PANTOPRAZOLE SODIUM
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use pantoprazole sodium delayed-release tablets, USP safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for pantoprazole sodium delayed-release tablets, USP. Pantoprazole Sodium Delayed-Release Tablets, USP Initial U.S. approval: 2000
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
- DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS
- PANTOPRAZOLE SODIUM CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- PANTOPRAZOLE SODIUM ADVERSE REACTIONS
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- PANTOPRAZOLE SODIUM DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- CLINICAL STUDIES
- HOW SUPPLIED
- INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
INDICATIONS & USAGE
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
|
Indication
|
Dose
|
Frequency
|
|---|---|---|
|
Short-Term Treatment of Erosive Esophagitis Associated With GERD
|
||
| Adults | 40 mg | Once daily for up to 8 weeks* |
|
Maintenance of Healing of Erosive Esophagitis
|
||
| Adults | 40 mg | Once daily |
|
Pathological Hypersecretory Conditions Including Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
|
||
| Adults | 40 mg | Twice daily** |
|
Formulation
|
Route
|
Instructions*
|
|---|---|---|
|
Delayed-Release Tablets
|
Oral | Swallowed whole, with or without food |
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS
- 40 mg yellow colored, biconvex oval shaped tablets plain on one side and imprinted with “W434” (brown ink) on other side.
- 20 mg yellow colored, biconvex oval shaped tablets plain on one side and imprinted with “W433” (brown ink) on other side.
PANTOPRAZOLE SODIUM CONTRAINDICATIONS
see Description (11)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
H. pylori
see Dosage and Administration (2) and Adverse Reactions (6.2)
see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)
See Drug Interactions (7.4).
PANTOPRAZOLE SODIUM ADVERSE REACTIONS
Adults
2
| Pantoprazole sodium delayed-release tablets (n=1473) % |
Comparators (n=345) % |
Placebo (n=82) % |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Headache Diarrhea Nausea Abdominal pain Vomiting Flatulence Dizziness Arthralgia |
12.2 8.8 7 6.2 4.3 3.9 3 2.8 |
12.8 9.6 5.2 4.1 3.5 2.9 2.9 1.4 |
8.5 4.9 9.8 6.1 2.4 3.7 1.2 1.2 |
Body as a Whole:
Gastrointestinal:
Hematologic:
Metabolic/Nutritional:
Musculoskeletal:
Nervous:
Skin and Appendages:
Special Senses:
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
Immune System Disorders:
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders:
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders:
Renal and Urinary Disorders:
Hepatobiliary Disorders:
Psychiatric Disorders:
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Concomitant use of atazanavir or nelfinavir with proton pump inhibitors is not recommended. Coadministration of atazanavir or nelfinavir with proton pump inhibitors is expected to substantially decrease atazanavir or nelfinavir plasma concentrations and may result in a loss of therapeutic effect and development of drug resistance.
There have been postmarketing reports of increased INR and prothrombin time in patients receiving proton pump inhibitors, including pantoprazole sodium delayed-release tablets, and warfarin concomitantly. Increases in INR and prothrombin time may lead to abnormal bleeding and even death. Patients treated with proton pump inhibitors and warfarin concomitantly should be monitored for increases in INR and prothrombin time.
Pantoprazole causes long-lasting inhibition of gastric acid secretion. Therefore, pantoprazole may interfere with absorption of drugs where gastric pH is an important determinant of their bioavailability (e.g., ketoconazole, ampicillin esters, and iron salts).
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy CategoryB
see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2)
Pantoprazole and its metabolites are excreted in the milk of rats. Pantoprazole excretion in human milk has been detected in a study of a single nursing mother after a single 40 mg oral dose. The clinical relevance of this finding is not known. Many drugs which are excreted in human milk have a potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants. Based on the potential for tumorigenicity shown for pantoprazole in rodent carcinogenicity studies, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the benefit of the drug to the mother.
The effectiveness of pantoprazole sodium delayed-release tablets for treating symptomatic GERD in pediatric patients has not been established.
