Cystadane
Cystadane® (betaine anhydrous for oral solution)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- CYSTADANE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- CYSTADANE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- PRECAUTIONS
- CYSTADANE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- CYSTADANE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Rx only
CYSTADANE DESCRIPTION
Cystadane® (betaine anhydrous for oral solution) is an agent for the treatment of homocystinuria. Cystadane is a white, granular, hygroscopic powder. It contains no ingredients other than anhydrous betaine. Betaine anhydrous powder is very soluble in water, soluble in methanol and ethanol, and sparingly soluble in ether.
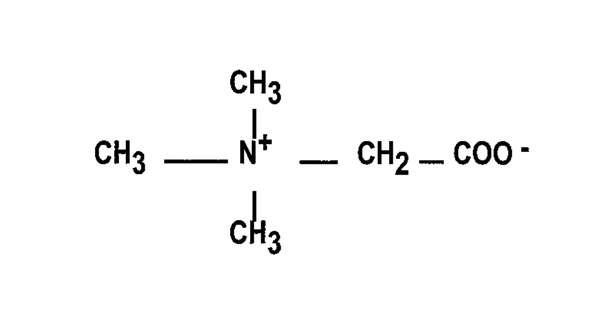
The chemical name of betaine anhydrous powder is trimethylglycine. It has a molecular weight of 117.15. The structural formula is:
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
When administered in recommended oral dosage to children or adults, Cystadane acts as a methyl group donor in the remethylation of homocysteine to methionine in patients with homocystinuria. As a result, toxic blood levels of homocysteine are reduced in these patients, usually to 20-30 percent or less of pre-treatment levels.
Elevated homocysteine blood levels are associated with clinical problems such as a cardiovascular thrombosis, osteoporosis, skeletal abnormalities, and optic lens dislocation. Plasma levels of homocysteine were decreased in nearly all patients treated with betaine. In observational studies without concurrent controls, clinical improvement was reported by the treating physicians in about three-fourths of patients taking betaine. Many of these patients were also taking other therapies such as vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), vitamin B12 (cobalamin), and folate with variable biochemical responses. In most cases studied, adding betaine resulted in a further reduction of homocysteine.
Betaine was observed to lower plasma homocysteine levels in the three types of homocystinuria, i.e., cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS) deficiency; 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) deficiency; and cobalamin cofactor metabolism (cbl) defect.
Betaine has also been demonstrated to increase low plasma methionine and S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) levels in patients with MTHFR deficiency and cbl defect.
In CBS-deficient patients, large increases in methionine levels over baseline have been observed.
Betaine occurs naturally in the body. It is a metabolite of choline and is present in small amounts in foods such as beets, spinach, cereals, and seafood.
Pharmacokinetic studies of betaine are not available. Plasma levels of betaine have not been measured in patients and have not been correlated to homocysteine levels. However, pharmacodynamic measurements, i.e., monitoring of plasma homocysteine levels, have demonstrated that the onset of action of betaine is within several days and that a steady state in response to dosage is achieved within several weeks. Patients have taken betaine for many years without evidence of tolerance.
CYSTADANE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Cystadane (betaine anhydrous for oral solution) is indicated for the treatment of homocystinuria to decrease elevated homocysteine blood levels. Included within the category of homocystinuria are deficiencies or defects in:
- cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS),
- 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR),
- cobalamin cofactor metabolism (cbl).
Patient response to Cystadane can be monitored by homocysteine plasma levels (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). Response usually occurs within a week and steady state within a month.
Cystadane has been administered concomitantly with vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), vitamin B12 (cobalamin), and folate.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Therapy with Cystadane should be directed by physicians knowledgeable in the management of patients with homocystinuria.
Hypermethioninemia
Patients with homocystinuria due to cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS) deficiency may also have elevated plasma methionine concentrations. Treatment with Cystadane may further increase methionine concentrations due to the remethylation of homocysteine to methionine. Cerebral edema has been reported in patients with hypermethioninemia, including a few patients treated with Cystadane. Plasma methionine concentrations should be monitored in patients with CBS deficiency. Plasma methionine concentrations should be kept below 1,000 umol/L through dietary modification and, if necessary, a reduction of Cystadane dose.
Information for patients
- Shake bottle lightly before removing cap.
- Measure with the scoop provided.
