Niacin
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use Niacin Extended-Release Tablets USP safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Niacin Extended-Release Tablets USP. Niacin Extended-Release Tablets USP, extended release for oral use.Initial U.S. Approval: 1997RECENT MAJOR CHANGESIndications and Usage: Limitations of Use (1) 02/2013 Warnings and Precautions, Mortality and Coronary Heart Disease Morbidity (5.1) 02/2013INDICATIONS AND USAGENiacin Extended-Release Tablets USP contain extended-release niacin, USP (nicotinic acid), and is indicated: To reduce elevated TC, LDL-C, Apo B and TG, and to increase HDL-C in patients with primary hyperlipidemia and mixed dyslipidemia.(1) In combination with simvastatin or lovastatin: to treat primary hyperlipidemia and mixed dyslipidemia when treatment with Niacin Extended-Release Tablets USP, simvastatin, or lovastatin monotherapy is considered inadequate.(1) To reduce the risk of recurrent nonfatal myocardial infarction in patients with a history of myocardial infarction and hyperlipidemia.(1) In combination with a bile acid binding resin: Slows progression or promotes regression of atherosclerotic disease in patients with a history of coronary artery disease (CAD) and hyperlipidemia. (1) As an adjunct to diet to reduce elevated TC and LDL-C in adult patients with primary hyperlipidemia. (1) To reduce TG in adult patients with severe hypertriglyceridemia.(1) Limitations of Use: No incremental benefit of Niacin Extended-Release Tablets USP coadministered with simvastatin or lovastatin on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality over and above that demonstrated for niacin, USP, simvastatin and lovastatin monotherapy, has been established. Niacin Extended-Release Tablets USP, at doses of 1,500-2,000 mg/day, in combination with simvastatin, did not reduce the incidence of cardiovascular events more than simvastatin in a randomized controlled trial of patients with cardiovascular disease and mean baseline LDL-C levels of 74 mg per deciliter (5.1).DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Niacin Extended-Release Tablets should be taken at bedtime with a low-fat snack. (2) Dose range: 500 mg to 2000 mg once daily. (2) Therapy with Niacin Extended-Release Tablets must be initiated at 500 mg at bedtime in order to reduce the incidence and severity of side effects which may occur during early therapy and should not be increased by more than 500 mg in any four week period. (2) Maintenance dose: 1000 to 2000 mg once daily. (2) Doses greater than 2000 mg daily are not recommended. (2) Concomitant therapy with lovastatin: Initial dose of lovastatin is 20 mg once a day; combination therapy with Niacin Extended-Release Tablets and lovastatin should not exceed doses of 2000 mg and 40 mg daily, respectively. (2) Concomitant therapy with simvastatin: Initial dose of simvastatin is 20 mg once a day; combination therapy with Niacin Extended-Release Tablets and simvastatin should not exceed doses of 2000 mg and 40 mg daily, respectively. (2) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSCapsule-shaped, unscored, biconvex, debossed tablets for oral administration: 500 mg, 750 mg, and 1000 mg niacin extended-release. (3) CONTRAINDICATIONS Active liver disease, which may include unexplained persistent elevations in hepatic transaminase levels. (4, 5.3) Active peptic ulcer disease. (4) Arterial bleeding. (4) Known hypersensitivity to product components. (4, 6.1) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Severe hepatic toxicity has occurred in patients substituting sustained-release niacin for immediate-release niacin at equivalent doses. (5.3) Myopathy has been reported in patients taking niacin extended-release tablets. The risk for myopathy and rhabdomyolysis are increased when lovastatin or simvastatin are coadministered with niacin extended-release tablets, particularly in elderly patients and patients with diabetes, renal failure, or uncontrolled hypothyroidism. (5.2) Liver enzyme abnormalities and monitoring: Persistent elevations in hepatic transaminase can occur. Monitor liver enzymes before and during treatment. (5.3) Use with caution in patients with unstable angina or in the acute phase of an MI. (5) Niacin extended-release tablets can increase serum glucose levels. Glucose levels should be closely monitored in diabetic or potentially diabetic patients particularly during the first few months of use or dose adjustment. (5.4) Side EffectsMost common adverse reactions (incidence > 5% and greater than placebo) are flushing, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, increased cough, and pruritus.(6.1) Flushing of the skin may be reduced in frequency or severity by pretreatment with aspirin (up to the recommended dose of 325 mg taken 30 minutes prior to niacin extended-release tablets dose).(2) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact TEVA USA, PHARMACOVIGILANCE at: 1-866-832-8537 or drug.safety@tevapharm.com; or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.DRUG INTERACTIONS Statins: Caution should be used when prescribing niacin with statins as these agents can increase risk of myopathy/rhabdomyolysis.(5.2,7.1) Bile Acid Sequestrants: Bile acid sequestrants have a high niacin-binding capacity and should be taken at least 4 to 6 hours before niacin extended-release tablet administration. (7.2) USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Renal impairment: Niacin extended-release tablets should be used with caution in patients with renal impairment. (5, 8.6) Hepatic impairment: Niacin extended-release tablets are contraindicated in active liver disease or significant or unexplained hepatic dysfunction or unexplained elevations of serum transaminases. (4, 5, 5.3, 8.7)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- 1 NIACIN INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 NIACIN DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 NIACIN CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 6 NIACIN ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 NIACIN DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- PATIENT INFORMATION
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Therapy with lipid-altering agents should be only one component of multiple risk factor intervention in individuals at significantly increased risk for atherosclerotic vascular disease due to hyperlipidemia. Niacin, USP therapy is indicated as an adjunct to diet when the response to a diet restricted in saturated fat and cholesterol and other nonpharmacologic measures alone has been inadequate.
- Niacin Extended-Release Tablets USP are indicated to reduce elevated TC, LDL-C, Apo B and TG levels, and to increase HDL-C in patients with primary hyperlipidemia and mixed dyslipidemia.
- Niacin Extended-Release Tablets USP in combination with simvastatin or lovastatin are indicated for the treatment of primary hyperlipidemia and mixed dyslipidemia when treatment with Niacin Extended-Release Tablets USP, simvastatin, or lovastatin monotherapy is considered inadequate.
- In patients with a history of myocardial infarction and hyperlipidemia, niacin, USP is indicated to reduce the risk of recurrent nonfatal myocardial infarction.
- In patients with a history of coronary artery disease (CAD) and hyperlipidemia, niacin, USP, in combination with a bile acid binding resin, is indicated to slow progression or promote regression of atherosclerotic disease.
- Niacin Extended-Release Tablets USP in combination with a bile acid binding resin are indicated to reduce elevated TC and LDL-C levels in adult patients with primary hyperlipidemia.
- Niacin, USP is also indicated as adjunctive therapy for treatment of adult patients with severe hypertriglyceridemia who present a risk of pancreatitis and who do not respond adequately to a determined dietary effort to control them.
Limitations of Use
No incremental benefit of Niacin Extended-Release Tablets USP coadministered with simvastatin or lovastatin on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality over and above that demonstrated for niacin, USP, simvastatin, or lovastatin monotherapy has been established.
Niacin Extended-Release Tablets USP, at doses of 1,500-2,000 mg/day, in combination with simvastatin, did not reduce the incidence of cardiovascular events more than simvastatin in a randomized controlled trial of patients with cardiovascular disease and mean baseline LDL-C levels of 74 mg per deciliter [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 )].
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Niacin Extended-Release Tablets should be taken at bedtime, after a low-fat snack, and doses should be individualized according to patient response. Therapy with Niacin Extended-Release Tablets must be initiated at 500 mg at bedtime in order to reduce the incidence and severity of side effects which may occur during early therapy. The recommended dose escalation is shown in Table 1 below.
| Week(s) | Daily Dose | Niacin Extended-Release Tablets Dosage | |
| INITIAL TITRATION |
1 to 4 | 500 mg |
1 Niacin Extended-Release 500 mg Tablet at bedtime |
| SCHEDULE | 5 to 8 | 1000 mg |
1 Niacin Extended-Release 1000 mg Tablet or 2 Niacin Extended-Release 500 mg Tablets at bedtime |
 |
1500 mg |
2 Niacin Extended-Release 750 mg Tablets or 3 Niacin Extended-Release 500 mg Tablets at bedtime |
|
 |
2000 mg |
2 Niacin Extended-Release 1000 mg Tablets or 4 Niacin Extended-Release 500 mg Tablets at bedtime |
|
Maintenance Dose
The daily dosage of Niacin Extended-Release Tablets should not be increased by more than 500 mg in any 4 week period. The recommended maintenance dose is 1000 mg (two 500 mg tablets or one 1000 mg tablet) to 2000 mg (two 1000 mg tablets or four 500 mg tablets) once daily at bedtime. Doses greater than 2000 mg daily are not recommended. Women may respond at lower Niacin Extended-Release Tablet doses than men [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
Single-dose bioavailability studies have demonstrated that two of the 500 mg and one of the 1000 mg tablet strengths are interchangeable but three of the 500 mg and two of the 750 mg tablet strengths are not interchangeable.
