Neurontin
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- NEURONTIN DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
- NEURONTIN CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- NEURONTIN ADVERSE REACTIONS
- DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
- OVERDOSAGE
- DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- STORAGE AND HANDLING
- MEDICATION GUIDE
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
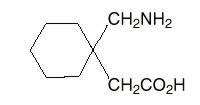
NEURONTIN DESCRIPTION
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of ActionPharmacokinetics and Drug Metabolism
All pharmacological actions following gabapentin administration are due to the activity of the parent compound; gabapentin is not appreciable matebolized in humans.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Special Populations: Adult Patients With Renal Insufficiency, below). In elderly patients, and in patients with impaired renal function, gabapentin plasma clearance is reduced. Gabapentin can be removed from plasma by hemodialysis.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION, Table 6).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). Pediatric patients with renal insufficiency have not been studied.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
PRECAUTIONS, Geriatric Use, andDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
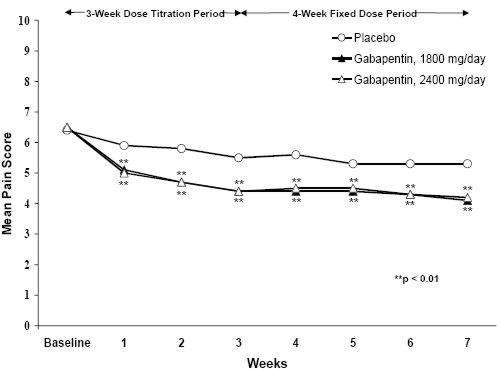
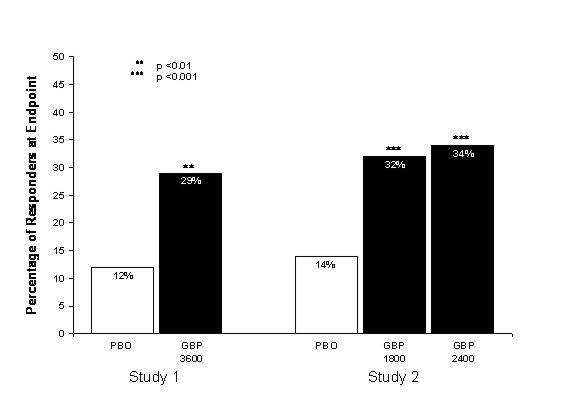
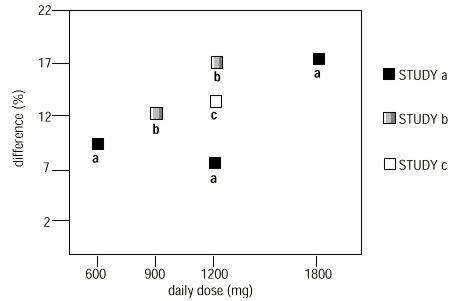
Clinical Studies
TABLE 1. Controlled PHN Studies: Duration, Dosages, and Number of Patients
Study Study Duration Gabapentin (mg/day) *Target Dose Patients Receiving Gabapentin Patients Receiving Placebo *

INDICATIONS & USAGE
Postherpetic NeuralgiaEpilepsy
NEURONTIN CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS
Suicidal Behavior and IdeationTable 2 Risk by indication for antiepileptic drugs in the pooled analysis
Indication Placebo Patients with Events Per 1000 Patients Drug Patients with Events Per 1000 Patients Relative Risk: Incidence of Events in Drug Patients/Incidence in Placebo Patients Risk Difference: Additional Drug Patients with Events Per 1000 Patients
Neuropsychiatric Adverse Events-Pediatric Patients 3years of age
Withdrawal Precipitated Seizure, Status Epilepticus
Tumorigenic Potential
PRECAUTIONS, Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility.) The clinical significance of this finding is unknown. Clinical experience during gabapentin's premarketing development provides no direct means to assess its potential for inducing tumors in humans.
Sudden and Unexplained Death in Patients With Epilepsy
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)/Multiorgan hypersensitivity
PRECAUTIONS
Information for PatientsPRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions).
PRECAUTIONS, Pregnancy).
Laboratory Tests
Drug Interactions
PRECAUTIONS). Morphine pharmacokinetic parameter values were not affected by administration of Neurontin 2 hours after morphine. The magnitude of interaction at other doses is not known.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Gabapentin was given in the diet to mice at 200, 600, and 2000 mg/kg/day and to rats at 250, 1000, and 2000 mg/kg/day for 2 years. A statistically significant increase in the incidence of pancreatic acinar cell adenomas and carcinomas was found in male rats receiving the high dose; the no-effect dose for the occurrence of carcinomas was 1000 mg/kg/day. Peak plasma concentrations of gabapentin in rats receiving the high dose of 2000 mg/kg were 10 times higher than plasma concentrations in humans receiving 3600 mg per day, and in rats receiving 1000 mg/kg/day, peak plasma concentrations were 6.5 times higher than in humans receiving 3600 mg/day. The pancreatic acinar cell carcinomas did not affect survival, did not metastasize, and were not locally invasive. The relevance of this finding to carcinogenic risk in humans is unclear.
