oxaliplatin
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Oxaliplatin Injection, USP safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Oxaliplatin Injection, USP.Oxaliplatin Injection, USP concentrate, for solution for intavenous use Initial U.S. Approval: 2002 RECENT MAJOR CHANGES2.25.15.2BOXED WARNING WARNING: ANAPHYLACTIC REACTIONS See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning. Anaphylactic reactions to Oxaliplatin have been reported, and may occur within minutes of Oxaliplatin administration. Epinephrine, corticosteroids, and antihistamines have been employed to alleviate symptoms. (5.1) INDICATIONS AND USAGE1DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION• Administer oxaliplatin in combination with 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin every 2 weeks. (2.1):- Day 1: Oxaliplatin 85 mg/m2 intravenous infusion in 250 to 500 mL 5% Dextrose Injection, USP and leucovorin 200 mg/m2 intravenous infusion in 5% Dextrose Injection, USP both given over 120 minutes at the same time in separate bags using a Y-line, followed by 5-fluorouracil 400 mg/m2 intravenous bolus given over 2 to 4 minutes, followed by 5-fluorouracil 600 mg/m2 intravenous infusion in 500 mL 5% Dextrose Injection, USP (recommended) as a 22-hour continuous infusion.- Day 2: Leucovorin 200 mg/m2 intravenous infusion over 120 minutes, followed by 5-fluorouracil 400 mg/m2 intravenous bolus given over 2 to 4 minutes, followed by 5-fluorouracil 600 mg/m2 intravenous infusion in 500 mL 5% Dextrose Injection, USP (recommended) as a 22-hour continuous infusion.• Reduce the dose of oxaliplatin to 75 mg/m2 (adjuvant setting) or 65 mg/m2 (advanced colorectal cancer) (2.2):- if there are persistent grade 2 neurosensory events that do not resolve.- after recovery from grade 3/4 gastrointestinal toxicities (despite prophylactic treatment) or grade 4 neutropenia or grade 3/4 thrombocytopenia. Delay next dose until neutrophils ≥1.5 x 109/L and platelets ≥75 x 109/L.• For patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- WARNING: ANAPHYLACTIC REACTIONS
- 1 OXALIPLATIN INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 OXALIPLATIN DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 OXALIPLATIN CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 6 OXALIPLATIN ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 OXALIPLATIN DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 14.1 Combination Adjuvant Therapy with Oxaliplatin and Infusional 5-Fluorouracil /Leucovorin in Patients with Stage II or III Colon Cancer
- 14.2 Combination Therapy with Oxaliplatin and 5-Fluorouracil/Leucovorin in Patients Previously Untreated for Advanced Colorectal Cancer
- 14.3 Combination Therapy with Oxaliplatin and 5-Fluorouracil/Leucovorin in Previously Treated Patients with Advanced Colorectal Cancer
- 15 REFERENCES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL-Oxaliplatin Injection, USP
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: ANAPHYLACTIC REACTIONS
Anaphylactic reactions to Oxaliplatin have been reported, and may occur within minutes of Oxaliplatin administration. Epinephrine, corticosteroids, and antihistamines have been employed to alleviate symptoms of anaphylaxis [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 )].
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Oxaliplatin Injection should be administered under the supervision of a qualified physician experienced in the use of cancer chemotherapeutic agents. Appropriate management of therapy and complications is possible only when adequate diagnostic and treatment facilities are readily available.
2.1 Dosage
2222
222
Figure 1
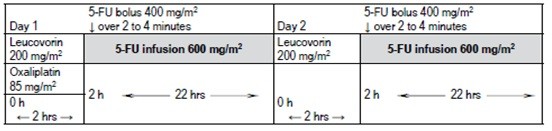
3
2.2 Dose Modification Recommendations
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
Adjuvant Therapy in Patients with Stage III Colon Cancer
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
2
22299
Dose Modifications in Therapy in Previously Untreated and Previously Treated Patients with Advanced Colorectal Cancer
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
2
299
Dose Modifications in Therapy for Patients with Renal Impairment
22[see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
2.3 Preparation of Infusion Solution
A final dilution must never be performed with a sodium chloride solution or other chloride-containing solutions.
6 hours at room temperature [20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F)] or up to 24 hours under refrigeration [2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F)].
The infusion line should be flushed with 5% Dextrose Injection, USP prior to administration of any concomitant medication.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Oxaliplatin Injection is supplied in single-use vials containing 50 mg or 100 mg of oxaliplatin as a sterile, preservative-free, aqueous solution at a concentration of 5 mg/mL.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Allergic Reactions
See boxed warning
[4]
5.2 Neurologic Toxicity
Neuropathy
An acute, reversible, primarily peripheral, sensory neuropathy that is of early onset, occurring within hours or one to two days of dosing, that resolves within 14 days, and that frequently recurs with further dosing.
A persistent (>14 days), primarily peripheral, sensory neuropathy that is usually characterized by paresthesias, dysesthesias, hypoesthesias, but may also include deficits in proprioception that can interfere with daily activities (e.g., writing, buttoning, swallowing, and difficulty walking from impaired proprioception).
| Grade | Definition |
|---|---|
| Grade 0 |
No change or none |
| Grade 1 |
Mild paresthesias, loss of deep tendon reflexes |
| Grade 2 |
Mild or moderate objective sensory loss, moderate paresthesias |
| Grade 3 |
Severe objective sensory loss or paresthesias that interfere with function |
| Grade 4 |
Not applicable |
| Grade | Definition |
|---|---|
| Grade 1 |
Resolved and did not interfere with functioning |
| Grade 2 |
Interfered with function but not daily activities |
| Grade 3 |
Pain or functional impairment that interfered with daily activities |
| Grade 4 |
Persistent impairment that is disabling or life-threatening |
Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome
[see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]
5.3 Pulmonary Toxicity
Oxaliplatin has been associated with pulmonary fibrosis (<1% of study patients), which may be fatal. The combined incidence of cough and dyspnea was 7.4% (any grade) and <1% (grade 3) with no grade 4 events in the oxaliplatin plus infusional 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin arm compared to 4.5% (any grade) and no grade 3 and 0.1% grade 4 events in the infusional 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin alone arm in adjuvant colon cancer patients. In this study, one patient died from eosinophilic pneumonia in the oxaliplatin combination arm. The combined incidence of cough, dyspnea and hypoxia was 43% (any grade) and 7% (grade 3 and 4) in the oxaliplatin plus 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin arm compared to 32% (any grade) and 5% (grade 3 and 4) in the irinotecan plus 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin arm of unknown duration for patients with previously untreated colorectal cancer. In case of unexplained respiratory symptoms such as non-productive cough, dyspnea, crackles, or radiological pulmonary infiltrates, oxaliplatin should be discontinued until further pulmonary investigation excludes interstitial lung disease or pulmonary fibrosis.
5.4 Hepatotoxicity
Hepatotoxicity as evidenced in the adjuvant study, by increase in transaminases (57% vs. 34%) and alkaline phosphatase (42% vs. 20%) was observed more commonly in the oxaliplatin combination arm than in the control arm. The incidence of increased bilirubin was similar on both arms. Changes noted on liver biopsies include: peliosis, nodular regenerative hyperplasia or sinusoidal alterations, perisinusoidal fibrosis, and veno-occlusive lesions. Hepatic vascular disorders should be considered, and if appropriate, should be investigated in case of abnormal liver function test results or portal hypertension, which cannot be explained by liver metastases [see Clinical Trials Experience ( 6.1 )].
5.5 Use in Pregnancy
[see Use In Specific Populations (8.1)]
5.6 Recommended Laboratory Tests
[see Dosage and Administration (2)].
