Labetalol Hydrochloride
Gland Pharma Limited
Gland Pharma Limited
Rx only
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- LABETALOL HYDROCHLORIDE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
- LABETALOL HYDROCHLORIDE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- LABETALOL HYDROCHLORIDE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
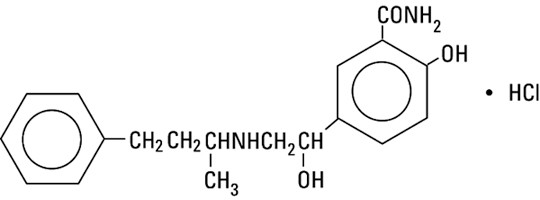
LABETALOL HYDROCHLORIDE DESCRIPTION
1
192423
Labetalol HCl is a white or off-white crystalline powder, soluble in water. Labetalol hydrochloride injection is a clear, colorless to light yellow, aqueous, sterile, isotonic solution for intravenous (IV) injection. It has a pH range of 3.0 to 4.5. Each mL contains 5 mg labetalol hydrochloride USP, 45 mg anhydrous dextrose, 0.10 mg edetate disodium; 0.80 mg of methylparaben and 0.10 mg of propylparaben as preservatives; and citric acid monohydrate and sodium hydroxide, as necessary, to bring the solution into the pH range.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
121
Pharmacodynamics:
12
Single oral doses of labetalol HCl administered to patients with coronary artery disease had no significant effect on sinus rate, intraventricular conduction, or QRS duration. The atrioventricular (A-V) conduction time was modestly prolonged in two of seven patients. In another study, intravenous labetalol HCl slightly prolonged A-V nodal conduction time and atrial effective refractory period with only small changes in heart rate. The effects on A-V nodal refractoriness were inconsistent.
Labetalol HCl produces dose-related falls in blood pressure without reflex tachycardia and without significant reduction in heart rate, presumably through a mixture of its alpha- and beta-blocking effects. Hemodynamic effects are variable, with small, nonsignificant changes in cardiac output seen in some studies but not others, and small decreases in total peripheral resistance. Elevated plasma renins are reduced.
Doses of labetalol HCl that controlled hypertension did not affect renal function in mildly to severely hypertensive patients with normal renal function.
Due to the alpha1-receptor blocking activity of labetalol HCl, blood pressure is lowered more in the standing than in the supine position, and symptoms of postural hypotension can occur. During dosing with intravenous labetalol HCl, the contribution of the postural component should be considered when positioning the patient for treatment, and the patient should not be allowed to move to an erect position unmonitored until his ability to do so is established.
In a clinical pharmacologic study in severe hypertensives, an initial 0.25-mg/kg injection of labetalol HCl administered to patients in the supine position decreased blood pressure by an average of 11/7 mmHg. Additional injections of 0.5 mg/kg at 15-minute intervals up to a total cumulative dose of 1.75 mg/kg of labetalol HCl caused further dose-related decreases in blood pressure. Some patients required cumulative doses of up to 3.25 mg/kg. The maximal effect of each dose level occurred within 5 minutes. Following discontinuation of intravenous treatment with labetalol HCl, the blood pressure rose gradually and progressively, approaching pretreatment baseline values within an average of 16 to 18 hours in the majority of patients.
Similar results were obtained in the treatment of patients with severe hypertension who required urgent blood pressure reduction with an initial dose of 20 mg (which corresponds to 0.25 mg/kg for an 80-kg patient) followed by additional doses of either 40 or 80 mg at 10-minute intervals to achieve the desired effect, or up to a cumulative dose of 300 mg.
Labetalol HCl administered as a continuous intravenous infusion, with a mean dose of 136 mg (27 to 300 mg) over a period of 2 to 3 hours (mean of 2 hours and 39 minutes), lowered the blood pressure by an average of 60/35 mmHg.
Exacerbation of angina and, in some cases, myocardial infarction and ventricular dysrhythmias have been reported after abrupt discontinuation of therapy with beta-adrenergic blocking agents in patients with coronary artery disease. Abrupt withdrawal of these agents in patients without coronary artery disease has resulted in transient symptoms, including tremulousness, sweating, palpitation, headache, and malaise. Several mechanisms have been proposed to explain these phenomena, among them increased sensitivity to catecholamines because of increased numbers of beta receptors.