Pregnancy
Use in Nursing Mothers
Pediatric Use
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Clinical Studies).
Geriatric Use
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY,ADVERSE REACTIONS, andDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
NEURONTIN ADVERSE REACTIONS
Postherpetic NeuralgiaTABLE 3. Treatment-Emergent Adverse Event Incidence in Controlled Trials in Postherpetic Neuralgia (Events in at least 1% of Neurontin-Treated Patients and Numerically More Frequent Than in the Placebo Group)
Body System/ Neurontin Placebo Preferred Term N=336
% N=227
% *
Body as a Whole Digestive System Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders Nervous System Respiratory System Skin and Appendages Special Senses *
Epilepsy
WARNINGS, Neuropsychiatric Adverse Events-Pediatric Patients 3years of age).
TABLE 4. Treatment-Emergent Adverse Event Incidence in Controlled Add-On Trials In Patients >12 years of age (Events in at least 1% of Neurontin patients and numerically more frequent than in the placebo group)
Body System/ Neurontin * Placebo * Adverse Event N=543
% N=378
% *
Body As A Whole Cardiovascular Digestive System Hematologic and Lymphatic Systems Nervous System Respiratory System Skin and Appendages Urogenital System Special Senses Laboratory Deviations
TABLE 5. Treatment-Emergent Adverse Event Incidence in Pediatric Patients Age 3 to 12 Years in a Controlled Add-On Trial (Events in at least 2% of Neurontin patients and numerically more frequent than in the placebo group)
Body System/ Neurontin * Placebo * Adverse Event N=119
% N=128
% *
Body As A Whole Digestive System Nervous System Respiratory System
Body As A Whole:Frequent:asthenia, malaise, face edema; Infrequent: allergy, generalized edema, weight decrease, chill; Rare: strange feelings, lassitude, alcohol intolerance, hangover effect.
Cardiovascular System:Frequent: hypertension; Infrequent: hypotension, angina pectoris, peripheral vascular disorder, palpitation, tachycardia, migraine, murmur; Rare: atrial fibrillation, heart failure, thrombophlebitis, deep thrombophlebitis, myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular accident, pulmonary thrombosis, ventricular extrasystoles, bradycardia, premature atrial contraction, pericardial rub, heart block, pulmonary embolus, hyperlipidemia, hypercholesterolemia, pericardial effusion, pericarditis.
Digestive System:salivary gland enlarged, lip hemorrhage, esophagitis, hiatal hernia, hematemesis, proctitis, irritable bowel syndrome, rectal hemorrhage, esophageal spasm.
Endocrine System:Rare: hyperthyroid, hypothyroid, goiter, hypoestrogen, ovarian failure, epididymitis, swollen testicle, cushingoid appearance.
Hematologic and Lymphatic Systems:Frequent: purpura most often described as bruises resulting from physical trauma; Infrequent: anemia, thrombocytopenia, lymphadenopathy; Rare: WBC count increased, lymphocytosis, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, bleeding time increased.
Musculoskeletal System:Frequent: arthralgia; Infrequent: tendinitis, arthritis, joint stiffness, joint swelling, positive Romberg test; Rare: costochondritis, osteoporosis, bursitis, contracture.
Nervous System:Frequent: vertigo, hyperkinesia, paresthesia, decreased or absent reflexes, increased reflexes, anxiety, hostility; Infrequent: CNS tumors, syncope, dreaming abnormal, aphasia, hypesthesia, intracranial hemorrhage, hypotonia, dysesthesia, paresis, dystonia, hemiplegia, facial paralysis, stupor, cerebellar dysfunction, positive Babinski sign, decreased position sense, subdural hematoma, apathy, hallucination, decrease or loss of libido, agitation, paranoia, depersonalization, euphoria, feeling high, dope-up sensation, psychosis; Rare: choreoathetosis, orofacial dyskinesia, encephalopathy, nerve palsy, personality disorder, increased libido, subdued temperament, apraxia, fine motor control disorder, meningismus, local myoclonus, hyperesthesia, hypokinesia, mania, neurosis, hysteria, antisocial reaction.