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
[see Warnings and Precautions (5)]
Combination Adjuvant Therapy with Oxaliplatin and Infusional 5-Fluorouracil/Leucovorin in Patients with Colon Cancer
[see Clinical Studies (14)]
[see Clinical Studies (14)]
| Adverse Reaction (WHO/Pref) | Oxaliplatin + 5-FU/LV (N=1108) |
5-FU/LV (N=1111) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) |
Grade 3/4 (%) |
All Grades (%) |
Grade 3/4 (%) |
|
| Any Event |
100 |
70 |
99 |
31 |
|
Allergy/Immunology
|
||||
| Allergic Reaction |
10 |
3 |
2 |
<1 |
|
Constitutional Symptoms/Pain
|
||||
| Fatigue |
44 |
4 |
38 |
1 |
| Abdominal Pain |
18 |
1 |
17 |
2 |
|
Dermatology/Skin
|
||||
| Skin Disorder |
32 |
2 |
36 |
2 |
| Injection Site Reaction1
|
11 |
3 |
10 |
3 |
|
Gastrointestinal
|
||||
| Nausea |
74 |
5 |
61 |
2 |
| Diarrhea |
56 |
11 |
48 |
7 |
| Vomiting |
47 |
6 |
24 |
1 |
| Stomatitis |
42 |
3 |
40 |
2 |
| Anorexia |
13 |
1 |
8 |
<1 |
|
Fever/Infection
|
||||
| Fever |
27 |
1 |
12 |
1 |
| Infection |
25 |
4 |
25 |
3 |
|
Neurology
|
||||
| Overall Peripheral Sensory Neuropathy |
92 |
12 |
16 |
<1 |
1
[see Clinical Studies (14)]
Table 4 - Adverse Reactions Reported in Patients with Colon Cancer receiving Adjuvant
Treatment (≥5% of all patients, but with <1% NCI Grade 3/4 events)
| Adverse Reaction (WHO/Pref) |
Oxaliplatin + 5-FU/LV (N=1108) |
5-FU/LV (N=1111) |
|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | All Grades (%) | |
|
Allergy/Immunology
|
||
| Rhinitis |
6 |
8 |
|
Constitutional Symptoms/Pain/Ocular/Visual
|
||
| Epistaxis |
16 |
12 |
| Weight Increase |
10 |
10 |
| Conjunctivitis |
9 |
15 |
| Headache |
7 |
5 |
| Dyspnea |
5 |
3 |
| Pain |
5 |
5 |
| Lacrimation Abnormal |
4 |
12 |
|
Dermatology/Skin
|
||
| Alopecia |
30 |
28 |
|
Gastrointestinal
|
||
| Constipation |
22 |
19 |
| Taste Perversion |
12 |
8 |
| Dyspepsia |
8 |
5 |
|
Metabolic
|
||
| Phosphate Alkaline increased |
42 |
20 |
|
Neurology
|
||
| Sensory Disturbance |
8 |
1 |
Patients Previously Untreated for Advanced Colorectal Cancer
[see Clinical Studies (14)]
[see Clinical Studies (14)]
| Adverse Reaction (WHO/Pref) |
Oxaliplatin + 5-FU/LV (N=259) |
irinotecan + 5-FU/LV (N=256) |
Oxaliplatin + irinotecan (N=258) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) |
Grade 3/4 (%) |
All Grades (%) |
Grade 3/4 (%) |
All Grades (%) |
Grade 3/4 (%) |
|
|
*Not otherwise specified **Absolute neutrophil count |
||||||
| Any Event |
99 |
82 |
98 |
70 |
99 |
76 |
|
Allergy/Immunology
|
||||||
| Hypersensitivity |
12 |
2 |
5 |
0 |
6 |
1 |
|
Cardiovascular
|
||||||
| Thrombosis |
6 |
5 |
6 |
6 |
3 |
3 |
| Hypotension |
5 |
3 |
6 |
3 |
4 |
3 |
|
Constitutional Symptoms/Pain/Ocular/Visual
|
||||||
| Fatigue |
70 |
7 |
58 |
11 |
66 |
16 |
| Abdominal Pain |
29 |
8 |
31 |
7 |
39 |
10 |
| Myalgia |
14 |
2 |
6 |
0 |
9 |
2 |
| Pain |
7 |
1 |
5 |
1 |
6 |
1 |
| Vision abnormal |
5 |
0 |
2 |
1 |
6 |
1 |
| Neuralgia |
5 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
1 |
|
Dermatology/Skin
|
||||||
| Skin reaction – hand/foot |
7 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
| Injection site reaction |
6 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
4 |
1 |
|
Gastrointestinal
|
||||||
| Nausea |
71 |
6 |
67 |
15 |
83 |
19 |
| Diarrhea |
56 |
12 |
65 |
29 |
76 |
25 |
| Vomiting |
41 |
4 |
43 |
13 |
64 |
23 |
| Stomatitis |
38 |
0 |
25 |
1 |
19 |
1 |
| Anorexia |
35 |
2 |
25 |
4 |
27 |
5 |
| Constipation |
32 |
4 |
27 |
2 |
21 |
2 |
| Diarrhea-colostomy |
13 |
2 |
16 |
7 |
16 |
3 |
| Gastrointestinal NOS* |
5 |
2 |
4 |
2 |
3 |
2 |
|
Hematology/Infection
|
||||||
| Infection normal ANC** |
10 |
4 |
5 |
1 |
7 |
2 |
| Infection low ANC** |
8 |
8 |
12 |
11 |
9 |
8 |
| Lymphopenia |
6 |
2 |
4 |
1 |
5 |
2 |
| Febrile neutropenia |
4 |
4 |
15 |
14 |
12 |
11 |
|
Hepatic/Metabolic/Laboratory/Renal
|
||||||
| Hyperglycemia |
14 |
2 |
11 |
3 |
12 |
3 |
| Hypokalemia |
11 |
3 |
7 |
4 |
6 |
2 |
| Dehydration |
9 |
5 |
16 |
11 |
14 |
7 |
| Hypoalbuminemia |
8 |
0 |
5 |
2 |
9 |
1 |
| Hyponatremia |
8 |
2 |
7 |
4 |
4 |
1 |
| Urinary frequency |
5 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
3 |
1 |
|
Neurology
|
||||||
| Overall Neuropathy |
82 |
19 |
18 |
2 |
69 |
7 |
| Paresthesias |
77 |
18 |
16 |
2 |
62 |
6 |
| Pharyngo-laryngeal dysesthesias |
38 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
28 |
1 |
| Neuro-sensory |
12 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
9 |
1 |
| Neuro NOS* |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
|
Pulmonary
|
||||||
| Cough |
35 |
1 |
25 |
2 |
17 |
1 |
| Dyspnea |
18 |
7 |
14 |
3 |
11 |
2 |
| Hiccups |
5 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
3 |
2 |
[see Clinical Studies (14)]
Table 6 - Adverse Reactions Reported in Patients Previously Untreated for Advanced Colorectal Cancer Clinical Trial (≥5% of all patients but with < 1% NCI Grade 3/4 events)
| Adverse Reaction (WHO/Pref) | Oxaliplatin + 5-FU/LV (N=259) |
irinotecan + 5-FU/LV (N=256) |
Oxaliplatin + irinotecan (N=258) |
|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) |
All Grades (%) |
All Grades (%) |
|
|
* Absolute neutrophil count |
|||
|
Allergy/Immunology
|
|||
| Rash |
11 |
4 |
7 |
| Rhinitis allergic |
10 |
6 |
6 |
|
Cardiovascular
|
|||
| Edema |
15 |
13 |
10 |
|
Constitutional Symptoms/Pain/Ocular/Visual
|
|||
| Headache |
13 |
6 |
9 |
| Weight loss |
11 |
9 |
11 |
| Epistaxis |
10 |
2 |
2 |
| Tearing |
9 |
1 |
2 |
| Rigors |
8 |
2 |
7 |
| Dysphasia |
5 |
3 |
3 |
| Sweating |
5 |
6 |
12 |
| Arthralgia |
5 |
5 |
8 |
|
Dermatology/Skin
|
|||
| Alopecia |
38 |
44 |
67 |
| Flushing |
7 |
2 |
5 |
| Pruritus |
6 |
4 |
2 |
| Dry Skin |
6 |
2 |
5 |
|
Gastrointestinal
|
|||
| Taste perversion |
14 |
6 |
8 |
| Dyspepsia |
12 |
7 |
5 |
| Flatulence |
9 |
6 |
5 |
| Mouth Dryness |
5 |
2 |
3 |
|
Hematology/Infection
|
|||
| Fever normal ANC* |
16 |
9 |
9 |
|
Hepatic/Metabolic/Laboratory/Renal
|
|||
| Hypocalcemia |
7 |
5 |
4 |
| Elevated Creatinine |
4 |
4 |
5 |
|
Neurology
|
|||
| Insomnia |
13 |
9 |
11 |
| Depression |
9 |
5 |
7 |
| Dizziness |
8 |
6 |
10 |
| Anxiety |
5 |
2 |
6 |
Previously Treated Patients with Advanced Colorectal Cancer
[see Clinical Studies (14)]
Thirteen percent of patients in the oxaliplatin and 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin combination arm and 18% in the 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin arm of the previously treated study had to discontinue treatment because of adverse effects related to gastrointestinal, or hematologic adverse reactions, or neuropathies. Both 5-fluorouracil and oxaliplatin are associated with gastrointestinal and hematologic adverse reactions. When oxaliplatin is administered in combination with 5-fluorouracil, the incidence of these events is increased.