- One level scoop (1.7 cc) is equivalent to 1 gram of betaine anhydrous powder. Measure the number of scoops your physician has prescribed.
- Mix with 4 to 6 ounces (120 to 180 mL) of water, juice, milk, or formula until completely dissolved, or mix with food, then ingest immediately.
Always replace the cap tightly after using. Protect from moisture.
Carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, impairment of fertility
Long-term carcinogenicity and fertility studies have not been conducted on betaine. No evidence of genotoxicity was demonstrated in the following tests: Metaphase Analysis of Human Lymphocytes; Bacterial Reverse Mutation Assay; and Mouse Micronucleus Test.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with betaine. It is also not known whether betaine can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Cystadane (betaine anhydrous for oral solution) should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Nursing mothers
It is not known whether betaine is excreted in human milk (although its metabolic precursor, choline, occurs at high levels in human milk). Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when Cystadane is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric use
The majority of case studies of homocystinuria patients treated with betaine have been pediatric patients. The disorder, in its most severe form, can be manifested within the first months or years of life by lethargy, failure to thrive, developmental delays, seizures, or optic lens displacement. Patients have been treated successfully without adverse effects within the first months or years of life with dosages of 6 grams per day or more of betaine with resultant biochemical and clinical improvement. However, dosage titration may be preferable in pediatric patients (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
CYSTADANE ADVERSE REACTIONS
Adverse reactions to betaine have been minimal. In a survey study of physicians who had treated a total of 111 homocystinuria patients with betaine, the types of adverse effects and the number of patients experiencing them were as follows:
| Nausea | 2 | “Caused odor” | 1 |
| GI distress | 2 | Questionable psychological changes | 1 |
| Diarrhea | 1 | “Aspirated the powder” | 1 |
| Unspecified problem | 1 |
A few cases of cerebral edema have been reported secondary to severe hypermethioninemia in patients with cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS) deficiency treated with Cystadane. See PRECAUTIONS: Hypermethioninemia.
OVERDOSAGE
In an acute toxicology study in rats, death frequently occurred at doses equal to or greater than 10,000 mg/kg.
CYSTADANE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The usual dosage used in adult and pediatric patients is 6 grams per day administered orally in divided doses of 3 grams two times per day. Dosages of up to 20 grams per day have been necessary to control homocysteine levels in some patients. In pediatric patients less than 3 years of age, dosage may be started at 100 mg/kg/day and then increased weekly by 50 mg/kg increments. In one study by Matthewsi et al., pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic simulation indicated minimal benefit from exceeding a twice-daily dosing schedule and a 150 mg/kg/day dosage for betaine. Dosage in all patients can be gradually increased until plasma total homocysteine is undetectable or present only in small amounts. Plasma methionine concentrations should be monitored in patients with CBS-deficiency. See PRECAUTIONS: Hypermethioninemia.
The prescribed amount of Cystadane (betaine anhydrous for oral solution) should be measured with the measuring scoop provided (one level 1.7 cc scoop is equal to 1 gram of betaine anhydrous powder) and then dissolved in 4 to 6 ounces (120 to 180 mL) of water, juice, milk, or formula, or mixed with food for immediate ingestion.
HOW SUPPLIED
Cystadane is available in plastic bottles containing 180 grams of betaine anhydrous. Each bottle is equipped with a plastic child-resistant cap and is supplied with a polystyrene measuring scoop. One level scoop (1.7 cc) is equal to 1 gram of betaine anhydrous powder.
NDC 68727-400-01
180g/bottle
DIN 02238526
Store at room temperature, 15° - 30°C (59° - 86°F).
For questions of a medical nature in the U.S. or Canada, call
1-888-867-7426.
Cystadane® can be ordered by calling Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Customer Service at 1-800-359-4304 or by contacting your local wholesaler.
Distributed in the U.S. by:
Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Palo Alto, CA 94304
Distributed in Canada by:
Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Scarborough, Ontario
M1H 2W4
Revision Date: August 2006
Part No. CYS PI-8585
i Matthews A, Johnson TN, Rostami-Hodjegan A, Chakrapani A, et al. An indirect response model of homocysteine suppression by betaine: optimizing the dosage regimen of betaine in homocystinuria. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2002; 54:140-146.
Cystadanebetaine, anhydrous POWDER, FOR SOLUTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||