Respiratory System:Frequent: pneumonia; Infrequent: epistaxis, dyspnea, apnea; Rare: mucositis, aspiration pneumonia, hyperventilation, hiccup, laryngitis, nasal obstruction, snoring, bronchospasm, hypoventilation, lung edema.
Dermatological:Infrequent: alopecia, eczema, dry skin, increased sweating, urticaria, hirsutism, seborrhea, cyst, herpes simplex; Rare: herpes zpster, skin discolor, skin papules, photosensitive reaction, leg ulcer, scalp seborrhea, psoriasis, desquamation, maceration, skin nodules, subcutaneous nodule, melanosis, skin necrosis, local swelling.
Urogenital System:Infrequent: hematuria, dysuria, urination frequency, cystitis, urinary retention, urinary incontinence, vaginal hemorrhage, amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea, menorrhagia, breast cancer, unable to climax, ejaculation abnormal; rare: kidney pain, leukorrhea, pruritus genital, renal stone, acute renal failure, anuria, glycosuria, nephrosis, nocturia, pyuria, urination urgency, vagainal pain, breast pain, testical pain.
Special Senses:Frequent: abnormal vision; Infrequent: cataract, conjunctivitis, eyes dry, eye pain, visual field defect, photophobia, bilateral or unilateral ptosis, eye hemorrhage, hordeolum, hearing loss, earache, tinnitus, inner ear infection, otitis, taste loss, unusual taste, eye twitching, ear fullness; Rare: eye itching, abnormal accommodation, perforated ear drum, sensitivity to noise, eye focusing problem, watery eyes, retinopathy, glaucoma, iritis, corneal disorders, lacrimal dysfunction, degenerative eye changes, blindness, retinal degeneration, miosis, chorioretinitis, strabismus, eustachian tube dysfunction, labyrinthitis, otitis externa, odd smell.
Body as a Whole:dehydration, infectious mononucleosis
Digestive System:hepatitis
Hematologic and Lymphatic Systems:coagulation defect
Nervous System:aura disappeared, occipital neuralgia
Psychobiologic Function:sleepwalking
Respiratory System:pseudocroup, hoarseness
Body as a Whole:Infrequent: chest pain, cellilitis, malaise, neck pain, face edema, allergic reaction, abscess, chills, chills and fever, mucous membrane disorder; Rare: body odor, cyst, fever, hernia, abnormal BUN value, lump in neck, pelvic pain, sepsis, viral infection.
Cardiovascular System:Infrequent: hypertension, syncope, palpitation, migraine, hypotension, peripheral vascualr disorder, cardiovascular disorder, cerebrovascualr accident, congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction, vasodilatation; Rare: angina pectoris, heart failure, increased capillary fragility, phlebitis, thrombophlebitis, varicose vein.
Digestive System:Infrequent: gastroenteritis, increased appetite, gastrointestinal disorder, oral moniliasis, gastritis, tongue disorder, thirst, tooth disorder, abnormal stools, anorexia, liver function test abnormal, periodontal abscess; Rare: cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, duodenal ulcer, fecal incontinence, gamma glutamyl transpeptidase increased, gingivitis, intestinal obstruction, intestinal ulcer, melena, mouth ulceration, rectal disorder, rectal hemorrhage, stomatitis.
Endocrine System:Infrequent: diabetes mellitus.
Hematologic and Lymphatic Systems:Infrequent: ecchymosis, anemia; Rare: lymphadenopathy, lymphoma-like reaction, prothrombin decreased.
Metabolic and Nutritional:Infrequent: edema, gout, hypoglycemia, weight loss; Rare: alkaline phosphatase increased, diabetic ketoacidosis, lactic dehydrogenase increased.
Musculoskeletal:Infrequent: arthritis, arthralgia, myalgia, arthrosis, leg cramps, myasthenia; Rare: shin bone pain, joint disorder, tendon disorder.
Nervous System:Frequent: condusion, depression; Infrequent: vertigo, nervousness, paresthesia, insomnia, neuropathy, libido decreased, anxiety, depersonalization, reflexes decreased, speech disorder, abnormal dreams, dysarthria, emotional lability, nystagmus, stupor, circumoral paresthesia, euphoria, hyperesthesia, hypokinesia; Rare: agitation, hypertonia, libido increased, movement disorder, myoclonus, vestibular disorder.
Respiratory System:Infrequent: cough increased, bronchitis, rhinitis, sinusitis, pneumonia, ashtma, lung disoder, epistxis; Rare: hemoptysis, voice alteration.
Skin and Appendages:Infrequent: pruritus, skin ulcer, dry skin, herpes zoster, skin disorder, fungal dermatitis, furunculosis, herpes simplex, psoriasis, sweating, urticaria, vesiculobullous rash; Rare: acne, hair disorder, maculopapular rash, nail disorder, skin carcinoma, skin discoloration, skin hypertrophy.