The incidence of death within 30 days of treatment in the previously treated study, regardless of causality, was 5% with the oxaliplatin and 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin combination, 8% with oxaliplatin alone, and 7% with 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin. Of the 7 deaths that occurred on the oxaliplatin and 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin combination arm within 30 days of stopping treatment, 3 may have been treatment related, associated with gastrointestinal bleeding or dehydration.
The following table provides adverse reactions reported in the previously treated study [see Clinical Studies (14)] by body system and in decreasing order of frequency in the oxaliplatin and 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin combination arm for events with overall incidences ≥5% and for grade 3/4 events with incidences ≥1%. This table does not include hematologic and blood chemistry abnormalities; these are shown separately below.
Table 7 – Adverse Reactions Reported in Previously Treated Colorectal Cancer Clinical Trial (≥5% of all patients and with ≥1% NCI Grade 3/4 events)
|
|
5-FU/LV
(N = 142) |
Oxaliplatin
(N = 153) |
Oxaliplatin +
5-FU/LV (N = 150) |
|||
|
Adverse Reaction
(WHO/Pref) |
All
Grades (%) |
Grade
3/4 (%) |
All
Grades (%) |
Grade
3/4 (%) |
All
Grades (%) |
Grade
3/4 (%) |
| Any Event |
98 |
41 |
100 |
46 |
99 |
73 |
|
Cardiovascular
|
||||||
| Dyspnea |
11 |
2 |
13 |
7 |
20 |
4 |
| Coughing |
9 |
0 |
11 |
0 |
19 |
1 |
| Edema |
13 |
1 |
10 |
1 |
15 |
1 |
| Thromboembolism |
4 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
9 |
8 |
| Chest Pain |
4 |
1 |
5 |
1 |
8 |
1 |
|
Constitutional Symptoms/Pain
|
||||||
| Fatigue |
52 |
6 |
61 |
9 |
68 |
7 |
| Back Pain |
16 |
4 |
11 |
0 |
19 |
3 |
| Pain |
9 |
3 |
14 |
3 |
15 |
2 |
|
Dermatology/Skin
|
||||||
| Injection Site Reaction |
5 |
1 |
9 |
0 |
10 |
3 |
|
Gastrointestinal
|
||||||
| Diarrhea |
44 |
3 |
46 |
4 |
67 |
11 |
| Nausea |
59 |
4 |
64 |
4 |
65 |
11 |
| Vomiting |
27 |
4 |
37 |
4 |
40 |
9 |
| Stomatitis |
32 |
3 |
14 |
0 |
37 |
3 |
| Abdominal Pain |
31 |
5 |
31 |
7 |
33 |
4 |
| Anorexia |
20 |
1 |
20 |
2 |
29 |
3 |
| Gastroesophageal Reflux |
3 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
5 |
2 |
|
Hematology/Infection
|
||||||
| Fever |
23 |
1 |
25 |
1 |
29 |
1 |
| Febrile Neutropenia |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
6 |
6 |
|
Hepatic/Metabolic/Laboratory/Renal
|
||||||
| Hypokalemia |
3 |
1 |
3 |
2 |
9 |
4 |
| Dehydration |
6 |
4 |
5 |
3 |
8 |
3 |
|
Neurology
|
||||||
| Neuropathy |
17 |
0 |
76 |
7 |
74 |
7 |
| Acute |
10 |
0 |
65 |
5 |
56 |
2 |
| Persistent |
9 |
0 |
43 |
3 |
48 |
6 |
The following table provides adverse reactions reported in the previously treated study [see Clinical Studies (14)] by body system and in decreasing order of frequency in the oxaliplatin and 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin combination arm for events with overall incidences ≥5% but with incidences <1% NCI Grade 3/4 events.