If lipid response to Niacin Extended-Release Tablets alone is insufficient or if higher doses of Niacin Extended-Release Tablets are not well tolerated, some patients may benefit from combination therapy with a bile acid binding resin or statin [see Drug Interactions (7.3), Concomitant Therapy below and Clinical Studies (14.3, 14.4)].
Flushing of the skin [see Adverse Reactions ( 6.1)] may be reduced in frequency or severity by pretreatment with aspirin (up to the recommended dose of 325 mg taken 30 minutes prior to Niacin Extended-Release Tablet dose). Tolerance to this flushing develops rapidly over the course of several weeks. Flushing, pruritus, and gastrointestinal distress are also greatly reduced by slowly increasing the dose of niacin and avoiding administration on an empty stomach. Concomitant alcoholic, hot drinks or spicy foods may increase the side effects of flushing and pruritus and should be avoided around the time of Niacin Extended-Release Tablet ingestion.
Equivalent doses of Niacin Extended-Release Tablets should not be substituted for sustained-release (modified-release, timed-release) niacin preparations or immediate-release (crystalline) niacin [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5 )]. Patients previously receiving other niacin products should be started with the recommended Niacin Extended-Release Tablet titration schedule (see Table 1 ), and the dose should subsequently be individualized based on patient response.
If Niacin Extended-Release Tablet therapy is discontinued for an extended period, reinstitution of therapy should include a titration phase (see Table 1 ).
Niacin Extended-Release Tablets should be taken whole and should not be broken, crushed or chewed before swallowing.
Concomitant Therapy
Concomitant Therapy With Lovastatin or Simvastatin
Patients already receiving a stable dose of lovastatin or simvastatin who require further TG-lowering or HDL-raising (e.g., to achieve NCEP non-HDL-C goals), may receive concomitant dosage titration with Niacin Extended-Release Tablets per Niacin Extended-Release Tablets recommended initial titration schedule [see Dosage and Administration ( 2)]. For patients already receiving a stable dose of Niacin Extended-Release Tablets who require further LDL-lowering (e.g., to achieve NCEP LDL-C goals), the usual recommended starting dose of lovastatin and simvastatin is 20 mg once a day. Dose adjustments should be made at intervals of 4 weeks or more. Combination therapy with Niacin Extended-Release Tablets and lovastatin or Niacin Extended-Release Tablets and simvastatin should not exceed doses of 2000 mg Niacin Extended-Release Tablets and 40 mg lovastatin or simvastatin daily.
Dosage in Patients with Renal or Hepatic Impairment
Use of Niacin Extended-Release Tablets in patients with renal or hepatic impairment has not been studied. Niacin Extended-Release Tablets are contraindicated in patients with significant or unexplained hepatic dysfunction. Niacin Extended-Release Tablets should be used with caution in patients with renal impairment [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5)].
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 500 mg white to off-white, capsule-shaped, unscored, biconvex, debossed tablets
- 750 mg white to off-white, capsule-shaped, unscored, biconvex, debossed tablets
- 1000 mg white to off-white, capsule-shaped, unscored, biconvex, debossed tablets
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Niacin extended-release tablets are contraindicated in the following conditions:
- Active liver disease or unexplained persistent elevations in hepatic transaminases [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Patients with active peptic ulcer disease
- Patients with arterial bleeding
- Hypersensitivity to niacin or any component of this medication [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Niacin extended-release tablet preparations should not be substituted for equivalent doses of immediate-release (crystalline) niacin. For patients switching from immediate-release niacin to niacin extended-release tablets, therapy with niacin extended-release tablets should be initiated with low doses (i.e., 500 mg at bedtime) and the niacin extended-release tablet dose should then be titrated to the desired therapeutic response [see Dosage and Administration ( 2)] .
Caution should also be used when niacin extended-release tablets are used in patients with unstable angina or in the acute phase of an MI, particularly when such patients are also receiving vasoactive drugs such as nitrates, calcium channel blockers, or adrenergic blocking agents.
Niacin is rapidly metabolized by the liver, and excreted through the kidneys. Niacin extended-release tablets are contraindicated in patients with significant or unexplained hepatic impairment [see Contraindications ( 4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] and should be used with caution in patients with renal impairment. Patients with a past history of jaundice, hepatobiliary disease, or peptic ulcer should be observed closely during niacin extended-release tablet therapy.
5.1 Mortality and Coronary Heart Disease Morbidity
The Atherothrombosis Intervention in Metabolic Syndrome with Low HDL/High Triglycerides: Impact on Global Health Outcomes (AIM-HIGH) trial was a randomized placebo-controlled trial of 3414 patients with stable, previously diagnosed cardiovascular disease. Mean baseline lipid levels were LDL-C 74 mg/dL, HDL-C 35 mg/dL, non-HDL-C 111 mg/dL and median triglyceride level of 163 to 177 mg/dL. Ninety-four percent of patients were on background statin therapy prior to entering the trial. All participants received simvastatin, 40 to 80 mg per day, plus ezetimibe 10 mg per day if needed, to maintain an LDL-C level of 40 to 80 mg/dL, and were randomized to receive niacin extended-release tablets 1500 to 2000 mg/day (n = 1718) or matching placebo (IR Niacin, 100 to 150 mg, n = 1696). On-treatment lipid changes at two years for LDL-C were -12% for the simvastatin plus niacin extended-release tablets group and -5.5% for the simvastatin plus placebo group. HDL-C increased by 25% to 42 mg/dL in the simvastatin plus niacin extended-release tablets group and by 9.8% to 38 mg/dL in the simvastatin plus placebo group (P < 0.001). Triglyceride levels decreased by 28.6% in the simvastatin plus niacin extended-release tablets group and by 8.1% in the simvastatin plus placebo group. The primary outcome was an ITT composite of the first study occurrence of coronary heart disease death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, hospitalization for acute coronary syndrome or symptom-driven coronary or cerebral revascularization procedures. The trial was stopped after a mean follow-up period of 3 years owing to a lack of efficacy. The primary outcome occurred in 282 patients in the simvastatin plus niacin extended-release tablets group (16.4%) and in 274 patients in the simvastatin plus placebo group (16.2%) (HR 1.02 [95% CI, 0.87-1.21], P = 0.79. In an ITT analysis, there were 42 cases of first occurrence of ischemic stroke reported, 27 (1.6%) in the simvastatin plus niacin extended-release tablets group and 15 (0.9%) in the simvastatin plus placebo group, a non-statistically significant result (HR 1.79, [95%CI = 0.95 to 3.36], p = 0.071). The on-treatment ischemic stroke events were 19 for the simvastatin plus niacin extended-release tablets group and 15 for the simvastatin plus placebo group [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.2 Skeletal Muscle
Cases of rhabdomyolysis have been associated with concomitant administration of lipid-altering doses (≥ 1 g/day) of niacin and statins. Physicians contemplating combined therapy with statins and niacin extended-release tablets should carefully weigh the potential benefits and risks and should carefully monitor patients for any signs and symptoms of muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness, particularly during the initial months of therapy and during any periods of upward dosage titration of either drug. Periodic serum creatine phosphokinase (CPK) and potassium determinations should be considered in such situations, but there is no assurance that such monitoring will prevent the occurrence of severe myopathy.
The risk for myopathy and rhabdomyolysis are increased when lovastatin or simvastatin are coadministered with niacin extended-release tablets, particularly in elderly patients and patients with diabetes, renal failure, or uncontrolled hypothyroidism.
5.3 Liver Dysfunction
Cases of severe hepatic toxicity, including fulminant hepatic necrosis, have occurred in patients who have substituted sustained-release (modified-release, timed-release) niacin products for immediate-release (crystalline) niacin at equivalent doses.
Niacin extended-release tablets should be used with caution in patients who consume substantial quantities of alcohol and/or have a past history of liver disease. Active liver diseases or unexplained transaminase elevations are contraindications to the use of niacin extended-release tablets.
Niacin preparations have been associated with abnormal liver tests. In three placebo-controlled clinical trials involving titration to final daily niacin extended-release tablet doses ranging from 500 to 3000 mg, 245 patients received niacin extended-release tablets for a mean duration of 17 weeks. No patient with normal serum transaminase levels (AST, ALT) at baseline experienced elevations to more than 3 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) during treatment with niacin extended-release tablets. In these studies, fewer than 1% (2/245) of niacin extended-release tablet patients discontinued due to transaminase elevations greater than 2 times the ULN.