Although beta-adrenergic receptor blockade is useful in the treatment of angina and hypertension, there are also situations in which sympathetic stimulation is vital. For example, in patients with severely damaged hearts, adequate ventricular function may depend on sympathetic drive. Beta-adrenergic blockade may worsen A-V block by preventing the necessary facilitating effects of sympathetic activity on conduction. Beta2-adrenergic blockade results in passive bronchial constriction by interfering with endogenous adrenergic bronchodilator activity in patients subject to bronchospasm, and it may also interfere with exogenous bronchodilators in such patients.
Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism:
The metabolism of labetalol is mainly through conjugation to glucuronide metabolites. The metabolites are present in plasma and are excreted in the urine and, via the bile, into the feces. Approximately 55% to 60% of a dose appears in the urine as conjugates or unchanged labetalol within the first 24 hours of dosing.
Labetalol has been shown to cross the placental barrier in humans. Only negligible amounts of the drug crossed the blood-brain barrier in animal studies. Labetalol is approximately 50% protein bound. Neither hemodialysis nor peritoneal dialysis removes a significant amount of labetalol HCl from the general circulation (<1%).
INDICATIONS & USAGE
Labetalol hydrochloride injection is indicated for control of blood pressure in severe hypertension.
LABETALOL HYDROCHLORIDE CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS
WARNINGS
Hepatic Injury: Severe hepatocellular injury, confirmed by rechallenge in at least one case, occurs rarely with labetalol therapy. The hepatic injury is usually reversible, but hepatic necrosis and death have been reported. Injury has occurred after both short- and long-term treatment and may be slowly progressive despite minimal symptomatology. Similar hepatic events have been reported with a related research compound, dilevalol HCl, including two deaths. Dilevalol HCl is one of the four isomers of labetalol HCl. Thus, for patients taking labetalol, periodic determination of suitable hepatic laboratory tests would be appropriate. Appropriate laboratory testing should be done at the first symptom/sign of liver dysfunction (e.g., pruritus, dark urine, persistent anorexia, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, or unexplained “flulike” symptoms). If the patient has laboratory evidence of liver injury or jaundice, labetalol should be stopped and not restarted.
Cardiac Failure: Sympathetic stimulation is a vital component supporting circulatory function in congestive heart failure. Beta-blockade carries a potential hazard of further depressing myocardial contractility and precipitating more severe failure. Although beta-blockers should be avoided in overt congestive heart failure, if necessary, labetalol HCl can be used with caution in patients with a history of heart failure who are well compensated. Congestive heart failure has been observed in patients receiving labetalol HCl. Labetalol HCl does not abolish the inotropic action of digitalis on heart muscle.
In Patients Without a History of Cardiac Failure: In patients with latent cardiac insufficiency, continued depression of the myocardium with beta-blocking agents over a period of time can, in some cases, lead to cardiac failure. At the first sign or symptom of impending cardiac failure, patients should be fully digitalized and/or be given a diuretic, and the response should be observed closely. If cardiac failure continues despite adequate digitalization and diuretic, therapy with Labetalol hydrochloride injection should be withdrawn (gradually, if possible).
Ischemic Heart Disease: Angina pectoris has not been reported upon labetalol HCl discontinuation. However, following abrupt cessation of therapy with some beta-blocking agents in patients with coronary artery disease, exacerbations of angina pectoris and, in some cases, myocardial infarction have been reported. Therefore, such patients should be cautioned against interruption of therapy without the physician’s advice. Even in the absence of overt angina pectoris, when discontinuation of labetalol hydrochloride injection is planned, the patient should be carefully observed and should be advised to limit physical activity. If angina markedly worsens or acute coronary insufficiency develops, administration of Labetalol hydrochloride injection should be reinstituted promptly, at least temporarily, and other measures appropriate for the management of unstable angina should be taken.
Nonallergic Bronchospasm (e.g., Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema): Since labetalol hydrochloride injection at the usual intravenous therapeutic doses has not been studied in patients with nonallergic bronchospastic disease, it should not be used in such patients.