Table 8 - Adverse Reactions Reported in Previously Treated Colorectal Cancer Clinical Trial (≥5% of all patients but with < 1% NCI Grade 3/4 events)
| |
5-FU/LV
(N = 142) |
Oxaliplatin
(N = 153) |
Oxaliplatin +
5-FU/LV (N = 150) |
|
Adverse Reaction
(WHO/Pref) |
All Grades (%)
|
All Grades (%)
|
All Grades (%)
|
|
Allergy/Immunology
|
|||
| Rhinitis |
4 |
6 |
15 |
| Allergic Reaction |
1 |
3 |
10 |
| Rash |
5 |
5 |
9 |
|
Cardiovascular
|
|||
| Peripheral Edema |
11 |
5 |
10 |
|
Constitutional Symptoms/Pain/Ocular/Visual
|
|||
| Headache |
8 |
13 |
17 |
| Arthralgia |
10 |
7 |
10 |
| Epistaxis |
1 |
2 |
9 |
| Abnormal Lacrimation |
6 |
1 |
7 |
| Rigors |
6 |
9 |
7 |
|
Dermatology/Skin
|
|||
| Hand-Foot Syndrome |
13 |
1 |
11 |
| Flushing |
2 |
3 |
10 |
| Alopecia |
3 |
3 |
7 |
|
Gastrointestinal
|
|||
| Constipation |
23 |
31 |
32 |
| Dyspepsia |
10 |
7 |
14 |
| Taste Perversion |
1 |
5 |
13 |
| Mucositis |
10 |
2 |
7 |
| Flatulence |
6 |
3 |
5 |
|
Hepatic/Metabolic/Laboratory/Renal
|
|||
| Hematuria |
4 |
0 |
6 |
| Dysuria |
1 |
1 |
6 |
|
Neurology
|
|||
| Dizziness |
8 |
7 |
13 |
| Insomnia |
4 |
11 |
9 |
|
Pulmonary
|
|||
| Upper Resp. Tract Infection |
4 |
7 |
10 |
| Pharyngitis |
10 |
2 |
9 |
| Hiccup |
0 |
2 |
5 |
Hematologic Changes
Table 9 - Adverse Hematologic Reactions in Patients with Colon Cancer Receiving Adjuvant Therapy (≥5% of patients)
| |
Oxaliplatin + 5-FU/LV
(N=1108) |
5-FU/LV
(N=1111) |
||
|
Hematology Parameter
|
All Grades
(%) |
Grade 3/4
(%) |
All Grades
(%) |
Grade 3/4
(%) |
| Anemia |
76 |
1 |
67 |
<1 |
| Neutropenia |
79 |
41 |
40 |
5 |
| Thrombocytopenia |
77 |
2 |
19 |
<1 |
Table 10 – Adverse Hematologic Reactions in Patients Previously Untreated for Advanced Colorectal Cancer (≥5% of patients)
| Oxaliplatin + 5-FU/LV (N=259) |
irinotecan + 5-FU/LV (N=256) |
Oxaliplatin + Irinotecan (N=258) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hematology Parameter | All Grades (%) | Grade 3/4 (%) |
All Grades (%) | Grade 3/4 (%) |
All Grades (%) | Grade 3/4 (%) |
| Anemia |
27 |
3 |
28 |
4 |
25 |
3 |
| Leukopenia |
85 |
20 |
84 |
23 |
76 |
24 |
| Neutropenia |
81 |
53 |
77 |
44 |
71 |
36 |
| Thrombocytopenia |
71 |
5 |
26 |
2 |
44 |
4 |
Table 11 – Adverse Hematologic Reactions in Previously Treated Patients (≥5% of patients)
| 5-FU/LV (N=142) |
Oxaliplatin (N=153) | Oxaliplatin + 5-FU/LV (N=150) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hematology Parameter | All Grades (%) |
Grade 3/4 (%) |
All Grades (%) |
Grade 3/4 (%) |
All Grades (%) |
Grade 3/4 (%) |
| Anemia |
68 |
2 |
64 |
1 |
81 |
2 |
| Leukopenia |
34 |
1 |
13 |
0 |
76 |
19 |
| Neutropenia |
25 |
5 |
7 |
0 |
73 |
44 |
| Thrombocytopenia |
20 |
0 |
30 |
3 |
64 |
4 |
Thrombocytopenia and Bleeding
The incidence of Grade 3/4 thrombocytopenia was 2% in adjuvant patients with colon cancer. In patients treated for advanced colorectal cancer the incidence of Grade 3/4 thrombocytopenia was 3 to 5%, and the incidence of these events was greater for the combination of oxaliplatin and 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin over the irinotecan plus 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin or 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin control groups. Grade 3/4 gastrointestinal bleeding was reported in 0.2% of adjuvant patients receiving oxaliplatin and 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin. In the previously untreated patients, the incidence of epistaxis was 10% in the oxaliplatin and 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin arm, and 2% and 1%, respectively, in the irinotecan plus 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin or irinotecan plus oxaliplatin arms.
Neutropenia
Gastrointestinal
The incidence of gastrointestinal adverse reactions in the previously untreated and previously treated patients appears to be similar across cycles. Premedication with antiemetics, including 5-HT3 blockers, is recommended. Diarrhea and mucositis may be exacerbated by the addition of oxaliplatin to 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin, and should be managed with appropriate supportive care. Since cold temperature can exacerbate acute neurological symptoms, ice (mucositis prophylaxis) should be avoided during the infusion of oxaliplatin.
Dermatologic
Intravenous Site Reactions
Anticoagulation and Hemorrhage
Renal
Hepatic
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
Table 12 - Adverse Hepatic Reactions in Patients with Stage II or III Colon Cancer Receiving Adjuvant Therapy (≥5% of patients)
| Oxaliplatin + 5-FU/LV (N=1108) |
5-FU/LV (N=1111) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatic Parameter | All Grades (%) |
Grade 3/4 (%) |
All Grades (%) |
Grade 3/4 (%) |
| Increase in transaminases |
57 |
2 |
34 |
1 |
| ALP increased |
42 |
<1 |
20 |
<1 |
| Bilirubinaemia |
20 |
4 |
20 |
5 |
Table 13 – Adverse Hepatic – Clinical Chemistry Abnormalities in Patients Previously Untreated for Advanced Colorectal Cancer (≥5% of patients)
| Oxaliplatin + 5-FU/LV (N=259) |
irinotecan + 5-FU/LV (N=256) |
Oxaliplatin + irinotecan (N=258) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Chemistry | All Grades (%) |
Grade 3/4 (%) |
All Grades (%) |
Grade 3/4 (%) |
All Grades (%) |
Grade 3/4 (%) |
| ALT (SGPT-ALAT) |
6 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
5 |
2 |
| AST (SGOT-ASAT) |
17 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
11 |
1 |
| Alkaline Phosphatase |
16 |
0 |
8 |
0 |
14 |
2 |
| Total Bilirubin |
6 |
1 |
3 |
1 |
3 |
2 |
Table 14 – Adverse Hepatic – Clinical Chemistry Abnormalities in Previously Treated Patients (≥5% of patients)
| 5-FU/LV (N=142) |
Oxaliplatin (N=153) |
Oxaliplatin + 5-FU/LV (N=150) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Chemistry | All Grades (%) |
Grade 3/4 (%) |
All Grades (%) |
Grade 3/4 (%) |
All Grades (%) |
Grade 3/4 (%) |
| ALT (SGPT-ALAT) |
28 |
3 |
36 |
1 |
31 |
0 |
| AST (SGOT-ASAT) |
39 |
2 |
54 |
4 |
47 |
0 |
| Total Bilirubin |
22 |
6 |
13 |
5 |
13 |
1 |
Thromboembolism
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Body as a whole:
Central and peripheral nervous system disorders:
Liver and Gastrointestinal system disorders:
Clostridium difficile
Hearing and vestibular system disorders:
Platelet, bleeding, and clotting disorders:
Red Blood Cell disorders:
Renal disorders:
Respiratory system disorders:
Vision disorders:
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
No specific cytochrome P-450-based drug interaction studies have been conducted. No pharmacokinetic interaction between 85 mg/m2 oxaliplatin and 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin has been observed in patients treated every 2 weeks. Increases of 5-fluorouracil plasma concentrations by approximately 20% have been observed with doses of 130 mg/m2 oxaliplatin dosed every 3 weeks. Because platinum-containing species are eliminated primarily through the kidney, clearance of these products may be decreased by coadministration of potentially nephrotoxic compounds; although, this has not been specifically studied [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3 )].
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether oxaliplatin or its derivatives are excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from oxaliplatin, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric Use
2 22
222222
2
2<
max0-48inf2max0-48inf 2
8.5 Geriatric Use
[see Clinical Studies (14)]
[see Clinical Studies (14)][see Clinical Studies (14)]
8.6 Patients with Renal Impairment
The exposure (AUC) of unbound platinum in plasma ultrafiltrate tends to increase in renally impaired patients [see Pharmacokinetics ( 12.3 )]. Caution and close monitoring should be exercised when oxaliplatin is administered to patients with renal impairment. The starting oxaliplatin dose does not need to be reduced in patients with mild (creatinine clearance=50 to 80 mL/min) or moderate (creatinine clearance=30 to 49 mL/min) renal impairment. However, the starting dose of oxaliplatin should be reduced in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance < 30 mL/min) [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.2 )].
