Metoprolol Tartrate
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- BOXED WARNING
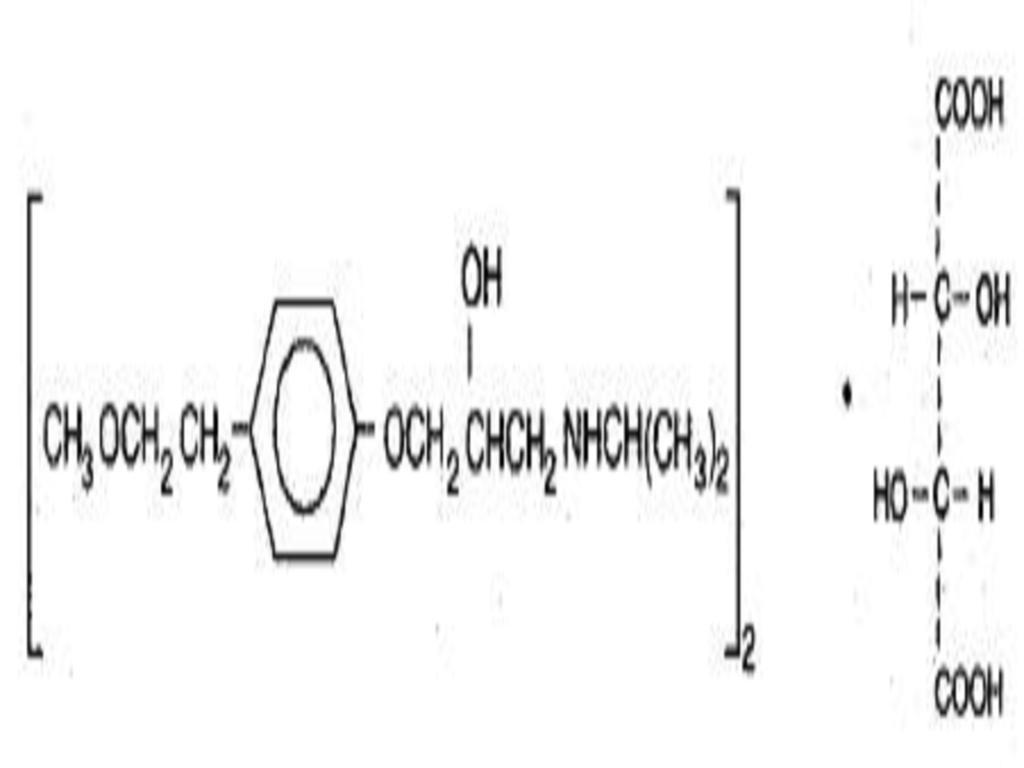
- METOPROLOL TARTRATE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- PHARMACOKINETICS
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
- METOPROLOL TARTRATE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
- PREGNANCY
- NURSING MOTHERS
- PEDIATRIC USE
- GERIATRIC USE
- METOPROLOL TARTRATE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- STORAGE AND HANDLING
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
BOXED WARNING
Ischemic Heart Disease: Following abrupt cessation of therapy with certain beta-blocking agents, exacerbations of angina pectoris and, in some cases, myocardial infarction have occurred. When discontinuing chronically administered metoprolol particularly in patients with ischemic heart disease, the dosage should be gradually reduced over a period of 1 to 2 weeks and the patient should be carefully monitored. If angina markedly worsens or acute coronary insufficiency develops, metoprolol administration should be reinstated promptly, at least temporarily, and other measures appropriate for the management of unstable angina should be taken. Patients should be warned against interruption or discontinuation of therapy without the physician's advice. Because coronary artery disease is common and may be unrecognized, it may be prudent not to discontinue metoprolol therapy abruptly even in patients treated only for hypertension.METOPROLOL TARTRATE DESCRIPTION
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
PHARMACOKINETICS
INDICATIONS & USAGE
HypertensionAngina Pectoris
Myocardial Infarction
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONCONTRAINDICATIONSWARNINGSDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
METOPROLOL TARTRATE CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypertension and AnginaWARNINGS
Myocardial Infarction
WARNINGS
WARNINGS
Hypertension and AnginaCardiac Failure:
In Patients Without a History of Cardiac Failure:
Ischemic Heart Disease:
Bronchospastic Diseases: PATIENTS WITH BRONCHOSPASTIC DISEASES SHOULD, IN GENERAL, NOT RECEIVE BETA BLOCKERS, including metoprolol. Because of its relative beta1 selectivity, however, metoprolol may be used with caution in patients with bronchospastic disease who do not respond to, or cannot tolerate, other antihypertensive treatment. Since beta1 selectivity is not absolute, a beta2-stimulating agent should be administered concomitantly, and the lowest possible dose of metoprolol tartrate should be used. In these circumstances it would be prudent initially to administer metoprolol in smaller doses three times daily, instead of larger doses two times daily, to avoid the higher plasma levels associated with the longer dosing interval. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
Major Surgery:
Diabetes and Hypoglycemia:
Pheochromocytoma:
Thyrotoxicosis:
Myocardial Infarction
Cardiac Failure:
Bradycardia:
AV Block:
Hypotension:
Bronchospastic Diseases: PATIENTS WITH BRONCHOSPASTIC DISEASES SHOULD, IN GENERAL, NOT RECEIVE BETA BLOCKERS, including metoprolol. Because of its relative beta1 selectivity, metoprolol may be used with extreme caution in patients with bronchospastic disease. Because it is unknown to what extent beta2-stimulating agents may exacerbate myocardial ischemia and the extent of infarction, these agents should not be used prophylactically. If bronchospasm not related to congestive heart failure occurs, metoprolol should be discontinued. A theophylline derivative or a beta2 agonist may be administered cautiously, depending on the clinical condition of the patient. Both theophylline derivatives and beta2 agonists may produce serious cardiac arrhythmias.
PRECAUTIONS
GeneralINFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Risk of Anaphylactic Reaction:
General Anesthetics
WARNINGS, Major Surgery
CYP2D6 Inhibitors
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYPharmacokinetics section
Clonidine
CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
PREGNANCY
NURSING MOTHERS
PEDIATRIC USE
GERIATRIC USE
METOPROLOL TARTRATE ADVERSE REACTIONS
Hypertension and AnginaCentral Nervous System:
Cardiovascular:CONTRAINDICATIONSWARNINGSPRECAUTIONS
Respiratory:WARNINGS
Gastrointestinal:
Hypersensitive Reactions:
Miscellaneous:
Myocardial Infarction
Central Nervous System:
Cardiovascular:CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Respiratory:
Gastrointestinal:
Dermatologic:
Miscellaneous:
Potential Adverse Reactions
Central Nervous System:
Cardiovascular:CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hematologic:
Hypersensitive Reactions:
Post-Marketing Experience
OVERDOSAGE
Acute ToxicitySigns and Symptoms
Treatment
WARNINGSMyocardial Infarction
Elimination of the Drug:
Bradycardia
Hypotension:
Bronchospasm:
Cardiac Failure:
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
HypertensionAngina Pectoris
Myocardial Infarction
Early Treatment:
Late Treatment:
HOW SUPPLIED
STORAGE AND HANDLING
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION

PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Metoprolol TartrateMetoprolol Tartrate TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!