In three safety and efficacy studies with a combination tablet of niacin extended-release and lovastatin involving titration to final daily doses (expressed as mg of niacin/mg of lovastatin) 500 mg/10 mg to 2500 mg/40 mg, ten of 1028 patients (1%) experienced reversible elevations in AST/ALT to more than 3 times the ULN. Three of ten elevations occurred at doses outside the recommended dosing limit of 2000 mg/40 mg; no patient receiving 1000 mg/20 mg had 3 fold elevations in AST/ALT.
Niacin extended-release and simvastatin can cause abnormal liver tests. In a simvastatin-controlled, 24 week study with a fixed dose combination of niacin extended-release tablets and simvastatin in 641 patients, there were no persistent increases (more than 3x the ULN) in serum transaminases. In three placebo-controlled clinical studies of extended-release niacin there were no patients with normal serum transaminase levels at baseline who experienced elevations to more than 3x the ULN. Persistent increases (more than 3x the ULN) in serum transaminases have occurred in approximately 1% of patients who received simvastatin in clinical studies. When drug treatment was interrupted or discontinued in these patients, the transaminases levels usually fell slowly to pretreatment levels. The increases were not associated with jaundice or other clinical signs or symptoms. There was no evidence of hypersensitivity.
In the placebo-controlled clinical trials and the long-term extension study, elevations in transaminases did not appear to be related to treatment duration; elevations in AST levels did appear to be dose related. Transaminase elevations were reversible upon discontinuation of niacin extended-release tablets.
Liver function tests should be performed on all patients during therapy with niacin extended-release tablets. Serum transaminase levels, including AST and ALT (SGOT and SGPT), should be monitored before treatment begins, every 6 to 12 weeks for the first year, and periodically thereafter (e.g., at approximately 6 month intervals). Special attention should be paid to patients who develop elevated serum transaminase levels, and in these patients, measurements should be repeated promptly and then performed more frequently. If the transaminase levels show evidence of progression, particularly if they rise to 3 times ULN and are persistent, or if they are associated with symptoms of nausea, fever, and/or malaise, the drug should be discontinued.
5.4 Laboratory Abnormalities
Increase in Blood Glucose: Niacin treatment can increase fasting blood glucose. Frequent monitoring of blood glucose should be performed to ascertain that the drug is producing no adverse effects. Diabetic patients may experience a dose-related increase in glucose intolerance. Diabetic or potentially diabetic patients should be observed closely during treatment with niacin extended-release tablets, particularly during the first few months of use or dose adjustment; adjustment of diet and/or hypoglycemic therapy may be necessary.
Reduction in Platelet Count: Niacin extended-release tablets have been associated with small but statistically significant dose-related reductions in platelet count (mean of -11% with 2000 mg). Caution should be observed when niacin extended-release tablets are administered concomitantly with anticoagulants; platelet counts should be monitored closely in such patients.
Increase in Prothrombin Time (PT): Niacin extended-release tablets have been associated with small but statistically significant increases in prothrombin time (mean of approximately +4%); accordingly, patients undergoing surgery should be carefully evaluated. Caution should be observed when niacin extended-release tablets are administered concomitantly with anticoagulants; prothrombin time should be monitored closely in such patients.
Increase in Uric Acid: Elevated uric acid levels have occurred with niacin therapy, therefore use with caution in patients predisposed to gout.
Decrease in Phosphorus: In placebo-controlled trials, niacin extended-release tablets have been associated with small but statistically significant, dose-related reductions in phosphorus levels (mean of -13% with 2000 mg). Although these reductions were transient, phosphorus levels should be monitored periodically in patients at risk for hypophosphatemia.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
In the placebo-controlled clinical trials database of 402 patients (age range 21 to 75 years, 33% women, 89% Caucasians, 7% Blacks, 3% Hispanics, 1% Asians) with a median treatment duration of 16 weeks, 16% of patients on niacin extended-release tablets and 4% of patients on placebo discontinued due to adverse reactions. The most common adverse reactions in the group of patients treated with niacin extended-release tablets that led to treatment discontinuation and occurred at a rate greater than placebo were flushing (6% vs. 0%), rash (2% vs. 0%), diarrhea (2% vs. 0%), nausea (1% vs. 0%), and vomiting (1% vs. 0%). The most commonly reported adverse reactions (incidence > 5% and greater than placebo) in the niacin extended-release tablets controlled clinical trial database of 402 patients were flushing, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, increased cough and pruritus.
In the placebo-controlled clinical trials, flushing episodes (i.e., warmth, redness, itching and/or tingling) were the most common treatment-emergent adverse reactions (reported by as many as 88% of patients) for niacin extended-release tablets. Spontaneous reports suggest that flushing may also be accompanied by symptoms of dizziness, tachycardia, palpitations, shortness of breath, sweating, burning sensation/skin burning sensation, chills, and/or edema, which in rare cases may lead to syncope. In pivotal studies, 6% (14/245) of niacin extended-release tablet patients discontinued due to flushing. In comparisons of immediate-release (IR) niacin and niacin extended-release tablets, although the proportion of patients who flushed was similar, fewer flushing episodes were reported by patients who received niacin extended-release tablets. Following 4 weeks of maintenance therapy at daily doses of 1500 mg, the incidence of flushing over the 4 week period averaged 8.6 events per patient for IR niacin versus 1.9 following niacin extended-release tablets.
Other adverse reactions occurring in ≥ 5% of patients treated with niacin extended-release tablets and at an incidence greater than placebo are shown in Table 2 below.
|
Placebo-Controlled Studies Niacin Extended-Release Tablets Treatment  |
|||||
|
Recommended Daily Maintenance Doses  |
|||||
|
Placebo (n = 157) % |
500 mg (n = 87) % |
1000 mg (n = 110) % |
1500 mg (n = 136) % |
2000 mg (n = 95) % |
|
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | |||||
| Diarrhea | 13 | 7 | 10 | 10 | 14 |
| Nausea | 7 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 11 |
| Vomiting | 4 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 9 |
| Respiratory | |||||
| Cough, Increased | 6 | 3 | 2 | < 2 | 8 |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | |||||
| Pruritus | 2 | 8 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| Rash | 0 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 0 |
| Vascular Disorders | |||||
Flushing |
19 | 68 | 69 | 63 | 55 |
|
Note: Percentages are calculated from the total number of patients in each column. |
|||||
In general, the incidence of adverse events was higher in women compared to men.
Atherothrombosis Intervention in Metabolic Syndrome With Low HDL/High Triglycerides: Impact on Global Health Outcomes (AIM-HIGH)
In AIM-HIGH involving 3414 patients (mean age of 64 years, 15% women, 92% Caucasians, 34% with diabetes mellitus) with stable, previously diagnosed cardiovascular disease, all patients received simvastatin, 40 to 80 mg per day, plus ezetimibe 10 mg per day if needed, to maintain an LDL-C level of 40 to 80 mg/dL, and were randomized to receive niacin extended-release tablets 1500 to 2000 mg/day (n = 1718) or matching placebo (IR Niacin, 100 to 150 mg, n = 1696). The incidence of the adverse reactions of “blood glucose increased” (6.4% vs. 4.5%) and “diabetes mellitus” (3.6% vs. 2.2%) was significantly higher in the simvastatin plus niacin extended-release tablets group as compared to the simvastatin plus placebo group. There were 5 cases of rhabdomyolysis reported, 4 (0.2%) in the simvastatin plus niacin extended-release tablets group and one (< 0.1%) in the simvastatin plus placebo group [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Because the below reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is generally not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The following additional adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of niacin extended-release tablets:
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, angioedema, urticaria, flushing, dyspnea, tongue edema, larynx edema, face edema, peripheral edema, laryngismus, and vesiculobullous rash; maculopapular rash; dry skin; tachycardia; palpitations; atrial fibrillation; other cardiac arrhythmias; syncope; hypotension; postural hypotension; blurred vision; macular edema; peptic ulcers; eructation; flatulence; hepatitis; jaundice; decreased glucose tolerance; gout; myalgia; myopathy; dizziness; insomnia; asthenia; nervousness; paresthesia; dyspnea; sweating; burning sensation/skin burning sensation; skin discoloration, and migraine.
Clinical Laboratory Abnormalities
Chemistry: Elevations in serum transaminases [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3)], LDH, fasting glucose, uric acid, total bilirubin, amylase and creatine kinase, and reduction in phosphorus.
Hematology: Slight reductions in platelet counts and prolongation in prothrombin time [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.4)].
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Statins
Caution should be used when prescribing niacin (≥1 gm/day) with statins as these drugs can increase risk of myopathy/rhabdomyolysis. Combination therapy with niacin extended-release tablets and lovastatin or niacin extended-release tablets and simvastatin should not exceed doses of 2000 mg niacin extended-release tablets and 40 mg lovastatin or simvastatin daily [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.2 Bile Acid Sequestrants
An in vitro study results suggest that the bile acid-binding resins have high niacin binding capacity. Therefore, 4 to 6 hours, or as great an interval as possible, should elapse between the ingestion of bile acid-binding resins and the administration of niacin extended-release tablets [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.3 Aspirin
Concomitant aspirin may decrease the metabolic clearance of nicotinic acid. The clinical relevance of this finding is unclear.