10 OVERDOSAGE
3
11 DESCRIPTION
Oxaliplatin Injection, USP is an antineoplastic agent with the molecular formula C8H14N2O4Pt and the chemical name of cis-[(1 R,2 R)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine-N,N’] [oxalato(2-)-O,O’] platinum. Oxaliplatin is an organoplatinum complex in which the platinum atom is complexed with 1,2-diaminocyclohexane(DACH) and with an oxalate ligand as a leaving group.
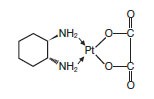
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
N7
In vivoin vitroin vivo
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
1/2α1/2β1/2γ2max
0-48hr
Distribution
2
Metabolism
in vitro
Elimination
Pharmacokinetics in Special Populations
Pediatric
[See Use In Specific Patient Populations (8.4)].
Renal Impairment
22max[see Use In Specific Populations (8.6)] [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Drug - Drug Interactions
22In vitroIn vitro
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
in vitroin vitroin vivo
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Combination Adjuvant Therapy with Oxaliplatin and Infusional 5-Fluorouracil /Leucovorin in Patients with Stage II or III Colon Cancer
341-299
| Treatment Arm | Dose | Regimen |
|---|---|---|
| Oxaliplatin + 5-FU/LV (FOLFOX4) (N =1123) |
Day 1: Oxaliplatin: 85 mg/m2 (2-hour infusion) + LV: 200 mg/m2 (2-hour infusion), followed by 5-FU: 400 mg/m2 (bolus), 600 mg/m2 (22-hour infusion) Day 2: LV: 200 mg/m2 (2-hour infusion), followed by 5-FU: 400 mg/m2 (bolus), 600 mg/m2 (22-hour infusion) |
every 2 weeks 12 cycles |
| 5-FU/LV (N=1123) |
Day 1: LV: 200 mg/m2 (2-hour infusion), followed by 5-FU: 400 mg/m2 (bolus), 600 mg/m2 (22-hour infusion) Day 2: LV: 200 mg/m2 (2-hour infusion), followed by 5-FU: 400 mg/m2 (bolus), 600 mg/m2 (22-hour infusion) |
every 2 weeks 12 cycles |
The following tables show the baseline characteristics and dosing of the patient population entered into this study. The baseline characteristics were well balanced between arms.
| Oxaliplatin + infusional 5-FU/LV (N=1123) |
Infusional 5-FU/LV (N=1123) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Sex: Male (%) |
56.1 |
52.4 |
| Female (%) |
43.9 |
47.6 |
| Median age (years) |
61 |
60 |
| <65 years of age (%) |
64.4 |
66.2 |
| ≥65 years of age (%) |
35.6 |
33.8 |
|
Karnofsky Performance Status (KPS) (%)
|
||
| 100 |
29.7 |
30.5 |
| 90 |
52.2 |
53.9 |
| 80 |
4.4 |
3.3 |
| 70 |
13.2 |
11.9 |
| <60 |
0.6 |
0.4 |
|
Primary site (%)
|
||
| Colon including cecum |
54.6 |
54.4 |
| Sigmoid |
31.9 |
33.8 |
| Recto sigmoid |
12.9 |
10.9 |
| Other including rectum |
0.6 |
0.9 |
|
Bowel obstruction (%)
|
||
| Yes |
17.9 |
19.3 |
|
Perforation (%)
|
||
| Yes |
6.9 |
6.9 |
|
Stage at Randomization (%)
|
||
| II (T=3,4, N=0, M=0) |
40.1 |
39.9 |
| III (T=any, N=1,2, M=0) |
59.6 |
59.3 |
| IV (T=any, N=any, M=1) |
0.4 |
0.8 |
|
Staging – T (%)
|
||
| T1 |
0.5 |
0.7 |
| T2 |
4.5 |
4.8 |
| T3 |
76 |
75.9 |
| T4 |
19 |
18.5 |
|
Staging – N (%)
|
||
| N0 |
40.2 |
39.9 |
| N1 |
39.4 |
39.4 |
| N2 |
20.4 |
20.7 |
|
Staging – M (%)
|
||
| M1 |
0.4 |
0.8 |
| Oxaliplatin + infusional 5-FU/LV (N=1108) |
Infusional 5-FU/LV (N=1111) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Median Relative Dose Intensity (%) |
||
| 5-FU |
84.4 |
97.7 |
| Oxaliplatin |
80.5 |
N/A |
| Median Number of Cycles |
12 |
12 |
| Median Number of cycles with oxaliplatin |
11 |
N/A |
The following table and figures summarize the disease-free survival (DFS) results in the overall randomized population and in patients with stage II and III disease based on an ITT analysis. The median duration of follow-up was approximately 77 months.
| Parameter | Oxaliplatin +infusional 5-FU/LV |
infusional 5-FU/LV |
|---|---|---|
|
Data cut off for disease-free survival 1 June 2006 * Disease-free survival at 5 years **A hazard ratio of less than 1 favors Oxaliplatin + Infusional 5-fluorouracil/leocovorin |
||
|
Overall
|
||
| N |
1123 |
1123 |
| Number of events – relapse or death (%) |
304 (27.1) |
360 (32.1) |
| Disease-free survival % [95% CI] * |
73.3 [70.7, 76] |
67.4 [64.6, 70.2] |
| Hazard Ratio [95% CI] ** |
0.8 [0.68, 0.93] |
|
| Stratified Logrank test |
p=0.003 |
|
|
Stage III (Dukes’ C)
|
||
| N |
672 |
675 |
| Number of events –relapse or death (%) |
226 (33.6) |
271 (40.1) |
| Disease-free survival % [95% CI] * |
66.4 [62.7, 70] |
58.9 [55.2, 62.7] |
| Hazard Ratio [95% CI] ** |
0.78 [0.65, 0.93] |
|
| Logrank test |
p=0.005 |
|
|
Stage II (Dukes’ B2)
|
||
| N |
451 |
448 |
| Number of events – relapse or death (%) |
78 (17.3) |
89 (19.9) |
| Disease-free survival % [95% CI] * |
83.7 [80.2, 87.1] |
79.9 [76.2, 83.7] |
| Hazard Ratio [95% CI] ** |
0.84 [0.62, 1.14] |
|
| Logrank test |
p=0.258 |
|
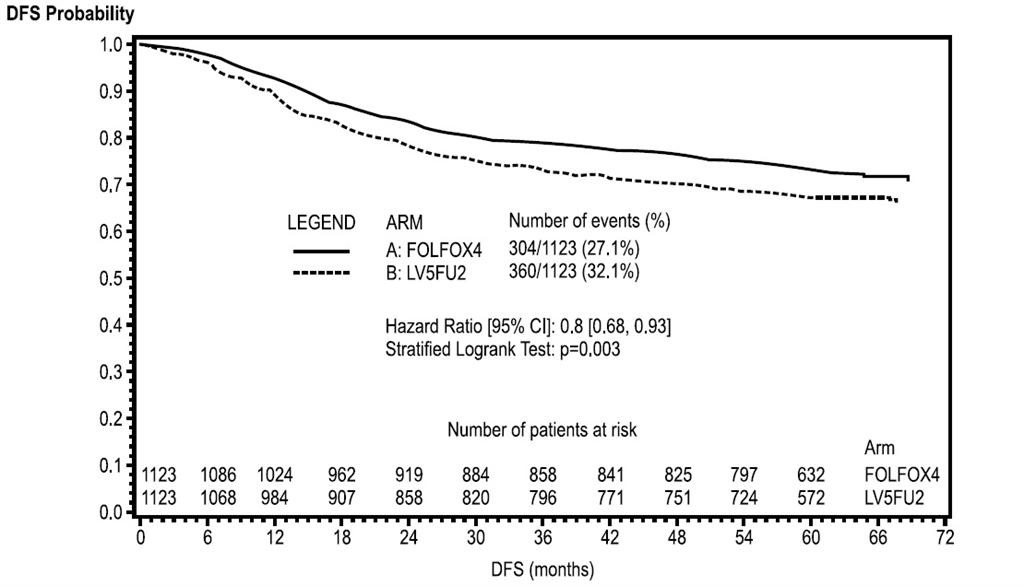
