Propantheline Bromide
Roxane Laboratories, Inc.
Roxane Laboratories, Inc.
PROPANTHELINE BROMIDE Tablets USP
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- PROPANTHELINE BROMIDE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- PROPANTHELINE BROMIDE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- PROPANTHELINE BROMIDE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- PROPANTHELINE BROMIDE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- PROPANTHELINE BROMIDE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- Package Label -
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
PROPANTHELINE BROMIDE DESCRIPTION
Each tablet for oral administration contains:
Propantheline bromide.................................................. 15 mg
Propantheline bromide, a synthetic quaternary ammonium compound, occurs as white or nearly white crystals. It is odorless and has a bitter taste, and is very soluble in water and chloroform; practically insoluble in ether, acetone and ethyl acetate. It is designated chemically as (2-Hydroxyethyl) diisopropylmethyl-ammonium bromide xanthene-9-carboxylate.
The structural formula is:
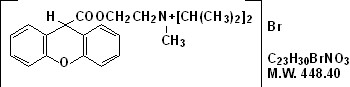
Inactive Ingredients
The tablets contain hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, lactose, magnesium stearate, starch, sterotex, and other ingredients.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Propantheline bromide inhibits gastrointestinal motility and diminishes gastric acid secretion. The drug also inhibits the action of acetylcholine at the postganglionic nerve endings of the parasympathetic nervous system.
Propantheline bromide is extensively metabolized in man primarily by hydrolysis to the inactive materials xanthene-9-carboxylic acid and (2-hydroxyethyl) diisopropylmethylammonium bromide. In a bioavailability study, peak plasma concentrations of propantheline were achieved in about one hour, following a single oral dose.
The plasma elimination half-life of propantheline is about 1.6 hours. Approximately 70% of the dose is excreted in the urine, mostly as metabolites. The urinary excretion of propantheline is about 3% after oral tablet administration.
PROPANTHELINE BROMIDE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Propantheline bromide is effective as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of peptic ulcer.
PROPANTHELINE BROMIDE CONTRAINDICATIONS
Propantheline is contraindicated in patients with:
- Glaucoma, since mydriasis is to be avoided.
- Obstructive disease of the gastrointestinal tract (pyloroduodenal stenosis, achalasia, paralytic ileus, etc.).
- Obstructive uropathy (e.g., bladder-neck obstruction due to prostatic hypertrophy).
- Intestinal atony of elderly or debilitated patients.
- Severe ulcerative colitis or toxic megacolon complicating ulcerative colitis.
- Unstable cardiovascular adjustment in acute hemorrhage.
- Myasthenia gravis.
WARNINGS
In the presence of a high environmental temperature, heat prostration (fever and heat stroke due to decreased sweating) can occur with the use of propantheline.
Diarrhea may be an early symptom of incomplete intestinal obstruction, especially in patients with ileostomy or colostomy. In this instance treatment with this drug would be inappropriate and possibly harmful.
With overdose, a curare-like action may occur (i.e., neuromuscular blockade leading to muscular weakness and possible paralysis). Propantheline may cause increased heart rate and therefore, should be used with caution in patients with heart disease.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Propantheline should be used with caution in the elderly and in all patients with autonomic neuropathy, hepatic or renal disease, hyperthyroidism, coronary heart disease, congestive heart failure, cardiac tachyarrhythmias, hypertension, or hiatal hernia associated with reflux esophagitis, since anticholinergics may aggravate this condition.
In patients with ulcerative colitis, large doses of propantheline may suppress intestinal motility to the point of producing paralytic ileus and, for this reason, may precipitate or aggravate toxic megacolon, a serious complication of the disease.
Information for Patients
Propantheline may produce drowsiness or blurred vision. The patient should be cautioned regarding activities requiring mental alertness, such as operating a motor vehicle or other machinery or performing hazardous work, while taking this drug.
Drug Interactions
Anticholinergics may delay absorption of other medication given concomitantly. Excessive cholinergic blockade may occur if propantheline is given concomitantly with belladonna alkaloids or synthetic and semisynthetic anticholinergic agents, narcotic analgesics such as meperidine, Type 1 antiarrhythmic drugs (e.g., disopyramide, procainamide, or quinidine), antihistamines, phenothiazines, tricyclic antidepressants, or other psychoactive drugs. Propantheline may also potentiate the sedative effect of phenothiazines. Increased intraocular pressure may result from concurrent administration of anticholinergics and corticosteroids.
Concurrent use of propantheline with slow-dissolving tablets of digoxin may cause increased serum digoxin levels. This interaction can be avoided by using only those digoxin tablets that rapidly dissolve by USP standards.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No long-term fertility, carcinogenicity, or mutagenicity studies have been done with propantheline.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with propantheline. It is also not known whether propantheline can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Propantheline should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when propantheline is administered to a nursing woman. Suppression of lactation may occur with anticholinergic drugs.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in children have not been established.
PROPANTHELINE BROMIDE ADVERSE REACTIONS
Varying degrees of drying of salivary secretions may occur as well as decreased sweating. Ophthalmic side effects include blurred vision, mydriasis, cycloplegia, and increased ocular tension. Other reported adverse reactions include urinary hesitancy and retention, tachycardia, palpitations, loss of the sense of taste, headache, nervousness, mental confusion, drowsiness, weakness, dizziness, insomnia, nausea, vomiting, constipation, bloated feeling, impotence, suppression of lactation, and allergic reactions or drug idiosyncracies including anaphylaxis, urticaria and other dermal manifestations.
OVERDOSAGE
The symptoms of overdosage with propantheline progress from an intensification of the usual side effects to CNS disturbances (from restlessness and excitement to psychotic behavior), circulatory changes (flushing, fall in blood pressure, circulatory failure), respiratory failure, paralysis, and coma.
Measures to be taken are (1) immediate induction of emesis or lavage of the stomach and (2) injection of physostigmine 0.5 to 2 mg intravenously, and repeated as necessary up to a total of 5 mg, and (3) monitoring of vital signs and managing as necessary.
Fever may be treated symptomatically (cooling blanket or alcohol sponging). Excitement of a degree which demands attention may be managed with thiopental sodium 2% solution given slowly intravenously or diazepam, 5 to 10 mg intravenously or 10 mg intramuscularly. In the event of progression of the curare-like effect to paralysis of the respiratory muscles, mechanical respiration should be instituted and maintained until effective respiratory action returns.
The oral LD50 of propantheline bromide is 780 mg/kg in the mouse and 370 mg/kg in the rat.
PROPANTHELINE BROMIDE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The usual initial adult dose of propantheline bromide tablets is 15 mg taken 30 minutes before each meal and 30 mg at bedtime (a total of 75 mg daily). Subsequent dosage adjustment should be made according to the patient’s individual response and tolerance.
HOW SUPPLIED
Propantheline Bromide Tablets USP
15 mg white film-coated tablets
(Identified 54 303).
NDC 0054-4721-25: Bottles of 100 tablets.
Dispense in tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP/NF.
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]
Roxane Laboratories, Inc.
Columbus, Ohio 43216
4071101//05 Revised October 2012
© RLI, 2012
Package Label -
NDC 0054-4721-25: Bottles of 100 tablets.
Rx Only

Propantheline BromidePropantheline Bromide TABLET, FILM COATED
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||