Pheochromocytoma: Intravenous labetalol HCl has been shown to be effective in lowering blood pressure and relieving symptoms in patients with pheochromocytoma; higher than usual doses may be required. However, paradoxical hypertensive responses have been reported in a few patients with this tumor; therefore, use caution when administering labetalol HCl to patients with pheochromocytoma.
Diabetes Mellitus and Hypoglycemia: Beta-adrenergic blockade may prevent the appearance of premonitory signs and symptoms (e.g., tachycardia) of acute hypoglycemia. This is especially important with labile diabetics. Beta-blockade also reduces the release of insulin in response to hyperglycemia; it may therefore be necessary to adjust the dose of antidiabetic drugs.
Major Surgery:
PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions
Rapid Decreases of Blood Pressure: Caution must be observed when reducing severely elevated blood pressure. A number of adverse reactions, including cerebral infarction, optic nerve infarction, angina, and ischemic changes in the electrocardiogram, have been reported with other agents when severely elevated blood pressure was reduced over time courses of several hours to as long as 1 or 2 days. The desired blood pressure lowering should therefore be achieved over as long a period of time as is compatible with the patient’s status.
PRECAUTIONS
General Precautions
Impaired Hepatic Function:
Hypotension:
Intraoperative Floppy Iris Syndrome (IFIS)
Following Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery: In one uncontrolled study, patients with low cardiac indices and elevated systemic vascular resistance following intravenous labetalol HCl experienced significant declines in cardiac output with little change in systemic vascular resistance. One of these patients developed hypotension following labetalol treatment. Therefore, use of labetalol HCl should be avoided in such patients.
High Dose Labetalol:
Jaundice or Hepatic Dysfunction: WARNINGS
Information for Patients
The following information is intended to aid in the safe and effective use of this medication. It is not a disclosure of all possible adverse or intended effects. During and immediately following (for up to 3 hours) labetalol hydrochloride injection, the patient should remain supine. Subsequently, the patient should be advised on how to proceed gradually to become ambulatory and should be observed at the time of first ambulation.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
WARNINGSADVERSE REACTIONS
Laboratory Tests
Drug Interactions
Since Labetalol hydrochloride injection may be administered to patients already being treated with other medications, including other antihypertensive agents, careful monitoring of these patients is necessary to detect and treat promptly any undesired effect from concomitant administration.
In one survey, 2.3% of patients taking labetalol HCl orally in combination with tricyclic antidepressants experienced tremor as compared to 0.7% reported to occur with labetalol HCl alone. The contribution of each of the treatments to this adverse reaction is unknown, but the possibility of a drug interaction cannot be excluded.
Drugs possessing beta-blocking properties can blunt the bronchodilator effect of beta-receptor agonist drugs in patients with bronchospasm; therefore, doses greater than the normal antiasthmatic dose of beta-agonist bronchodilator drugs may be required.
Cimetidine has been shown to increase the bioavailability of labetalol HCl administered orally. Since this could be explained either by enhanced absorption or by an alteration of hepatic metabolism of labetalol HCl, special care should be used in establishing the dose required for blood pressure control in such patients.
Synergism has been shown between halothane anesthesia and intravenously administered labetalol HCl. During controlled hypotensive anesthesia using labetalol HCl in association with halothane, high concentrations (3% or above) of halothane should not be used because the degree of hypotension will be increased and because of the possibility of a large reduction in cardiac output and an increase in central venous pressure. The anesthesiologist should be informed when a patient is receiving labetalol HCl.
Labetalol HCl blunts the reflex tachycardia produced by nitroglycerin without preventing its hypotensive effect. If labetalol HCl is used with nitroglycerin in patients with angina pectoris, additional antihypertensive effects may occur.
