Phytonadione
Amphastar Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
PHYTONADIONE INJECTABLEEMULSION, USP
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- WARNING — INTRAVENOUS USE
- PHYTONADIONE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- PHYTONADIONE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- CONTRAINDICATION
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- PHYTONADIONE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- PHYTONADIONE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- IMS Saf-T-Jet™ Safety NeedleUSER GUIDE
- Carton - SAF-T-JET 1 mg per 0.5 mL
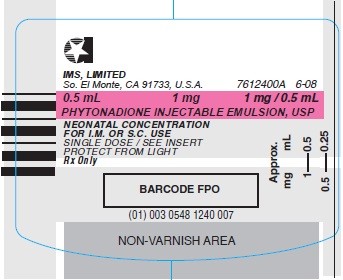
- Vial Label - SAF-T-JET 1 mg per 0.5 mL
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Aqueous Colloidal Solution of Vitamin K1
Rx Only
WARNING — INTRAVENOUS USE
Severe reactions, including fatalities, have occurred during and immediately after the parenteral administration of Phytonadione. Typically these severe reactions have resembled hypersensitivity or anaphylaxis, including shock and cardiac and/or respiratory arrest. Some patients have exhibited these severe reactions on receiving Phytonadione for the first time. The majority of these reported events occurred following intravenous administration, even when precautions have been taken to dilute the Phytonadione and to avoid rapid infusion. Therefore, the INTRAVENOUS route should be restricted to those situations where another route is not feasible and the increased risk involved is considered justified.
PHYTONADIONE DESCRIPTION
31462
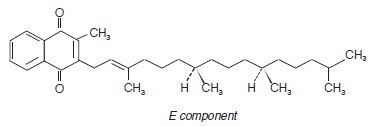
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
1PHYTONADIONE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
CONTRAINDICATION
Hypersensitivity to any component of this medication.
WARNINGS
PRECAUTIONS
Drug Interactions
Temporary resistance to prothrombin-depressing anticoagulants may result, especially when larger doses of phytonadione are used. If relatively large doses have been employed, it may be necessary when reinstituting anticoagulant therapy to use somewhat larger doses of the prothrombin-depressing anticoagulant, or to use one which acts on a different principle, such as heparin sodium.
Laboratory Tests
Prothrombin time should be checked regularly as clinical conditions indicate.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Studies of carcinogenicity, mutagenesis or impairment of fertility have not been conducted with phytonadione.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with phytonadione. It is also not known whether phytonadione can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Phytonadione should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when phytonadione is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
Hemolysis, jaundice, and hyperbilirubinemia in newborns, particularly in premature infants, may be related to the dose of phytonadione. Therefore, the recommended dose should not be exceeded (see ADVERSE REACTIONS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
PHYTONADIONE ADVERSE REACTIONS
Severe hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactoid reactions and deaths have been reported following parenteral administration. The majority of these reported events occurred following intravenous administration (see Box Warning.)
The possibility of allergic sensitivity, including an anaphylactoid reaction, should be kept in mind following parenteral administration.
Transient "flushing sensations" and "peculiar" sensations of taste have been observed, as well as rare instances of dizziness, rapid and weak pulse, profuse sweating, brief hypotension, dyspnea, and cyanosis.
Pain, swelling, and tenderness at the injection site may occur.
Infrequently, usually after repeated injection, erythematous, indurated, pruritic plaques have occurred; rarely, these have progressed to scleroderma-like lesions that have persisted for long periods. In other cases, these lesions have resembled erythema perstans.
Hyperbilirubinemia has been observed in the newborn following administration of phytonadione. This has occurred rarely and primarily with doses above those recommended. (See PRECAUTIONS, Pediatric Use.)
OVERDOSAGE
The intravenous LD50 of Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP in the mouse is 41.5 and 52 mL/kg for the 0.2% and 1.0% concentrations, respectively.
PHYTONADIONE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Whenever possible, phytonadione should be given by the subcutaneous route (see Box WARNING). When intravenous or intramuscular administration is considered unavoidable, the drug should be injected very slowly, not exceeding 1 mg per minute.
Protect from light at all times.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
Directions for Dilution
Phytonadione may be diluted with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, 5% Dextrose Injection, or 5% Dextrose and Sodium Chloride Injection. Benzyl alcohol as a preservative has been associated with toxicity in newborns. Therefore, all of the above diluents should be preservative-free. (See WARNINGS) Other diluents should not be used. When dilutions are indicated, administration should be started immediately after mixture with the diluent, and unused portions of the dilution should be discarded, as well as unused contents of the vial.
Prophylaxis of Hemorrhagic Disease of the Newborn
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that vitamin K1 be given to the newborn. A single intramuscular dose of phytonadione 0.5 to 1 mg within one hour of birth is recommended.
Treatment of Hemorrhagic Disease of the Newborn
Empiric administration of vitamin K1 should not replace proper laboratory evaluation of the coagulation mechanism. A prompt response (shortening of the prothrombin time in 2 to 4 hours) following administration of vitamin K1 is usually diagnostic of hemorrhagic disease of the newborn, and failure to respond indicates another diagnosis or coagulation disorder.
Phytonadione 1 mg should be given either subcutaneously or intramuscularly. Higher doses may be necessary if the mother has been receiving oral anticoagulants.
Whole blood or component therapy may be indicated if bleeding is excessive. This therapy, however, does not correct the underlying disorder and phytonadione should be given concurrently.