7.4 Antihypertensive Therapy
Niacin may potentiate the effects of ganglionic blocking agents and vasoactive drugs resulting in postural hypotension.
7.5 Other
Vitamins or other nutritional supplements containing large doses of niacin or related compounds such as nicotinamide may potentiate the adverse effects of niacin extended-release tablets.
7.6 Laboratory Test Interactions
Niacin may produce false elevations in some fluorometric determinations of plasma or urinary catecholamines. Niacin may also give false-positive reactions with cupric sulfate solution (Benedict’s reagent) in urine glucose tests.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with niacin or with niacin extended-release tablets. It is also not known whether niacin at doses typically used for lipid disorders can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women or whether it can affect reproductive capacity. If a woman receiving niacin for primary hyperlipidemia becomes pregnant, the drug should be discontinued. If a woman being treated with niacin for hypertriglyceridemia conceives, the benefits and risks of continued therapy should be assessed on an individual basis.
All statins are contraindicated in pregnant and nursing women. When niacin extended-release tablets are administered with a statin in a woman of childbearing potential, refer to the pregnancy category and product labeling for the statin.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Niacin is excreted into human milk but the actual infant dose or infant dose as a percent of the maternal dose is not known. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from lipid-altering doses of nicotinic acid, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother. No studies have been conducted with niacin extended-release tablets in nursing mothers.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of niacin therapy in pediatric patients (≤ 16 years) have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of 979 patients in clinical studies of niacin extended-release tablets, 21% of the patients were age 65 and over. No overall differences in safety and effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No studies have been performed in this population. Niacin extended-release tablets should be used with caution in patients with renal impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No studies have been performed in this population. Niacin extended-release tablets should be used with caution in patients with a past history of liver disease and/or who consume substantial quantities of alcohol. Active liver disease, unexplained transaminase elevations and significant or unexplained hepatic dysfunction are contraindications to the use of niacin extended-release tablets [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
8.8 Gender
Data from the clinical trials suggest that women have a greater hypolipidemic response than men at equivalent doses of niacin extended-release tablets.
10 OVERDOSAGE
Supportive measures should be undertaken in the event of an overdose.
11 DESCRIPTION
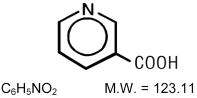
Niacin Extended-Release Tablets USP, contain niacin, USP, which at therapeutic doses is an antihyperlipidemic agent. Niacin, USP (nicotinic acid, or 3-pyridinecarboxylic acid) is a white, crystalline powder, very soluble in water, with the following structural formula:
Niacin Extended-Release Tablets USP are white to off-white, capsule-shaped, unscored, biconvex, debossed tablets for oral administration and are available in three tablet strengths containing 500 mg, 750 mg, and 1000 mg niacin, USP. Niacin Extended-Release Tablets USP also contain the following inactive ingredients: hypromellose, povidone, and stearic acid.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism by which niacin alters lipid profiles has not been well defined. It may involve several actions including partial inhibition of release of free fatty acids from adipose tissue, and increased lipoprotein lipase activity, which may increase the rate of chylomicron triglyceride removal from plasma. Niacin decreases the rate of hepatic synthesis of VLDL and LDL, and does not appear to affect fecal excretion of fats, sterols, or bile acids.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Niacin functions in the body after conversion to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) in the NAD coenzyme system. Niacin (but not nicotinamide) in gram doses reduces total cholesterol (TC), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and triglycerides (TG), and increases high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C). The magnitude of individual lipid and lipoprotein responses may be influenced by the severity and type of underlying lipid abnormality. The increase in HDL-C is associated with an increase in apolipoprotein A-I (Apo A-I) and a shift in the distribution of HDL subfractions. These shifts include an increase in the HDL2:HDL3 ratio, and an elevation in lipoprotein A-I (Lp A-I, an HDL-C particle containing only Apo A-I). Niacin treatment also decreases serum levels of apolipoprotein B-100 (Apo B), the major protein component of the very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) and LDL fractions, and of Lp(a), a variant form of LDL independently associated with coronary risk. In addition, preliminary reports suggest that niacin causes favorable LDL particle size transformations, although the clinical relevance of this effect requires further investigation. The effect of niacin-induced changes in lipids/proteins on cardiovascular morbidity or mortality in individuals without preexisting coronary disease has not been established.
A variety of clinical studies have demonstrated that elevated levels of TC, LDL-C, and Apo B promote human atherosclerosis. Similarly, decreased levels of HDL-C are associated with the development of atherosclerosis. Epidemiological investigations have established that cardiovascular morbidity and mortality vary directly with the level of Total-C and LDL-C, and inversely with the level of HDL-C.
Like LDL, cholesterol-enriched triglyceride-rich lipoproteins, including VLDL, intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL), and their remnants, can also promote atherosclerosis. Elevated plasma TG are frequently found in a triad with low HDL-C levels and small LDL particles, as well as in association with non-lipid metabolic risk factors for coronary heart disease (CHD). As such, total plasma TG has not consistently been shown to be an independent risk factor for CHD. Furthermore, the independent effect of raising HDL-C or lowering TG on the risk of coronary and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality has not been determined.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Due to extensive and saturable first-pass metabolism, niacin concentrations in the general circulation are dose dependent and highly variable. Time to reach the maximum niacin plasma concentrations was about 5 hours following niacin extended-release tablets. To reduce the risk of gastrointestinal (GI) upset, administration of niacin extended-release tablets with a low-fat meal or snack is recommended.
Single-dose bioavailability studies have demonstrated that the 500 mg and 1000 mg tablet strengths are dosage form equivalent but the 500 mg and 750 mg tablet strengths are not dosage form equivalent.
Metabolism
The pharmacokinetic profile of niacin is complicated due to extensive first-pass metabolism that is dose-rate specific and, at the doses used to treat dyslipidemia, saturable. In humans, one pathway is through a simple conjugation step with glycine to form nicotinuric acid (NUA). NUA is then excreted in the urine, although there may be a small amount of reversible metabolism back to niacin. The other pathway results in the formation of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD). It is unclear whether nicotinamide is formed as a precursor to, or following the synthesis of, NAD. Nicotinamide is further metabolized to at least N-methylnicotinamide (MNA) and nicotinamide-N-oxide (NNO). MNA is further metabolized to two other compounds, N-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide (2PY) and N-methyl-4-pyridone-5-carboxamide (4PY). The formation of 2PY appears to predominate over 4PY in humans. At the doses used to treat hyperlipidemia, these metabolic pathways are saturable, which explains the nonlinear relationship between niacin dose and plasma concentrations following multiple-dose niacin extended-release tablet administration.
Nicotinamide does not have hypolipidemic activity; the activity of the other metabolites is unknown.
Elimination
Following single and multiple doses, approximately 60 to 76% of the niacin dose administered as niacin extended-release tablets was recovered in urine as niacin and metabolites; up to 12% was recovered as unchanged niacin after multiple dosing. The ratio of metabolites recovered in the urine was dependent on the dose administered.
Pediatric Use
No pharmacokinetic studies have been performed in this population (≤ 16 years) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Geriatric Use
No pharmacokinetic studies have been performed in this population (> 65 years) [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.5)].
Renal Impairment
No pharmacokinetic studies have been performed in this population. Niacin extended-release tablets should be used with caution in patients with renal disease [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5)].
Hepatic Impairment
No pharmacokinetic studies have been performed in this population. Active liver disease, unexplained transaminase elevations and significant or unexplained hepatic dysfunction are contraindications to the use of niacin extended-release tablets [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Gender
Steady-state plasma concentrations of niacin and metabolites after administration of niacin extended-release tablets are generally higher in women than in men, with the magnitude of the difference varying with dose and metabolite. This gender difference observed in plasma levels of niacin and its metabolites may be due to gender-specific differences in metabolic rate or volume of distribution. Recovery of niacin and metabolites in urine, however, is generally similar for men and women, indicating that absorption is similar for both genders [see Gender ( 8.8)].