Information describing use in pediatric patients with erosive esophagitis associated with GERD is approved for Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Inc.'s pantoprazole sodium delayed-release tablets. However, due to Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Inc.'s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
In short-term U.S. clinical trials, erosive esophagitis healing rates in the 107 elderly patients (≥ 65 years old) treated with pantoprazole sodium delayed-release tablets were similar to those found in patients under the age of 65. The incidence rates of adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities in patients aged 65 years and older were similar to those associated with patients younger than 65 years of age.
Erosive esophagitis healing rates in the 221 women treated with pantoprazole sodium delayed-release tablets in U.S. clinical trials were similar to those found in men. In the 122 women treated long-term with pantoprazole sodium delayed-release tablets 40 mg or 20 mg, healing was maintained at a rate similar to that in men. The incidence rates of adverse reactions were also similar for men and women.
Doses higher than 40 mg/day have not been studied in patients with hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
OVERDOSAGE
PANTOPRAZOLE SODIUM DESCRIPTION
The active ingredient in pantoprazole sodium delayed-release tablets, USP is a substituted benzimidazole, sodium 5-(difluoromethoxy)-2-[[(3,4-dimethoxy-2-pyridinyl)methyl] sulfinyl]1H-benzimidazole sesquihydrate, a compound that inhibits gastric acid secretion. Its empirical formula is C16H14F2N3NaO4S x 1.5 H2O, with a molecular weight of 432.4. The structural formula is:
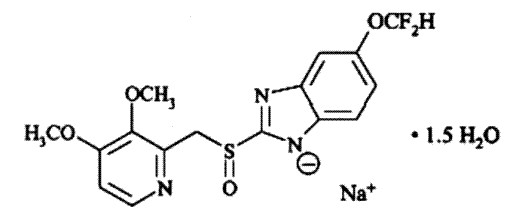
Pantoprazole sodium sesquihydrate, USP is a white to off-white powder and is racemic. Pantoprazole has weakly basic and acidic properties. Pantoprazole sodium sesquihydrate, USP is freely soluble in water and practically insoluble in hexane.
The stability of the compound in aqueous solution is pH-dependent. The rate of degradation increases with decreasing pH. At ambient temperature, the degradation half-life is approximately 2.8 hours at pH 5 and approximately 220 hours at pH 7.8.
Pantoprazole sodium is supplied as a delayed-release tablet for oral administration, available in 2 strengths (40 mg and 20 mg).
Each delayed-release tablet contains 45.1 mg or 22.56 mg of pantoprazole sodium sesquihydrate USP (equivalent to 40 mg or 20 mg pantoprazole, respectively) with the following inactive ingredients: aerosil 200, calcium stearate, colloidal silicon dioxide, mannitol, pregelatinized starch, shellac glaze, sodium carbonate anhydrous, sodium starch glycolate and talc. Each delayed-release tablet contains ammonium hydroxide, eudragit L 100-55, FD and C Blue #2, hypromellose, iron oxide black, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, polyethylene glycol 400, polyethylene glycol 4000, polyethylene glycol 6000, propylene glycol, sodium hydroxide, titanium dioxide and triethyl citrate as the coating ingredients.