Figure 2 - DFS Kaplan-Meier curves by treatment arm (cutoff: 1 June 2006) – ITT population
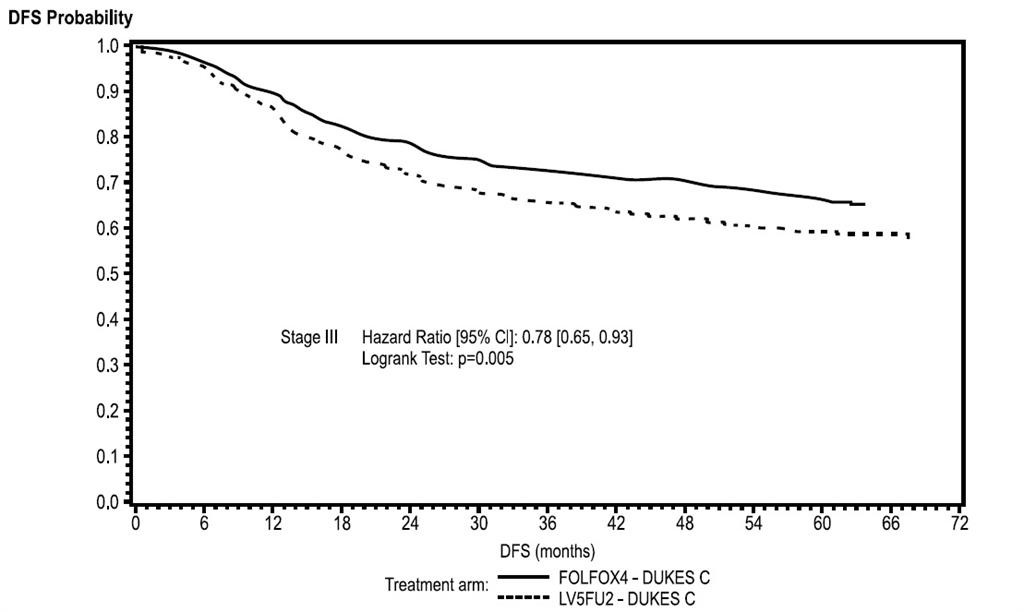
Figure 3 - DFS Kaplan-Meier curves by treatment arm in Stage III patients (cutoff: 1 June 2006) – ITT population
| Parameter | Oxaliplatin + infusional 5-FU/LV |
Infusional 5-FU/LV |
|---|---|---|
|
*A hazard ratio of less than 1 favors Oxaliplatin + Infusional 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin Data cut off for overall survival 16 January 2007 |
||
|
Overall
|
||
| N |
1123 |
1123 |
| Number of death events (%) |
245 (21.8) |
283 (25.2) |
| Hazard Ratio* [95% CI] |
0.84 [0.71, 1] |
|
|
Stage III (Dukes’ C)
|
||
| N |
672 |
675 |
| Number of death events (%) |
182 (27.1) |
220 (32.6) |
| Hazard Ratio* [95% CI] |
0.8 [0.65, 0.97] |
|
|
Stage II (Dukes’ B2)
|
||
| N |
451 |
448 |
| Number of death events (%) |
63 (14) |
63 (14.1) |
| Hazard Ratio* [95% CI] |
1 [0.7, 1.41] |
|
14.2 Combination Therapy with Oxaliplatin and 5-Fluorouracil/Leucovorin in Patients Previously Untreated for Advanced Colorectal Cancer
99
Table 20 – Dosing Regimens in Patients Previously Untreated for Advanced Colorectal Cancer Clinical Trial
| Treatment Arm | Dose | Regimen |
|---|---|---|
| Oxaliplatin + 5-FU/LV (FOLFOX4) (N=267) |
Day 1: Oxaliplatin: 85 mg/m2 (2-hour infusion) + LV 200 mg/m2 (2-hour infusion), followed by 5-FU: 400 mg/m2 (bolus), 600 mg/m2 (22-hour infusion) Day 2: LV 200 mg/m2 (2-hour infusion), followed by 5-FU: 400 mg/m2 (bolus), 600 mg/m2 (22-hour infusion) |
every 2 weeks |
| Irinotecan + 5-FU/LV (IFL) (N=264) |
Day 1: irinotecan 125 mg/m2 as a 90–min infusion + LV 20 mg/m2 as a 15-min infusion or intravenous push, followed by 5-FU 500 mg/m2 intravenous bolus weekly x 4 |
every 6 weeks |
| Oxaliplatin + Irinotecan (IROX) (N=264) |
Day 1: Oxaliplatin: 85 mg/m2 intravenous (2-hour infusion) + irinotecan 200 mg/m2 intravenous over 30 minutes |
every 3 weeks |
Table 21 – Patient Demographics in Patients Previously Untreated for Advanced Colorectal Cancer Clinical Trial
| Oxaliplatin + 5-FU/LV (N=267) |
irinotecan + 5-FU/LV (N=264) |
Oxaliplatin + irinotecan (N=264) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex: Male (%) |
58.8 |
65.2 |
61 |
| Female (%) |
41.2 |
34.8 |
39 |
| Median age (years) |
61 |
61 |
61 |
| <65 years of age (%) |
61 |
62 |
63 |
| ≥65 years of age (%) |
39 |
38 |
37 |
|
ECOG (%)
|
|||
| 0.1 |
94.4 |
95.5 |
94.7 |
| 2 |
5.6 |
4.5 |
5.3 |
|
Involved organs (%)
|
|||
| Colon only |
0.7 |
0.8 |
0.4 |
| Liver only |
39.3 |
44.3 |
39 |
| Liver + other |
41.2 |
38.6 |
40.9 |
| Lung only |
6.4 |
3.8 |
5.3 |
| Other (including lymph nodes) |
11.6 |
11 |
12.9 |
| Not reported |
0.7 |
1.5 |
1.5 |
| Prior radiation (%) |
3 |
1.5 |
3 |
| Prior surgery (%) |
74.5 |
79.2 |
81.8 |
| Prior adjuvant (%) |
15.7 |
14.8 |
15.2 |
Table 22 – Summary of Efficacy
| Oxaliplatin + 5-FU/LV (N=267) |
irinotecan + 5-FU/LV (N=264) |
Oxaliplatin + irinotecan (N=264) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
* Compared to irinotecan plus 5-FU/LV (IFL) arm ** Based on all patients with measurable disease at baseline The numbers in the response rate and TTP analysis are based on unblinded investigator assessment. *** A hazard ratio of less than 1 favors Oxaliplatin + Infusional 5-FU/LV |
|||
|
Survival (ITT)
|
|||
| Number of deaths N (%) |
155 (58.1) |
192 (72.7) |
175 (66.3) |
| Median survival (months) |
19.4 |
14.6 |
17.6 |
| Hazard Ratio and (95% confidence interval)*** |
0.65 (0.53 to 0.8)* |
||
| P-value |
<0.0001* |
- |
- |
|
TTP (ITT, investigator assessment)
|
|||
| Percentage of progressors |
82.8 |
81.8 |
89.4 |
| Median TTP (months) |
8.7 |
6.9 |
6.5 |
| Hazard Ratio and (95% confidence interval) *** |
0.74 (0.61 to 0.89)* |
|
|
| P-value |
0.0014* |
- |
- |
|
Response Rate (investigator assessment)**
|
|||
| Patients with measurable disease |
210 |
212 |
215 |
| Complete response N (%) |
13 (6.2) |
5 (2.4) |
7 (3.3) |
| Partial response N (%) |
82 (39) |
64 (30.2) |
67 (31.2) |
| Complete and partial response N (%) |
95 (45.2) |
69 (32.5) |
74 (34.4) |
| 95% confidence interval |
(38.5 to 52) |
(26.2 to 38.9) |
(28.1 to 40.8) |
| P-value |
0.008* |
- |
- |
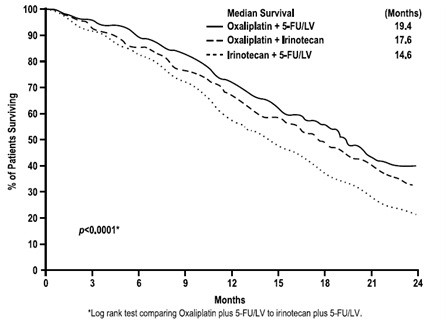
Figure 4 – Kaplan-Meier Overall Survival by treatment arm
14.3 Combination Therapy with Oxaliplatin and 5-Fluorouracil/Leucovorin in Previously Treated Patients with Advanced Colorectal Cancer
Table 23 – Dosing Regimens in Refractory and Relapsed Colorectal Cancer Clinical Trial
| Treatment Arm | Dose | Regimen |
|---|---|---|
| Oxaliplatin + 5-FU/LV (N =152) |
Day 1: Oxaliplatin: 85 mg/m2 (2-hour infusion) + LV 200 mg/m2 (2-hour infusion), followed by 5-FU: 400 mg/m2 (bolus), 600 mg/m2 (22-hour infusion) Day 2: LV 200 mg/m2 (2-hour infusion), followed by 5-FU: 400 mg/m2 (bolus), 600 mg/m2 (22-hour infusion) |
