality Control
INDICATIONS & USAGE
Urinary Tract Infections
Acute Otitis Media
Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Bronchitis in Adults
Shigellosis
Pneumocystis Carinii Pneumonia
TravelerDiarrhea in Adults
SULFAMETHOXAZOLE AND TRIMETHOPRIM CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS
FATALITIES ASSOCIATED WITH THE ADMINISTRATION OF SULFONAMIDES, ALTHOUGH RARE, HAVE OCCURRED DUE TO SEVERE REACTIONS, INCLUDING STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME, TOXIC EPIDERMAL NECROLYSIS, FULMINANT HEPATIC NECROSIS, AGRANULOCYTOSIS, APLASTIC ANEMIA AND OTHER BLOOD DYSCRASIAS.SULFONAMIDES, INCLUDING SULFONAMIDE-CONTAINING PRODUCTS SUCH AS SULFAMETHOXAZOLE/TRIMETHOPRIM, SHOULD BE DISCONTINUED AT THE FIRST APPEARANCE OF SKIN RASH OR ANY SIGN OF ADVERSE REACTION.In rare instances, a skin rash may be followed by a more severe reaction, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, hepatic necrosis, and serious blood
PRECAUTIONS). Clinical signs, such as rash, sore throat, fever, arthralgia, pallor, purpura or jaundice may be early indications of serious reactions.
Cough, shortness of breath, and pulmonary infiltrates are hypersensitivity reactions of the respiratory tract that have been reported in association with sulfonamide treatment.
Thrombocytopenia
PRECAUTIONS
GeneralCLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYandDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Use in the Treatment of and Prophylaxis for Pneumocystis Carinii Pneumonia in Patients with Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS)
WARNINGS).
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
LABORATORY TESTS
DRUG INTERACTIONS
DRUG & OR LABORATORY TEST INTERACTIONS
CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
PREGNANCY
CONTRAINDICATIONSsection.
NURSING MOTHERS
CONTRAINDICATIONSsection.PEDIATRIC USE
INDICATIONSandCONTRAINDICATIONSsections).GERIATRIC USE
WARNINGSandADVERSE REACTIONSsections), a specific decrease in platelets (with or withoutpurpura), and hyperkalemia are the most frequently reported severe adverse reactions in elderly patients. In those concurrently receiving certain diuretics, primarily thiazides, an increased incidence of thrombocytopenia with purpura has been reported. Increased digoxin blood levels can occur with concomitant sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim therapy, especially in elderly patients. Serum digoxin levels should be monitored. Hematological changes indicative of folic acid deficiency may occur in elderly patients. These effects are reversible by folinic acid therapy. Appropriate dosage adjustments should be made for patients with impaired kidney function and duration of use should be as short as possible to minimize risks of undesired reactions (seeDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONsection). The trimethoprim component of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim may cause hyperkalemia when administered to patients with underlying disorders of potassium metabolism, with renal insufficiency, or when given concomitantly with drugs known to induce hyperkalemia, such as angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. Close monitoring of serum potassium is warranted in these patients. Discontinuation of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim treatment is recommended to help lower potassium serum levels. Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim Double Strength Tablets contain 3.6 mg (0.16 mEq) of sodium per tablet.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Geriatric Pharmacokinetics).
SULFAMETHOXAZOLE AND TRIMETHOPRIM ADVERSE REACTIONS
FATALITIES ASSOCIATED WITH THE ADMINISTRATION OF SULFONAMIDES, ALTHOUGH RARE, HAVE OCCURRED DUE TO SEVERE REACTIONS, INCLUDING STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME, TOXIC EPIDERMAL NECROLYSIS, FULMINANT HEPATIC NECROSIS, AGRANULOCYTOSIS, APLASTIC ANEMIA AND OTHER BLOOD DYSCRASIAS (SEE WARNINGSSECTION).PRECAUTIONS: Use in the Treatment of and Prophylaxis for Pneumocystis Carinii Pneumonia in Patients with Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS).
WARNINGS).
Postmarketing Experience
OVERDOSAGE
AcuteChronic
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
Not recommended for use in pediatric patients less than 2 months of age.Urinary Tract Infections and Shigellosis in Adults and Pediatric Patients, and Acute Otitis Media in Children
Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Bronchitis in Adults
Pneumocystis Carinii Pneumonia
Prophylaxis
TravelerDiarrhea in Adults
HOW SUPPLIED
STORAGE AND HANDLING
REFERENCES
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION

Sulfamethoxazole and TrimethoprimSULFAMETHOXAZOLE AND TRIMETHOPRIM TABLET
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!