Pantoprazole sodium delayed-release tablets USP, 20 mg and 40 mg, meet USP Dissolution Test 3.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
++++
|
–––––––—––––––––Median pH on day 7—–––––––––––––
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | Placebo | 20 mg | 40 mg | 80 mg |
| 8 a.m. - 8 a.m. (24 hours) |
1.3 | 2.9* | 3.8*# | 3.9*# |
| 8 a.m. - 10 p.m. (Daytime) |
1.6 | 3.2* | 4.4*# | 4.8*# |
| 10 p.m. - 8 a.m. (Nighttime) |
1.2 | 2.1* | 3* | 2.6* |
see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)
max
maxmax
max
max
14
max
max
in vivo
In vivoin vivo
see Drug Interactions (7.2)
34
34
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
in vitroin vitroin vivoin vitroin vitroin vitroin vivo
CLINICAL STUDIES
Adult Patients
| –––––––––––Pantoprazole Sodium Delayed-Release Tablets––––––––––– | Placebo | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week | 10 mg daily (n = 153) |
20 mg daily (n = 158) |
40 mg daily (n = 162) |
(n = 68) |
| 4 | 45.6%+ | 58.4%+# | 75%+* | 14.3% |
| 8 | 66%+ | 83.5 %+# | 92.6%+* | 39.7% |
|
––––Pantoprazole Sodium Delayed-Release Tablets––––– |
Nizatidine
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Week | 20 mg daily (n = 72) |
40 mg daily (n = 70) |
150 mg twice daily (n = 70) |
| 4 | 61.4%+ | 64%+ | 22.2% |
| 8 | 79.2%+ | 82.9%+ | 41.4% |
| Pantoprazole Sodium Delayed-Release Tablets 20 mg daily |
Pantoprazole Sodium Delayed-Release Tablets 40 mg daily |
Ranitidine 150 mg twice daily |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Study 1
|
n = 75 | n = 74 | n = 75 |
| Month 1 Month 3 Month 6 Month 12 |
91* 82* 76* 70* |
99* 93*# 90*# 86*# |
68 54 44 35 |
|
Study 2
|
n = 74 | n = 88 | n = 84 |
| Month 1 Month 3 Month 6 Month 12 |
89* 78* 72* 72* |
92*# 91*# 88*# 83* |
62 47 39 37 |
| Pantoprazole Sodium Delayed-Release Tablet 40 mg daily |
Ranitidine 150 mg twice daily |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Month 1 | Daytime Nighttime |
5.1 ± 1.6* 3.9 ± 1.1* |
18.3 ± 1.6 11.9 ± 1.1 |
| Month 12 | Daytime Nighttime |
2.9 ± 1.5* 2.5 ± 1.2* |
17.5 ± 1.5 13.8 ± 1.3 |
In a multicenter, open-label trial of 35 patients with pathological hypersecretory conditions, such as Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, with or without multiple endocrine neoplasia-type I, pantoprazole sodium delayed-release tablets successfully controlled gastric acid secretion. Doses ranging from 80 mg daily to 240 mg daily maintained gastric acid output below 10 mEq/h in patients without prior acid-reducing surgery and below 5 mEq/h in patients with prior acid-reducing surgery.
Doses were initially titrated to the individual patient needs, and adjusted in some patients based on the clinical response with time [see Dosage and Administration (2)]. Pantoprazole sodium delayed-release tablet was well tolerated at these dose levels for prolonged periods (greater than 2 years in some patients).
HOW SUPPLIED
How Supplied
Pantoprazole sodium delayed-release tablets, USP are supplied as 20 mg yellow colored, biconvex oval shaped tablets plain on one side and imprinted with “W433” (brown ink) on other side.
HDPE bottle of 30 tablets.............................NDC 64679-433-01
HDPE bottle of 90 tablets.............................NDC 64679-433-04
HDPE bottle of 1000 tablets.........................NDC 64679-433-02
Unit dose packages of 100 tablets…..........NDC 64679-433-03
HDPE bottle of 100 tablets...........................NDC 64679-433-05
Pantoprazole sodium delayed-release tablets, USP are supplied as 40 mg yellow colored, biconvex oval shaped tablets plain on one side and imprinted with “W434” (brown ink) on other side.
HDPE bottle of 30 tablets............................NDC 64679-434-01
HDPE bottle of 90 tablets............................NDC 64679-434-04
HDPE bottle of 1000 tablets........................NDC 64679-434-02
Unit dose packages of 100 tablets.............NDC 64679-434-03
HDPE bottle of 100 tablets..........................NDC 64679-434-05
Storage
Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F); [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling.Patient Counseling
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION

PANTOPRAZOLE SODIUMPANTOPRAZOLE SODIUM TABLET, DELAYED RELEASE
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||