Drug Interactions
Fluvastatin
Niacin did not affect fluvastatin pharmacokinetics [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Lovastatin
When niacin extended-release tablets 2000 mg and lovastatin 40 mg were coadministered, niacin extended-release tablets increased lovastatin Cmax and AUC by 2% and 14%, respectively, and decreased lovastatin acid Cmax and AUC by 22% and 2%, respectively. Lovastatin reduced niacin extended-release tablet bioavailability by 2 to 3% [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Simvastatin
When niacin extended-release tablets 2000 mg and simvastatin 40 mg were coadministered, niacin extended-release tablets increased simvastatin Cmax and AUC by 1% and 9%, respectively, and simvastatin acid Cmax and AUC by 2% and 18%, respectively. Simvastatin reduced niacin extended-release tablet bioavailability by 2% [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Bile Acid Sequestrants
An in vitro study was carried out investigating the niacin-binding capacity of colestipol and cholestyramine. About 98% of available niacin was bound to colestipol, with 10 to 30% binding to cholestyramine [see Drug Interactions ( 7.2)].
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis and Impairment of Fertility
Niacin administered to mice for a lifetime as a 1% solution in drinking water was not carcinogenic. The mice in this study received approximately 6 to 8 times a human dose of 3000 mg/day as determined on a mg/m2 basis. Niacin was negative for mutagenicity in the Ames test. No studies on impairment of fertility have been performed. No studies have been conducted with niacin extended-release tablets regarding carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, or impairment of fertility.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Niacin Clinical Studies
The role of LDL-C in atherogenesis is supported by pathological observations, clinical studies, and many animal experiments. Observational epidemiological studies have clearly established that high TC or LDL-C and low HDL-C are risk factors for CHD. Additionally, elevated levels of Lp(a) have been shown to be independently associated with CHD risk.
Niacin’s ability to reduce mortality and the risk of definite, nonfatal myocardial infarction (MI) has been assessed in long-term studies. The Coronary Drug Project, completed in 1975, was designed to assess the safety and efficacy of niacin and other lipid-altering drugs in men 30 to 64 years old with a history of MI. Over an observation period of 5 years, niacin treatment was associated with a statistically significant reduction in nonfatal, recurrent MI. The incidence of definite, nonfatal MI was 8.9% for the 1,119 patients randomized to nicotinic acid versus 12.2% for the 2,789 patients who received placebo (p < 0.004). Total mortality was similar in the two groups at 5 years (24.4% with nicotinic acid versus 25.4% with placebo; p = N.S.). At the time of a 15 year follow-up, there were 11% (69) fewer deaths in the niacin group compared to the placebo cohort (52% versus 58.2%; p = 0.0004). However, mortality at 15 years was not an original endpoint of the Coronary Drug Project. In addition, patients had not received niacin for approximately 9 years, and confounding variables such as concomitant medication use and medical or surgical treatments were not controlled.
The Cholesterol-Lowering Atherosclerosis Study (CLAS) was a randomized, placebo-controlled, angiographic trial testing combined colestipol and niacin therapy in 162 non-smoking males with previous coronary bypass surgery. The primary, per-subject cardiac endpoint was global coronary artery change score. After 2 years, 61% of patients in the placebo cohort showed disease progression by global change score (n = 82), compared with only 38.8% of drug-treated subjects (n = 80), when both native arteries and grafts were considered (p < 0.005); disease regression also occurred more frequently in the drug-treated group (16.2% versus 2.4%; p = 0.002). In a follow-up to this trial in a subgroup of 103 patients treated for 4 years, again, significantly fewer patients in the drug-treated group demonstrated progression than in the placebo cohort (48% versus 85%, respectively; p < 0.0001).
The Familial Atherosclerosis Treatment Study (FATS) in 146 men ages 62 and younger with Apo B levels ≥ 125 mg/dL, established coronary artery disease, and family histories of vascular disease, assessed change in severity of disease in the proximal coronary arteries by quantitative arteriography. Patients were given dietary counseling and randomized to treatment with either conventional therapy with double placebo (or placebo plus colestipol if the LDL-C was elevated); lovastatin plus colestipol; or niacin plus colestipol. In the conventional therapy group, 46% of patients had disease progression (and no regression) in at least one of nine proximal coronary segments; regression was the only change in 11%. In contrast, progression (as the only change) was seen in only 25% in the niacin plus colestipol group, while regression was observed in 39%. Though not an original endpoint of the trial, clinical events (death, MI, or revascularization for worsening angina) occurred in 10 of 52 patients who received conventional therapy, compared with 2 of 48 who received niacin plus colestipol.
The Harvard Atherosclerosis Reversibility Project (HARP) was a randomized placebo-controlled, 2.5 year study of the effect of a stepped-care antihyperlipidemic drug regimen on 91 patients (80 men and 11 women) with CHD and average baseline TC levels less than 250 mg/dL and ratios of TC to HDL-C greater than 4. Drug treatment consisted of an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor administered alone as initial therapy followed by addition of varying dosages of either a slow-release nicotinic acid, cholestyramine, or gemfibrozil. Addition of nicotinic acid to the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor resulted in further statistically significant mean reductions in TC, LDL-C, and TG, as well as a further increase in HDL-C in a majority of patients (40 of 44 patients). The ratios of TC to HDL-C and LDL-C to HDL-C were also significantly reduced by this combination drug regimen [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2)].
14.2 Niacin Extended-Release Tablet Clinical Studies
Placebo-Controlled Clinical Studies in Patients With Primary Hyperlipidemia and Mixed Dyslipidemia: In two randomized, double-blind, parallel, multi-center, placebo-controlled trials, niacin extended-release tablets dosed at 1000, 1500 or 2000 mg daily at bedtime with a low-fat snack for 16 weeks (including 4 weeks of dose escalation) favorably altered lipid profiles compared to placebo ( Table 3 ). Women appeared to have a greater response than men at each niacin extended-release tablet dose level (see Gender Effect, below).
Mean Percent Change from Baseline to Week 16 |
|||||||||
| Treatment | n | TC | LDL-C | HDL-C | TC/HDL-C | TG | Lp(a) | Apo B | Apo A-I |
| Niacin Extended-Release Tablets 1000 mg at Bedtime | 41 | -3 | -5 | +18 | -17 | -21 | -13 | -6 | +9 |
| Niacin Extended-Release Tablets 2000 mg at Bedtime | 41 | -10 | -14 | +22 | -25 | -28 | -27 | -16 | +8 |
| Placebo | 40 | 0 | -1 | +4 | -3 | 0 | 0 | +1 | +3 |
| Niacin Extended-Release Tablets 1500 mg at Bedtime | 76 | -8 | -12 | +20 | -20 | -13 | -15 | -12 | +8 |
| Placebo | 73 | +2 | +1 | +2 | +1 | +12 | +2 | +1 | +2 |
|
n = number of patients at baseline. |
|||||||||
In a double-blind, multi-center, forced dose-escalation study, monthly 500 mg increases in niacin extended-release tablet dose resulted in incremental reductions of approximately 5% in LDL-C and Apo B levels in the daily dose range of 500 mg through 2000 mg ( Table 4 ). Women again tended to have a greater response to niacin extended-release tablets than men (see Gender Effect, below).
Mean Percent Change from Baseline |
|||||||||
| Treatment | n | TC | LDL-C | HDL-C | TC/HDL-C | TG | Lp(a) | Apo B | Apo A-I |
Placebo |
44 | -2 | -1 | +5 | -7 | -6 | -5 | -2 | +4 |
| Niacin Extended-Release Tablets | 87 | ||||||||
| 500 mg at Bedtime | -2 | -3 | +10 | -10 | -5 | -3 | -2 | +5 | |
| 1000 mg at Bedtime | -5 | -9 | +15 | -17 | -11 | -12 | -7 | +8 | |
| 1500 mg at Bedtime | -11 | -14 | +22 | -26 | -28 | -20 | -15 | +10 | |
| 2000 mg at Bedtime | -12 | -17 | +26 | -29 | -35 | -24 | -16 | +12 | |
|
n = number of patients enrolled. |
|||||||||
Pooled results for major lipids from these three placebo-controlled studies are shown below ( Table 5 ).
|
Mean Baseline and Median Percent Change from Baseline (25th, 75th Percentiles) |
||||
|
Niacin Extended-Release Tablets Dose |
n | LDL-C | HDL-C | TG |
| 1000 mg at bedtime | 104 | |||
| Baseline (mg/dL) | 218 | 45 | 172 | |
| Percent Change | -7 (-15, 0) | +14 (+7, +23) | -16 (-34, +3) | |
| 1500 mg at bedtime | 120 | |||
| Baseline (mg/dL) | 212 | 46 | 171 | |
| Percent Change | -13 (-21, -4) | +19 (+9, +31) | -25 (-45, -2) | |
| 2000 mg at bedtime | 85 | |||
| Baseline (mg/dL) | 220 | 44 | 160 | |
| Percent Change | -16 (-26, -7) | +22 (+15, +34) | -38 (-52, -14) | |
Gender Effect: Combined data from the three placebo-controlled niacin extended-release tablet studies in patients with primary hyperlipidemia and mixed dyslipidemia suggest that, at each niacin extended-release tablet dose level studied, changes in lipid concentrations are greater for women than for men ( Table 6 ).
| Mean Percent Change from Baseline | |||||||||
| Niacin Extended-Release Tablets | n | LDL-C | HDL-C | TG | Apo B | ||||
| Dose | (M/F) | M | F | M | F | M | F | M | F |
| 500 mg at bedtime | 50/37 | -2 | -5 | +11 | +8 | -3 | -9 | -1 | -5 |
| 1000 mg at bedtime | 76/52 | -6 |
-11 |
+14 | +20 | -10 | -20 | -5 |
-10 |
| 1500 mg at bedtime | 104/59 | -12 | -16 | +19 | +24 | -17 | -28 | -13 | -15 |
| 2000 mg at bedtime | 75/53 | -15 | -18 | +23 | +26 | -30 | -36 | -16 | -16 |
|
n = number of male/female patients enrolled. |
|||||||||
Other Patient Populations: In a double-blind, multi-center, 19 week study the lipid-altering effects of niacin extended-release tablets (forced titration to 2000 mg at bedtime) were compared to baseline in patients whose primary lipid abnormality was a low level of HDL-C (HDL-C ≤ 40 mg/dL, TG ≤ 400 mg/dL, and LDL-C ≤ 160, or < 130 mg/dL in the presence of CHD). Results are shown below ( Table 7 ).