Risk of Anaphylactic Reaction:
Drug & OR Laboratory Test Interactions
e.g., J Chromatogr
® ®
Carcinogenesis & Mutagenesis & Impairment Of Fertility
Long-term oral dosing studies with labetalol HCl for 18 months in mice and for 2 years in rats showed no evidence of carcinogenesis. Studies with labetalol HCl using dominant lethal assays in rats and mice and exposing microorganisms according to modified Ames tests showed no evidence of mutagenesis.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category C:
Nonteratogenic Effects:
Labor & Delivery
Labetalol HCl given to pregnant women with hypertension did not appear to affect the usual course of labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
Small amounts of labetalol (approximately 0.004% of the maternal dose) are excreted in human milk. Caution should be exercised when Labetalol hydrochloride injection is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
LABETALOL HYDROCHLORIDE ADVERSE REACTIONS
Labetalol hydrochloride injection is usually well tolerated. Most adverse effects have been mild and transient and, in controlled trials involving 92 patients, did not require labetalol HCl withdrawal. Symptomatic postural hypotension (incidence, 58%) is likely to occur if patients are tilted or allowed to assume the upright position within 3 hours of receiving Labetalol hydrochloride injection. Moderate hypotension occurred in 1 of 100 patients while supine. Increased sweating was noted in 4 of 100 patients, and flushing occurred in 1 of 100 patients.
The following also were reported with Labetalol hydrochloride injection with the incidence per 100 patients as noted:
Cardiovascular System: Ventricular arrhythmia in 1.
Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems: Dizziness in 9, tingling of the scalp/skin in 7, hypoesthesia (numbness) and vertigo in 1 each.
Gastrointestinal System: Nausea in 13, vomiting in 4, dyspepsia and taste distortion in 1 each.
Metabolic Disorders:
Psychiatric Disorders: Somnolence/yawning in 3.
Respiratory System:
Skin:
| Labetalol HCI Daily Dose (mg) |
200 |
300 |
400 |
600 |
800 |
900 |
1200 |
1600 |
2400 |
| Number of patients |
522 |
181 |
606 |
608 |
503 |
117 |
411 |
242 |
175 |
| Dizziness (%) |
2 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
5 |
1 |
9 |
13 |
16 |
| Fatigue |
2 |
1 |
4 |
4 |
5 |
3 |
7 |
6 |
10 |
| Nausea |
<1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
4 |
0 |
7 |
11 |
19 |
| Vomiting |
0 |
0 |
<1 |
<1 |
<1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
| Dyspepsia |
1 |
0 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
2 |
2 |
4 |
| Paresthesia |
2 |
0 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
5 |
5 |
| Nasal stuffiness |
1 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
| Ejaculation failure |
0 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
0 |
4 |
3 |
5 |
| Impotence |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
4 |
3 |
4 |
3 |
| Edema |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
Cardiovascular:
Liver and Biliary System:
Hypersensitivity: e.g.,
Clinical Laboratory Tests:
OVERDOSAGE
Excessive bradycardia
Cardiac failure
Hypotensione.g.,
Bronchospasm2
Seizures
Neither hemodialysis nor peritoneal dialysis removes a significant amount of labetalol from the general circulation (<1%).
The oral LD50 value of labetalol HCl in the mouse is approximately 600 mg/kg and in the rat is greater than 2 g/kg. The intravenous LD50 in these species is 50 to 60 mg/kg.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
Labetalol hydrochloride injection is intended for intravenous use in hospitalized patients. DOSAGE MUST BE INDIVIDUALIZED depending upon the severity of hypertension and the response of the patient during dosing.
Patients should always be kept in a supine position during the period of intravenous drug administration. A substantial fall in blood pressure on standing should be expected in these patients. The patient’s ability to tolerate an upright position should be established before permitting any ambulation, such as using toilet facilities.
Either of two methods of administration of Labetalol hydrochloride injection may be used: a) repeated intravenous injection, or b) slow continuous infusion.
Repeated Intravenous Injection: Initially, Labetalol hydrochloride injection should be given in a 20-mg dose (which corresponds to 0.25 mg/kg for an 80-kg patient) by slow intravenous injection over a 2-minute period.
Immediately before the injection and at 5 and 10 minutes after injection, supine blood pressure should be measured to evaluate response. Additional injections of 40 or 80 mg can be given at 10-minute intervals until a desired supine blood pressure is achieved or a total of 300 mg of labetalol HCl has been injected. The maximum effect usually occurs within 5 minutes of each injection.