Special Senses:Infrequent: abnormal vision, ear pain, eye disorder, taste perversion, deafness; Rare: conjunctival hyperemia, diabetic retinopathy, eye pain, fundi with microhemorrhage, retinal vein thrombosis, taste loss.
Urogenital System:Infrequent: urinary tract infection, dysuria, impotence, urinary incontinence, vaginal moniliasis, breast pain, menstrual disorder, polyuria, urinary retention; Rare: cystitis, ejaculation abnormal, swollen penis, gynecomastia, nocturia, pyelonephritis, swollen scrotum, urinary frequency, urinary urgency, urine abnormality.
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
Controlled SubstanceAbuse
Dependence
OVERDOSAGE
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
Postherpetic Neuralgia
Epilepsy
Patients >12 years of age:The effective dose of Neurontin is 900 to 1800 mg/day and given in divided doses (three times a day) using 300 or 400 mg capsules, or 600 or 800 mg tablets. The starting dose is 300 mg three times a day. If necessary, the dose may be increased using 300 or 400 mg capsules, or 600 or 800 mg tablets three times a day up to 1800 mg/day. Dosages up to 2400 mg/day have been well tolerated in long-term clinical studies. Doses of 3600 mg/day have also been administered to a small number of patients for a relatively short duration, and have been well tolerated. The maximum time between doses in the TID schedule should not exceed 12 hours.
Pediatric Patients Age 3years:The starting dose should range from 10mg/kg/day in 3 divided doses, and the effective dose reached by upward titration over a period of approximately 3 days. The effective dose of Neurontin in patients 5 years of age and older is 25mg/kg/day and given in divided doses (three times a day). The effective dose in pediatric patients ages 3 and 4 years is 40 mg/kg/day and given in divided doses (three times a day) (seeCLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pediatric). Neurontin may be administered as the oral solution, capsule, or tablet, or using combinations of these formulations. Dosages up to 50 mg/kg/day have been well tolerated in a long-term clinical study. The maximum time interval between doses should not exceed 12 hours.
Dosage in Renal Impairment
TABLE 6. Neurontin Dosage Based on Renal Function
Renal Function
Creatinine Clearance
(mL/min) Total Daily Dose Range
(mg/day) Dose Regimen
(mg)*
*
Dosage in Elderly
HOW SUPPLIED
STORAGE AND HANDLING
Storage (Capsules)Store at 25 C(77F); excursion permitted to 15-30 C (59-86 F)[see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Storage (Tablets)
Store at 25 C(77 F); excursions permitted to 15-30 C (59-86 F)[see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Storage (Oral Solution)
Store refrigerated, 2-8 C(36-46 F)
MEDICATION GUIDE
What is the most important information I should know about NEURONTIN?
Do not stop taking NEURONTIN without first talking to your healthcare provider.
NEURONTIN can cause serious side effects including:
1.
Like other antiepileptic drugs, NEURONTIN may cause suicidal thoughts or actions in a very small number of people, about 1 in 500.
Call a healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
How can I watch for early symptoms of suicidal thoughts and actions?
Do not stop taking NEURONTIN without first talking to a healthcare provider.
2.
Changes in behavior and thinking- Using NEURONTIN in children 3 to 12 years of age can cause emotional changes, aggressive behavior, problems with concentration, restlessness, changes in school performance, and hyperactivity.
3.
NEURONTIN may cause a serious or life-threatening allergic reactionthat may affect your skin or other parts of your body such as your liver or blood cells. You may or may not have rash when you get this type of reaction. It may cause you to be hospitalized or to stop NEURONTIN. Call a healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
What is NEURONTIN?
Who should not take NEURONTIN?
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking NEURONTIN?
Before taking NEURONTIN, tell your healthcare provider if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take,including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
How should I take NEURONTIN?
What should I avoid while taking NEURONTIN?
What are the possible side effects of NEURONTIN?
The most common side effects of NEURONTIN include:
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store NEURONTIN?
Keep NEURONTIN and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of NEURONTIN
What are the ingredients in NEURONTIN?
Active ingredient:gabapentin
Inactive ingredients in the capsules:lactose, cornstarch, and talc.
Inactive ingredients in the tablets:poloxamer 407, copolyvidonum, cornstarch, magnesium stearate, hydroxypropyl cellulose, talc, candelilla wax, and purified water.
Inactive ingredients in the oral solution:glycerin, xylitol, purified water, and artificial flavor.
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION

Neurontingabapentin CAPSULE
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!