every 2 weeks |
| 5-FU/LV (N=151) |
Day 1: LV 200 mg/m2 (2-hour infusion), followed by 5-FU: 400 mg/m2 (bolus), 600 mg/m2 (22-hour infusion) Day 2: LV 200 mg/m2 (2-hour infusion), followed by 5-FU: 400 mg/m2 (bolus), 600 mg/m2 (22-hour infusion) |
every 2 weeks |
| Oxaliplatin (N=156) |
Day 1: Oxaliplatin 85 mg/m2 (2-hour infusion) |
every 2 weeks |
Table 24 – Patient Demographics in Refractory and Relapsed Colorectal Cancer Clinical Trial
| 5-FU/LV (N = 151) |
Oxaliplatin (N = 156) |
Oxaliplatin + 5-FU/LV (N = 152) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex: Male (%) |
54.3 |
60.9 |
57.2 |
| Female (%) |
45.7 |
39.1 |
42.8 |
| Median age (years) |
60 |
61 |
59 |
| Range |
21 to 80 |
27 to 79 |
22 to 88 |
|
Race (%)
|
|||
| Caucasian |
87.4 |
84.6 |
88.8 |
| Black |
7.9 |
7.1 |
5.9 |
| Asian |
1.3 |
2.6 |
2.6 |
| Other |
3.3 |
5.8 |
2.6 |
|
KPS (%)
|
|||
| 70 to 100 |
94.7 |
92.3 |
95.4 |
| 50 to 60 |
2.6 |
4.5 |
2 |
| Not reported |
2.6 |
3.2 |
2.6 |
| Prior radiotherapy (%) |
25.2 |
19.2 |
25 |
| Prior pelvic radiation (%) |
18.5 |
13.5 |
21.1 |
|
Number of metastatic sites (%)
|
|||
| 1 |
27.2 |
31.4 |
25.7 |
| ≥2 |
72.2 |
67.9 |
74.3 |
|
Liver involvement (%)
|
|||
| Liver only |
22.5 |
25.6 |
18.4 |
| Liver + other |
60.3 |
59 |
53.3 |
Table 25 - Response Rates (ITT Analysis)
| Best Response | 5-FU/LV (N=151) |
Oxaliplatin (N=156) |
Oxaliplatin + 5 FU/LV (N=152) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CR |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| PR |
0 |
2 (1%) |
13 (9%) |
| p-value |
0.0002 for 5-FU/LV vs. Oxaliplatin + 5 FU/LV |
||
| 95%CI |
0 to 2.4% |
0.2 to 4.6% |
4.6 to 14.2% |
Table 26 - Summary of Radiographic Time to Progression*
| Arm | 5-FU/LV (N=151) |
Oxaliplatin (N=156) |
Oxaliplatin +5-FU/LV (N=152) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
*This is not an ITT analysis. Events were limited to radiographic disease progression documented by independent review of radiographs. Clinical progression was not included in this analysis, and 18% of patients were excluded from the analysis based on unavailability of the radiographs for independent review. |
|||
| No. of Progressors |
74 |
101 |
50 |
| No. of patients with no radiological evaluation beyond baseline |
22 (15%) |
16 (10%) |
17 (11%) |
| Median TTP (months) |
2.7 |
1.6 |
4.6 |
| 95% CI |
1.8 to 3 |
1.4 to 2.7 |
4.2 to 6.1 |
15 REFERENCES
- NIOSH Alert: Preventing occupational exposures to antineoplastic and other hazardous drugs in healthcare settings. 2004. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, DHHS (NIOSH) Publication No. 2004-165.
- OSHA Technical Manual, TED 1-0.15A, Section VI: Chapter 2. Controlling Occupational Exposure to Hazardous Drugs. OSHA, 1999. http://www.osha.gov/dts/osta/otm/otm_vi/otm_vi_2.html
- American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. (2006) ASHP Guidelines on Handling Hazardous Drugs.
- Polovich, M., White, J. M., & Kelleher, L.O. (eds.) 2005. Chemotherapy and biotherapy guidelines and recommendations for practice (2nd. ed.) Pittsburgh, PA: Oncology Nursing Society.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
| Product No. |
NDC No. |
Strength | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 765010 |
63323-650-10 |
50 mg/10 mL (5 mg/mL) |
10 mL single-use vial, packaged individually. |
| 765017 |
63323-650-17 |
50 mg/10 mL (5 mg/mL) |
10 mL single-use vial, in packages of 10. |
| 765020 |
63323-650-20 |
100 mg/20 mL (5 mg/mL) |
20 mL single-use vial, packaged individually. |
| 765027 |
63323-650-27 |
100 mg/20 mL (5 mg/mL) |
20 mL single-use vial, in packages of 10. |
16.2 Storage
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Do not freeze and protect from light (keep in original outer carton).
16.3 Handling and Disposal
As with other potentially toxic anticancer agents, care should be exercised in the handling and preparation of infusion solutions prepared from oxaliplatin injection. The use of gloves is recommended. If a solution of oxaliplatin injection contacts the skin, wash the skin immediately and thoroughly with soap and water. If oxaliplatin injection contacts the mucous membranes, flush thoroughly with water.
Procedures for the handling and disposal of anticancer drugs should be considered. Several guidelines on the subject have been published [see References ( 15 )]. There is no general agreement that all of the procedures recommended in the guidelines are necessary or appropriate.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Information for Patients
17.2 FDA-Approved Patient Labeling
Patient Information
OXALIPLATIN INJECTION, USP
concentrate, for solution for intravenous use
What is the most important information I should know about Oxaliplatin Injection?