Mean Baseline and Mean Percent Change From Baseline |
||||||||||
| n | TC | LDL-C | HDL-C | TC/HDL-C | TG |
Lp(a) |
Apo B |
Apo A-I |
Lp A-I |
|
| Baseline (mg/dL) |
88 | 190 | 120 | 31 | 6 | 194 | 8 | 106 | 105 | 32 |
| Week 19 (% Change) |
71 | -3 | 0 | +26 | -22 | -30 | -20 | -9 | +11 | +20 |
|
n = number of patients. |
||||||||||
At niacin extended-release 2000 mg/day, median changes from baseline (25th, 75th percentiles) for LDL-C, HDL-C, and TG were -3% (-14, +12%), +27% (+13, +38%), and -33% (-50, -19%), respectively.
14.3 Niacin Extended-Release and Lovastatin Clinical Studies
Combination Niacin Extended-Release and Lovastatin Study: In a multi-center, randomized, double-blind, parallel, 28 week study, a combination tablet of niacin extended-release and lovastatin was compared to each individual component in patients with Type IIa and IIb hyperlipidemia. Using a forced dose-escalation study design, patients received each dose for at least 4 weeks. Patients randomized to treatment with the combination tablet of niacin extended-release and lovastatin initially received 500 mg/20 mg (expressed as mg of niacin/mg of lovastatin) once daily before bedtime. The dose was increased by 500 mg at 4 week intervals (based on the niacin extended-release component) to a maximum dose of 1000 mg/20 mg in one-half of the patients and 2000 mg/40 mg in the other half. The niacin extended-release monotherapy group underwent a similar titration from 500 mg to 2000 mg. The patients randomized to lovastatin monotherapy received 20 mg for 12 weeks titrated to 40 mg for up to 16 weeks. Up to a third of the patients randomized to the combination tablet of niacin extended-release and lovastatin or niacin extended-release monotherapy discontinued prior to Week 28. Results from this study showed that combination therapy decreased LDL-C, TG and Lp(a), and increased HDL-C in a dose-dependent fashion ( Tables 8, 9, 10 , and 11 ). Results from this study for LDL-C mean percent change from baseline (the primary efficacy variable) showed that:
- LDL-lowering with the combination tablet of niacin extended-release and lovastatin was significantly greater than that achieved with lovastatin 40 mg only after 28 weeks of titration to a dose of 2000 mg/40 mg (p < 0.0001)
- The combination tablet of niacin extended-release and lovastatin at doses of 1000 mg/20 mg or higher achieved greater LDL-lowering than niacin extended-release tablets (p < 0.0001)
The LDL-C results are summarized in Table 8 .
| Week | Combination Tablet of Niacin Extended-Release and Lovastatin | Niacin Extended-Release Tablets | Lovastatin | ||||||
n
 |
Dose (mg/mg) | LDL |
n |
Dose (mg) |
LDL |
n |
Dose (mg) |
LDL | |
| Baseline | 57 | – | 190.9 mg/dL | 61 | – | 189.7 mg/dL | 61 | – | 185.6 mg/dL |
| 12 | 47 | 1000/20 | -30% | 46 | 1000 | -3% | 56 | 20 | -29% |
| 16 | 45 | 1000/40 | -36% | 44 | 1000 | -6% | 56 | 40 | -31% |
| 20 | 42 | 1500/40 | -37% | 43 | 1500 | -12% | 54 | 40 | -34% |
| 28 | 42 | 2000/40 | -42% | 41 | 2000 | -14% | 53 | 40 | -32% |
Combination therapy achieved significantly greater HDL-raising compared to lovastatin and niacin extended-release tablet monotherapy at all doses ( Table 9 ).
| Week | Combination Tablet of Niacin Extended-Release and Lovastatin | Niacin Extended-Release Tablets | Lovastatin | ||||||
n |
Dose (mg/mg) |
HDL |
n |
Dose (mg) |
HDL |
n |
Dose (mg) |
HDL | |
| Baseline | 57 | – | 45 mg/dL | 61 | – | 47 mg/dL | 61 | – | 43 mg/dL |
| 12 | 47 | 1000/20 | +20% | 46 | 1000 | +14% | 56 | 20 | +3% |
| 16 | 45 | 1000/40 | +20% | 44 | 1000 | +15% | 56 | 40 | +5% |
| 20 | 42 | 1500/40 | +27% | 43 | 1500 | +22% | 54 | 40 | +6% |
| 28 | 42 | 2000/40 | +30% | 41 | 2000 | +24% | 53 | 40 | +6% |
In addition, combination therapy achieved significantly greater TG lowering at doses of 1000 mg/20mg or greater compared to lovastatin and niacin extended-release tablet monotherapy ( Table 10 ).
| Week | Combination Tablet of Niacin Extended-Release and Lovastatin | Niacin Extended-Release Tablets | Lovastatin | ||||||
n |
Dose (mg/mg) | TG |
n |
Dose (mg) |
TG |
n |
Dose (mg) |
TG | |
| Baseline | 57 | – | 174 mg/dL | 61 | – | 186 mg/dL | 61 | – | 171 mg/dL |
| 12 | 47 | 1000/20 | -32% | 46 | 1000 | -22% | 56 | 20 | -20% |
| 16 | 45 | 1000/40 | -39% | 44 | 1000 | -23% | 56 | 40 | -17% |
| 20 | 42 | 1500/40 | -44% | 43 | 1500 | -31% | 54 | 40 | -21% |
| 28 | 42 | 2000/40 | -44% | 41 | 2000 | -31% | 53 | 40 | -20% |
The Lp(a)-lowering effects of combination therapy and niacin extended-release tablet monotherapy were similar, and both were superior to lovastatin ( Table 11 ). The independent effect of lowering Lp(a) with niacin extended-release tablets or combination therapy on the risk of coronary and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality has not been determined.
| Week | Combination Tablet of Niacin Extended-Release and Lovastatin | Niacin Extended-Release Tablets | Lovastatin | ||||||
n |
Dose (mg/mg) |
Lp(a) |
n |
Dose (mg) |
Lp(a) |
n |
Dose (mg) |
Lp(a) | |
| Baseline | 57 | – | 34 mg/dL | 61 | – | 41 mg/dL | 60 | – | 42 mg/dL |
| 12 | 47 | 1000/20 | -9% | 46 | 1000 | -8% | 55 | 20 | +8% |
| 16 | 45 | 1000/40 | -9% | 44 | 1000 | -12% | 55 | 40 | +8% |
| 20 | 42 | 1500/40 | -17% | 43 | 1500 | -22% | 53 | 40 | +6% |
| 28 | 42 | 2000/40 | -22% | 41 | 2000 | -32% | 52 | 40 | 0% |
14.4 Niacin Extended-Release and Simvastatin Clinical Studies
In a double-blind, randomized, multicenter, multi-national, active-controlled, 24 week study, the lipid effects of a combination tablet of niacin extended-release and simvastatin were compared to simvastatin 20 mg and 80 mg in 641 patients with type II hyperlipidemia or mixed dyslipidemia. Following a lipid qualification phase, patients were eligible to enter one of two treatment groups. In Group A, patients on simvastatin 20 mg monotherapy, with elevated non-HDL levels and LDL-C levels at goal per the NCEP guidelines, were randomized to one of three treatment arms: combination tablet of niacin extended-release and simvastatin 1000/20 mg, combination tablet of niacin extended-release and simvastatin 2000/20 mg, or simvastatin 20 mg. In Group B, patients on simvastatin 40 mg monotherapy, with elevated non-HDL levels per the NCEP guidelines regardless of attainment of LDL-C goals, were randomized to one of three treatment arms: combination tablet of niacin extended-release and simvastatin 1000/40 mg, combination tablet of niacin extended-release and simvastatin 2000/40 mg, or simvastatin 80 mg. Therapy was initiated at the 500 mg dose of combination tablet of niacin extended-release and simvastatin and increased by 500 mg every four weeks. Thus patients were titrated to the 1000 mg dose of combination tablet of niacin extended-release and simvastatin after four weeks and to the 2000 mg dose of combination tablet of niacin extended-release and simvastatin after 12 weeks. All patients randomized to simvastatin monotherapy received 50 mg immediate-release niacin daily in an attempt to keep the study from becoming unblinded due to flushing in the combination tablet of niacin extended-release and simvastatin groups. Patients were instructed to take one 325 mg aspirin or 200 mg ibuprofen 30 minutes prior to taking the double-blind medication to help minimize flushing effects.