Slow Continuous Infusion: Labetalol hydrochloride injection is prepared for continuous intravenous infusion by diluting the vial contents with commonly used intravenous fluids (see below). Examples of two methods of preparing the infusion solution are:
Add 40 mL of Labetalol hydrochloride injection to 160 mL of a commonly used intravenous fluid such that the resultant 200 mL of solution contains 200 mg of labetalol HCl, 1 mg/mL. The diluted solution should be administered at a rate of 2 mL /min to deliver 2 mg/min.
Alternatively, add 40 mL of Labetalol hydrochloride injection to 250 mL of a commonly used intravenous fluid. The resultant solution will contain 200 mg of labetalol HCl, approximately 2 mg/3 mL. The diluted solution should be administered at a rate of 3 mL /min to deliver approximately 2 mg/min.
The rate of infusion of the diluted solution may be adjusted according to the blood pressure response, at the discretion of the physician. To facilitate a desired rate of infusion, the diluted solution can be infused using a controlled administration mechanism, e.g., graduated burette or mechanically driven infusion pump.
Since the half-life of labetalol is 5 to 8 hours, steady-state blood levels (in the face of a constant rate of infusion) would not be reached during the usual infusion time period. The infusion should be continued until a satisfactory response is obtained and should then be stopped and oral labetalol HCl started (see below). The effective intravenous dose is usually in the range of 50 to 200 mg. A total dose of up to 300 mg may be required in some patients.
Blood Pressure Monitoring: The blood pressure should be monitored during and after completion of the infusion or intravenous injection. Rapid or excessive falls in either systolic or diastolic blood pressure during intravenous treatment should be avoided. In patients with excessive systolic hypertension, the decrease in systolic pressure should be used as an indicator of effectiveness in addition to the response of the diastolic pressure.
Initiation of Dosing With labetalol hydrochloride Tablets: Subsequent oral dosing with labetalol hydrochloride Tablets should begin when it has been established that the supine diastolic blood pressure has begun to rise. The recommended initial dose is 200 mg, followed in 6 to 12 hours by an additional dose of 200 or 400 mg, depending on the blood pressure response. Thereafter, inpatient titration with labetalol hydrochloride Tablets may proceed as follows:
|
Inpatient Titration Instructions
|
|
|
Regimen
|
Daily Dose* |
| 200 mg b.i.d. |
400 mg |
| 400 mg b.i.d. |
800 mg |
| 800 mg b.i.d. |
1600 mg |
| 1200 mg b.i.d. |
2400 mg |
| *If needed, the total daily dose may be given in three divided doses. |
|
The dosage of labetalol hydrochloride Tablets used in the hospital may be increased at 1-day intervals to achieve the desired blood pressure reduction.
For subsequent outpatient titration or maintenance dosing, see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION in the labetalol hydrochloride Tablets Product Information for additional recommendations.
Compatibility With Commonly Used Intravenous Fluids: Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration before administration whenever solution and container permit.
Labetalol hydrochloride injection was tested for compatibility with commonly used intravenous fluids at final concentrations of 1.25 to 3.75 mg of labetalol HCl per milliliter of the mixture. Labetalol hydrochloride injection was found to be compatible with and stable (for 24 hours refrigerated or at room temperature) in mixtures with the following solutions: ringer’s injection, USP; lactated ringer’s injection, USP; 5% dextrose and ringer’s injection; 5% lactated ringer’s and 5% dextrose injection; 5% dextrose injection, USP; 0.9% sodium chloride injection, USP; 5% dextrose and 0.2% sodium chloride injection, USP; 2.5% dextrose and 0.45% sodium chloride injection, USP; 5% dextrose and 0.9% sodium chloride injection, USP; and 5% dextrose and 0.33% sodium chloride injection, USP.
HOW SUPPLIED
Labetalol hydrochloride injection, 5 mg/mL, is supplied in:
NDC 68083-111-01, 100 mg/ 20 mL Multiple Dose Vial, Carton of 1.
NDC 68083-111-02, 200 mg/ 40 mL Multiple Dose Vial, Carton of 1.
Store at 20°C to 25ºC (68°F to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from freezing and light.
Manufactured by:
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
LABETALOL HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION, USP 100 mg/20 mL Vial Label

Labetalol HydrochlorideLabetalol Hydrochloride INJECTION, SOLUTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||