Serious side effects can happen in people taking Oxaliplatin Injection, including:
- Serious allergic reactions. Oxaliplatin injection can cause serious allergic reactions, including allergic reactions that may cause death. Oxaliplatin Injection is a platinum base medicine. Serious allergic reactions including death can occur in people who take oxaliplatin and who have had previous allergic reactions to platinum medicines. Serious allergic reactions can happen within a few minutes of your infusion or any time during your treatment with oxaliplatin injection.
Get emergency help right away if you:
- have trouble breathing.
- feel like your throat is closing up.
- rash
- flushed face
- hives
- itching
- swelling of your lips or tongue
- sudden cough
- dizziness or feel faint
- sweating
- chest pain
See “What are the possible side effects of Oxaliplatin Injection?” for information about other serious side effects.
What is Oxaliplatin Injection?
- stage III colon cancer after surgery to remove the tumor.
- advanced colon or rectal cancer (colorectal cancer).
Oxaliplatin injection with infusional 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin was shown to lower the chance of colon cancer returning when given to patients with stage III colon cancer after surgery to remove the tumor. Oxaliplatin injection also increases survival in patients with stage III colon cancer. Oxaliplatin injection with infusional 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin was also shown to increase survival, shrink tumors and delay growth of tumors in some patients with advanced colorectal cancer.
Who should not use Oxaliplatin Injection?
- Do not use oxaliplatin injection if you are allergic to any of the ingredients in oxaliplatin injection or other medicines that contain platinum. Cisplatin and carboplatin are other chemotherapy medicines that also contain platinum. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of the ingredients in oxaliplatin injection.
What should I tell my doctor before treatment with Oxaliplatin Injection?
Before receiving oxaliplatin injection, tell your doctor
- have kidney problems
- have any other medical conditions
- have had any allergic reactions to any medicines
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Oxaliplatin may harm your unborn child. You should avoid becoming pregnant while taking oxaliplatin injection. Talk with your doctor about how to avoid pregnancy.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if oxaliplatin injection passes into your breast milk. You and your doctor should decide whether you will stop breastfeeding or not take oxaliplatin injection.
How is Oxaliplatin Injection given to me?
- Your doctor will prescribe oxaliplatin injection in an amount that is right for you.
- Your doctor will treat you with several medicines for your cancer.
- It is very important that you do exactly what your doctor and nurse have taught you to do.
- Some medicines may be given to you before oxaliplatin injection to help prevent nausea and vomiting.
- Oxaliplatin injection is given with 2 other chemotherapy medicines, leucovorin and 5-fluorouracil.
- Each treatment course is given to you over 2 days. You will receive oxaliplatin injection on the first day only.
- There are usually 14 days between each chemotherapy treatment course.
Treatment Day 1:
Oxaliplatin injection and leucovorin are given through a thin plastic tube put into a vein (intravenous infusion or IV) and given for 2 hours. You will be watched by a healthcare provider during this time.
Treatment Day 2:
During your treatment with oxaliplatin injection:
- It is important for you to keep all appointments. Call your doctor if you must miss an appointment. There may be special instructions for you.
- Your doctor may change how often you get oxaliplatin injection, how much you get, or how long the infusion will take.
- You and your doctor will discuss how many times you will get oxaliplatin injection.
What activities should I avoid while on treatment with Oxaliplatin Injection?
- Avoid cold temperatures and cold objects. Cover your skin if you must go outside in cold temperatures.
- Do not drink cold drinks or use ice cubes in drinks.
- Do not put ice or ice packs on your body.
What are the possible side effects of Oxaliplatin Injection?
- Serious allergic reactions. See “What is the most important information I should know about oxaliplatin injection?”
- Nerve problems. Oxaliplatin injection can affect how your nerves work and make you feel. Tell your doctor right away if you get any signs of nerve problems listed below:
- very sensitive to cold temperatures and cold objects.
- trouble breathing, swallowing, or saying words, jaw tightness, odd feelings in your tongue, or chest pressure.
- pain, tingling, burning (pins and needles, numb feeling) in your hands, feet, or around your mouth or throat, which may cause problems walking or performing activities of daily living.
-
Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy (RPLS). RPLS is a rare condition that affects the brain. Tell your doctor right away if you have any of the following signs and symptoms of RPLS:
- headache
- confusion or a change in the way you think
- seizures
- vision problems, such as blurriness or vision loss. You should not drive, operate heavy machines, or engage in dangerous activities if you have vision problems while receiving oxaliplatin injection.
- Lung problems (interstitial fibrosis). Tell your doctor right away if you get a dry cough and have trouble breathing (shortness of breath) before your next treatment. These may be signs of a serious lung disease.
- Liver problems (hepatotoxicity). Your doctor will do blood tests to check your liver.
- Harm to an unborn baby. Oxaliplatin injection may cause harm to your unborn baby. See “What should I tell my doctor before treatment with oxaliplatin injection?”
- Decreased blood counts: Oxaliplatin injection can cause a decrease in neutrophils (a type of white blood cell important in fighting bacterial infections), red blood cells (blood cells that carry oxygen to the tissues), and platelets (important for clotting and to control bleeding).
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Infection. Call your doctor right away if you get any of the following signs of infection:
- fever (temperature of 100.5o F or greater)
- chills or shivering
- pain on swallowing
- sore throat
- cough that brings up mucus
- burning or pain on urination
- redness or swelling at intravenous site
- Bleeding or bruising. Tell your doctor about any signs or symptoms of bleeding or bruising.
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Constipation
- Mouth sores
- Stomach pain
- Decreased appetite
- Tiredness
- Injection site reactions. Reactions may include redness, swelling, pain, tissue damage at the site of injection.
- Hair loss (alopecia)
-
Dehydration (too much water loss). Call you doctor if you have signs of dehydration including:
|
|
How can I reduce the side effects caused by cold temperatures?
- Cover yourself with a blanket while you are getting your oxaliplatin injection infusion.
- Do not breathe deeply when exposed to cold air.
- Wear warm clothing in cold weather at all times. Cover your mouth and nose with a scarf or a pull-down cap (ski cap) to warm the air that goes to your lungs.
- Wear gloves when taking things from the freezer or refrigerator.
- Drink fluids warm or at room temperature.
- Always drink through a straw.
- Do not use ice chips if you have nausea or mouth sores. Ask your healthcare provider or doctor about what you can use.
- Be aware that most metals are cold to touch, especially in the winter. These include your car door and mailbox. Wear gloves to touch cold objects.
- Do not run the air-conditioning at high levels in the house or in the car in hot weather.
- If your body gets cold, warm-up the affected part. If your hands get cold, wash them with warm water.
- Always let your healthcare provider or doctor know before your next treatment how well you did since your last visit.
General information about the safe and effective use of oxaliplatin injection
What are the ingredients in Oxaliplatin injection?

PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL-Oxaliplatin Injection, USP
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 50 mg Carton Label
OXALIPLATIN
INJECTION, USP
50 mg/10 mL
FOR INTRAVENOUS USE ONLY
SINGLE USE VIAL
Must be diluted with 5%
Dextrose Injection before use.
Cytotoxic Agent
 PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 50 mg Vial Label
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 50 mg Vial LabelOXALIPLATIN
INJECTION, USP
50 mg/10 mL
FOR INTRAVENOUS USE ONLY
SINGLE USE VIAL
Must be diluted with 5%
Dextrose Injection before use.

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 50 mg Multi-Carton Label
OXALIPLATIN
INJECTION, USP
50 mg/10 mL
FOR INTRAVENOUS USE ONLY
Must be diluted with 5%
Dextrose Injection before use.
Cytotoxic Agent
10x10 mL Single Use Vials

oxaliplatinoxaliplatin INJECTION, SOLUTION, CONCENTRATE
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||