In Group A, the primary efficacy analysis was a comparison of the mean percent change in non-HDL levels between the combination tablet of niacin extended-release and simvastatin 2000/20 mg and simvastatin 20 mg groups, and if statistically significant, then a comparison was conducted between the combination tablet of niacin extended-release and simvastatin 1000/20 mg and simvastatin 20 mg groups. In Group B, the primary efficacy analysis was a determination of whether the mean percent change in non-HDL in the combination tablet of niacin extended-release and simvastatin 2000/40 mg group was non-inferior to the mean percent change in the simvastatin 80 mg group, and if so, whether the mean percent change in non-HDL in the combination tablet of niacin extended-release and simvastatin 1000/40 mg group was non-inferior to the mean percent change in the simvastatin 80 mg group.
In Group A, the non-HDL-C lowering with combination tablet of niacin extended-release and simvastatin 2000/20 and combination tablet of niacin extended-release and simvastatin 1000/20 was statistically significantly greater than that achieved with simvastatin 20 mg after 24 weeks (p<0.05; Table 12 ). The completion rate after 24 weeks was 72% for the combination tablet of niacin extended-release and simvastatin arms and 88% for the simvastatin 20 mg arm. In Group B, the non-HDL-C lowering with combination tablet of niacin extended-release and simvastatin 2000/40 and combination tablet of niacin extended-release and simvastatin 1000/40 was non-inferior to that achieved with simvastatin 80 mg after 24 weeks ( Table 13 ). The completion rate after 24 weeks was 78% for the combination tablet of niacin extended-release and simvastatin arms and 80% for the simvastatin 80 mg arm.
The combination tablet of niacin extended-release and simvastatin was not superior to simvastatin in lowering LDL-C in either Group A or Group B. However, the combination tablet of niacin extended-release and simvastatin was superior to simvastatin in both groups in lowering TG and raising HDL ( Tables 14 and 15 ).
| Group A | Combination Tablet of Niacin Extended-Release and Simvastatin 2000/20 | Combination Tablet of Niacin Extended-Release and Simvastatin 1000/20 | Simvastatin 20 | ||||||
| Week |
n |
Dose (mg/mg) |
Non-HDL |
n |
Dose (mg/mg) |
Non-HDL |
n |
Dose (mg/mg) |
Non-HDL |
| Baseline | 56 | – | 163.1 mg/dL | 108 | – | 164.8 mg/dL | 102 | – | 163.7 mg/dL |
| 4 | 52 | 500/20 | -12.9% | 86 | 500/20 | -12.8% | 91 | 20 | -8.3% |
| 8 | 46 | 1000/20 | -17.5% | 91 | 1000/20 | -15.5% | 95 | 20 | -8.3% |
| 12 | 46 | 1500/20 | -18.9% | 90 | 1000/20 | -14.8% | 96 | 20 | -6.4% |
| 24 | 40 | 2000/20 | -19.5% |
78 | 1000/20 | -13.6% |
90 | 20 | -5% |
| Dropouts by Week 24: | 28.6% | 27.8% | 11.8% | ||||||
| Group B | Combination Tablet of Niacin Extended-Release and Simvastatin 2000/40 | Combination Tablet of Niacin Extended-Release and Simvastatin 1000/40 | Simvastatin 80 | ||||||
| Week |
n |
Dose (mg/mg) |
Non-HDL |
n |
Dose (mg/mg) |
Non-HDL |
n |
Dose (mg/mg) |
Non-HDL |
| Baseline | 98 | – | 144.4 mg/dL | 111 | – | 141.2 mg/dL | 113 | – | 134.5 mg/dL |
| 4 | 96 | 500/40 | -6% | 108 | 500/40 | -5.9% | 110 | 80 | -11.3% |
| 8 | 93 | 1000/40 | -15.5% | 100 | 1000/40 | -16.2% | 104 | 80 | -13.7% |
| 12 | 90 | 1500/40 | -18.4% | 97 | 1000/40 | -12.6% | 100 | 80 | -9.5% |
| 24 | 80 | 2000/40 | -7.6% |
82 | 1000/40 | -6.7% |
90 | 80 | -6% |
| Dropouts by Week 24: | 18.4% | 26.1% | 20.4% | ||||||
| Treatment Group A | ||||||
| TREATMENT | N | LDL-C | Total-C | HDL-C |
TG |
Apo B |
Baseline (mg/dL) |
266 | 120 | 207 | 43 | 209 | 102 |
| Simvastatin 20 mg | 102 | -6.7% | -4.5% | 7.8% | -15.3% | -5.6% |
| Combination Tablet of Niacin Extended-Release and Simvastatin 1000/20 | 108 | -11.9% | -8.8% | 20.7% | -26.5% | -13.2% |
| Combination Tablet of Niacin Extended-Release and Simvastatin 2000/20 | 56 | -14.3% | -11.1% | 29% | -38% | -18.5% |
| Treatment Group B | ||||||
| TREATMENT | N | LDL-C | Total-C | HDL-C |
TG |
Apo B |
Baseline (mg/dL) |
322 | 108 | 187 | 47 | 145 | 93 |
| Simvastatin 80 mg | 113 | -11.4% | -6.2% | 0.1% | 0.3% | -7.5% |
| Combination Tablet of Niacin Extended-Release and Simvastatin 1000/40 | 111 | -7.1% | -3.1% | 15.4% | -22.8% | -7.7% |
| Combination Tablet of Niacin Extended-Release and Simvastatin 2000/40 | 98 | -5.1 | -1.6% | 24.4% | -31.8% | -10.5% |
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Niacin Extended-Release Tablets USP are supplied as follows:
500 mg: White to off-white, capsule-shaped, unscored, biconvex tablet. Debossed with stylized b 212 on one side and 500 on the other side. Available in bottles of 90 and 180 tablets.
750 mg: White to off-white, capsule-shaped, unscored, biconvex tablet. Debossed with stylized b 213 on one side and 750 on the other side. Available in bottles of 90 and 180 tablets.
1000 mg: White to off-white, capsule-shaped, unscored, biconvex tablet. Debossed with stylized b 214 on one side and 1000 on the other side. Available in bottles of 90 and 180 tablets.
Storage: Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP, with a child-resistant closure (as required).
KEEP THIS AND ALL MEDICATIONS OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Patient Counseling
Patients should be advised to adhere to their National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) recommended diet, a regular exercise program, and periodic testing of a fasting lipid panel.
Patients should be advised to inform other healthcare professionals prescribing a new medication that they are taking niacin extended-release tablets.
The patient should be informed of the following:
Dosing Time
Niacin extended-release tablets should be taken at bedtime, after a low-fat snack. Administration on an empty stomach is not recommended.
Tablet Integrity
Niacin extended-release tablets should not be broken, crushed or chewed, but should be swallowed whole.
Dosing Interruption
If dosing is interrupted for any length of time, their physician should be contacted prior to restarting therapy; re-titration is recommended.
Muscle Pain
Notify their physician of any unexplained muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness promptly. They should discuss all medication, both prescription and over the counter, with their physician.
Flushing
Flushing (warmth, redness, itching and/or tingling of the skin) is a common side effect of niacin therapy that may subside after several weeks of consistent niacin extended-release tablet use. Flushing may vary in severity and is more likely to occur with initiation of therapy, or during dose increases. By dosing at bedtime, flushing will most likely occur during sleep. However, if awakened by flushing at night, the patient should get up slowly, especially if feeling dizzy, feeling faint, or taking blood pressure medications. Advise patients of the symptoms of flushing and how they differ from the symptoms of a myocardial infarction.
Use of Aspirin Medication
Taking aspirin (up to the recommended dose of 325 mg) approximately 30 minutes before dosing can minimize flushing.
Diet
Avoid ingestion of alcohol, hot beverages and spicy foods around the time of taking niacin extended-release tablets to minimize flushing.