Anticoagulant-Induced Prothrombin Deficiency in Adults
To correct excessively prolonged prothrombin time caused by oral anticoagulant therapy — 2.5 to 10 mg or up to 25 mg initially is recommended. In rare instances 50 mg may be required. Frequency and amount of subsequent doses should be determined by prothrombin time response or clinical condition (see WARNINGS). If in 6 to 8 hours after parenteral administration the prothrombin time has not been shortened satisfactorily, the dose should be repeated.
| Newborns | Dosage |
|---|---|
| Hemorrhagic Disease of the Newborn |
|
|
Prophylaxis Treatment |
0.5 – 1 mg IM within 1 hour of birth 1 mg SC or IM (Higher doses may be necessary if the mother has been receiving oral anti-coagulants) |
| Adults | Initial Dosage |
|
Anticoagulant - Induced Prothrombin Deficiency (caused by coumarin or indanedione derivatives) |
2.5 mg – 10 mg or up to 25 mg (rarely 50 mg) |
|
Hypoprothrombinemia due to other causes (Antibiotics; Salicylates or other drugs; Factors limiting absorption or synthesis) |
2.5 mg – 25 mg or more (rarely up to 50 mg) |
In the event of shock or excessive blood loss, the use of whole blood or component therapy is indicated.
Hypoprothrombinemia Due to Other Causes in Adults
A dosage of 2.5 to 25 mg or more (rarely up to 50 mg) is recommended, the amount and route of administration depending upon the severity of the condition and response obtained.
If possible, discontinuation or reduction of the dosage of drugs interfering with coagulation mechanisms (such as salicylates, antibiotics) is suggested as an alternative to administering concurrent phytonadione. The severity of the coagulation disorder should determine whether the immediate administration of phytonadione is required in addition to discontinuation or reduction of interfering drugs.
HOW SUPPLIED
In unit use packages containing one single dose vial and a SAF-T-Jet™ vial injector, 27 G. × 1/2" needle.
Phytonadione Injection USP, 1 mg in 0.5 mL
Stock No. 1240 NDC 0548-1240-00
Packaged in units of 10 single use prefilled syringes.
Syringe Assembly Directions
See User Guide
USE ASEPTIC TECHNIQUE
Do not remove from carton or assemble until ready to use.
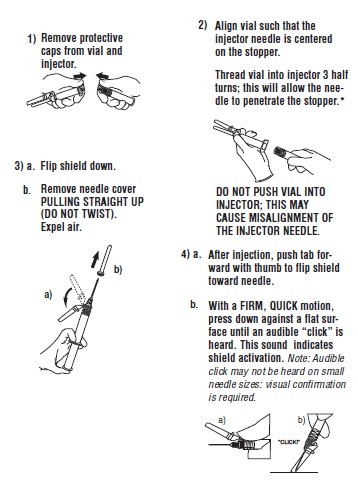
*CAUTION: IMPROPER ENGAGING MAY CAUSE GLASS BREAKAGE AND SUBSEQUENT INJURY.
Store at controlled room temperature 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP].
Protect from light.
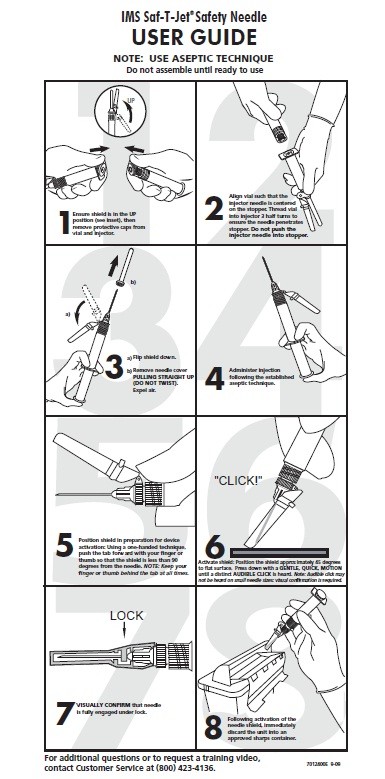
IMS Saf-T-Jet™ Safety NeedleUSER GUIDE
Carton - SAF-T-JET 1 mg per 0.5 mL
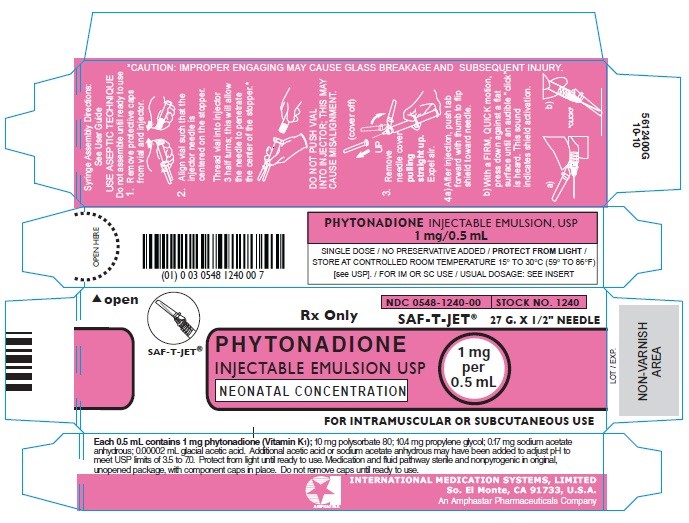
Vial Label - SAF-T-JET 1 mg per 0.5 mL
PhytonadionePhytonadione INJECTION, EMULSION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||