Supplements
Notify their physician if they are taking vitamins or other nutritional supplements containing niacin or nicotinamide.
Dizziness
Notify their physician if symptoms of dizziness occur.
Diabetics
If diabetic, to notify their physician of changes in blood glucose.
Pregnancy
Discuss future pregnancy plans with your patients, and discuss when to stop niacin extended-release tablets if they are trying to conceive. Patients should be advised that if they become pregnant, they should stop taking niacin extended-release tablets and call their healthcare professional.
Breastfeeding
Women who are breastfeeding should be advised to not use niacin extended-release tablets. Patients, who have a lipid disorder and are breastfeeding, should be advised to discuss the options with their healthcare professional.
TEVA PHARMACEUTICALS USA
Sellersville, PA 18960
Rev. B 2/2013
PATIENT INFORMATION
Niacin [nahy-uh-sin]
Extended-Release Tablets USP
Read this information carefully before you start taking niacin extended-release tablets and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment.
What are niacin extended-release tablets?
Niacin extended-release tablets are a prescription medicine used with diet and exercise to increase the good cholesterol (HDL) and lower the bad cholesterol (LDL) and fats (triglycerides) in your blood.
- Niacin extended-release tablets can be used by themselves or with other cholesterol-lowering medicines
- Niacin extended-release tablets are also used to lower the risk of heart attack in people who have had a heart attack and have high cholesterol.
- In people with coronary artery disease and high cholesterol, niacin extended-release tablets, when used with a bile acid-binding resin (another cholesterol medicine) can slow down or lessen the build-up of plaque (fatty deposits) in your arteries.
- In people with heart problems and well-controlled cholesterol, taking niacin extended-release tablets with another cholesterol-lowering medicine (simvastatin) has not been shown to reduce heart attacks or strokes more than taking simvastatin alone.
It is not known if niacin extended-release tablets are safe and effective in children 16 years of age and under.
Who should not take niacin extended-release tablets?
Do not take niacin extended-release tablets if you have:
- liver problems
- a stomach ulcer
- bleeding problems
- an allergy to niacin or any of the ingredients in niacin extended-release tablets. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in niacin extended-release tablets.
What should I tell my doctor before taking niacin extended-release tablets?
Before you take niacin extended-release tablets, tell your doctor, if you:
- have diabetes. Tell your doctor if your blood sugar levels change after you take niacin extended-release tablets.
- have gout
- have kidney problems
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if niacin extended-release tablets will harm your unborn baby. Talk to your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant while taking niacin extended-release tablets.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Niacin extended-release tablets can pass into your breast milk. You and your doctor should decide if you will take niacin extended-release tablets or breastfeed. You should not do both. Talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you take niacin extended-release tablets.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, herbal supplements or other nutritional supplements containing niacin or nicotinamide. Niacin extended-release tablets and other medicines may affect each other causing side effects. Niacin extended-release tablets may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how niacin extended-release tablets work.
Especially tell your doctor if you take:
- other medicines to lower cholesterol or triglycerides
- aspirin
- blood pressure medicines
- blood thinner medicines
- large amounts of alcohol
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take niacin extended-release tablets?
- Take niacin extended-release tablets exactly as your doctor tells you to take it.
- Take niacin extended-release tablets whole. Do not break, crush or chew niacin extended-release tablets before swallowing.
- Take niacin extended-release tablets 1 time a day at bedtime after a low-fat snack. Niacin extended-release tablets should not be taken on an empty stomach.
- All forms of niacin are not the same as niacin extended-release tablets. Do not switch between forms of niacin without first talking to your doctor as severe liver damage can occur.
- Do not change your dose or stop taking niacin extended-release tablets unless your doctor tells you to.
- If you need to stop taking niacin extended-release tablets, call your doctor before you start taking niacin extended-release tablets again. Your doctor may need to lower your dose of niacin extended-release tablets.
- If you forget to take a dose of niacin extended-release tablets, take it as soon as you remember.
- If you take too many niacin extended-release tablets, call your doctor right away.
- Medicines used to lower your cholesterol called bile acid resins, such as colestipol and cholestyramine, should not be taken at the same time of day as niacin extended-release tablets. You should take niacin extended-release tablets and the bile acid resin medicine at least 4 to 6 hours apart.
- Your doctor may do blood tests before you start taking niacin extended-release tablets and during your treatment. You should see your doctor regularly to check your cholesterol and triglyceride levels and to check for side effects.
What are the possible side effects of niacin extended-release tablets?
Niacin extended-release tablets may cause serious side effects, including:
-
severe liver problems. Signs of liver problems include:
- increased tiredness
- dark colored urine (tea-colored)
- loss of appetite
- light colored stools
- nausea
- right upper stomach (abdomen) pain
- yellowing of your skin or whites of your eye
- itchy skin
- unexplained muscle pain, tenderness or weakness
- high blood sugar level (glucose)
Call your doctor right away if you have any of the side effects listed above.
The most common side effects of niacin extended-release tablets include:
- flushing
- diarrhea
- nausea
- vomiting
- increased cough
- rash
Flushing is the most common side effect of niacin extended-release tablets. Flushing happens when tiny blood vessels near the surface of the skin (especially on the face, neck, chest and/or back) open wider. Symptoms of flushing may include any or all of the following:
- warmth
- redness
- itching
- tingling of the skin
Flushing does not always happen. If it does, it is usually within 2 to 4 hours after taking a dose of niacin extended-release tablets. Flushing may last for a few hours. Flushing is more likely to happen when you first start taking niacin extended-release tablets or when your dose of niacin extended-release tablets is increased. Flushing may get better after several weeks.
If you wake up at night because of flushing, get up slowly, especially if you:
- feel dizzy or faint
- take blood pressure medicines
To lower your chance of flushing:
- Ask your doctor if you can take aspirin to help lower the flushing side effect from niacin extended-release tablets. You can take aspirin (up to the recommended dose of 325 mg) about 30 minutes before you take niacin extended-release tablets to help lower the flushing side effect.
- Do not drink hot beverages (including coffee), alcohol, or eat spicy foods around the time you take niacin extended-release tablets.
- Take niacin extended-release tablets with a low-fat snack to lessen upset stomach.
People with high cholesterol and heart disease are at risk for a heart attack. Symptoms of a heart attack may be different from a flushing reaction from niacin extended-release tablets. The following may be symptoms of a heart attack due to heart disease and not a flushing reaction:
- chest pain
- pain in other areas of your upper body such as one or both arms, back, neck, jaw or stomach
- shortness of breath
- sweating
- nausea
- lightheadedness
The chest pain you have with a heart attack may feel like uncomfortable pressure, squeezing, fullness or pain that lasts more than a few minutes, or that goes away and comes back. Heart attacks may be sudden and intense, but often start slowly, with mild pain or discomfort.
Call your doctor right away if you have any symptoms of a heart attack.
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of niacin extended-release tablets. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store niacin extended-release tablets?
- Store niacin extended-release tablets at 20º to 25ºC (68º to 77ºF).
Keep niacin extended-release tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of niacin extended-release tablets:
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use niacin extended-release tablets for a condition for which they were not prescribed. Do not give niacin extended-release tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. They may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about niacin extended-release tablets. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about niacin extended-release tablets that is written for health professionals.
For more information, call 1-866-832-8537, MEDICAL AFFAIRS.
What are the ingredients in niacin extended-release tablets?
Active Ingredient:
Niacin, USP
Inactive Ingredients:
Hypromellose, povidone, and stearic acid.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
TEVA PHARMACEUTICALS USA
Sellersville, PA 18960
Rev. B 2/2013
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL

Niacin Extended-Release Tablets USP 500 mg 90s Label Text
NDC 0093-7392-98
NIACIN
Extended-Release
Tablets USP
500 mg
Once-Daily at Bedtime
PHARMACIST: PLEASE DISPENSE WITH
ATTACHED PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET
Rx only
90 TABLETS
TEVA
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL

Niacin Extended-Release Tablets USP 750 mg 90s Label Text
NDC 0093-7393-98
NIACIN
Extended-Release
Tablets USP
750 mg
Once-Daily at Bedtime
PHARMACIST: PLEASE DISPENSE WITH
ATTACHED PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET
Rx only
90 TABLETS
TEVA
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL

Niacin Extended-Release Tablets USP 1000 mg 90s Label Text
NDC 0093-7394-98
NIACIN
Extended-Release
Tablets USP
1000 mg
Once-Daily at Bedtime
PHARMACIST: PLEASE DISPENSE WITH
ATTACHED PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET
Rx only
90 TABLETS
TEVA
NiacinNiacin TABLET, EXTENDED RELEASE
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NiacinNiacin TABLET, EXTENDED RELEASE
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NiacinNiacin TABLET, EXTENDED RELEASE
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||