ibuprofen
Ibuprofen Tablets, USP 400mg, 600mg and 800mg
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- IBUPROFEN DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- IBUPROFEN INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- IBUPROFEN CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- IBUPROFEN ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- IBUPROFEN DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Cardiovascular Risk
- NSAIDs may cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may increase with duration of use. Patients with cardiovascular disease or risk factors for cardiovascular disease may be at greater risk (See WARNINGS ).
- IBUPROFEN tablets are contraindicated for treatment of peri-operative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (see WARNINGS ).
Gastrointestinal Risk
- NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients are at greater risk for serious gastrointestinal events. (See
WARNINGS
)
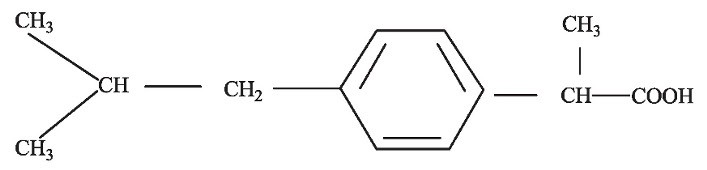
IBUPROFEN DESCRIPTION
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
ADVERSE REACTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS
IBUPROFEN INDICATIONS AND USAGE
WARNINGS
IBUPROFEN CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS, Anaphylactoid Reactions, PRECAUTIONS, Preexisting Asthma
WARNINGS
WARNINGS
CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTSCardiovascular Thrombotic EventsWARNINGS
CONTRAINDICATIONS Hypertension
Congestive Heart Failure and Edema
Gastrointestinal Effects - Risk of Ulceration, Bleeding, and Perforation
prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or gastrointestinal bleedingRenal Effects
Advanced Renal Disease
Anaphylactoid Reactions
CONTRAINDICATIONS PRECAUTIONS, Preexisting Asthma Skin Reactions
Pregnancy
PRECAUTIONS
GeneralHepatic effects
Hematological effects
Preexisting asthma
Ophthalmological effects
Aseptic Meningitis
Information for Patients
- IBUPROFEN tablets like other NSAIDs, may cause serious CV side effects, such as MI or stroke, which may result in hospitalization and even death. Although serious CV events can occur without warning symptoms, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness, slurring of speech, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative sign or symptoms. Patients should be apprised of the importance of this follow-up (see WARNINGS, Cardiovascular Effects ).
- IBUPROFEN tablets, like other NSAIDs, can cause GI discomfort and, rarely, serious GI side effects, such as ulcers and bleeding, which may result in hospitalization and even death. Although serious GI tract ulcerations and bleeding can occur without warning symptoms, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of ulcerations and bleeding, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative signs or symptoms including epigastric pain, dyspepsia, melena, and hematemesis. Patients should be apprised of the importance of this follow-up (see WARNINGS, Gastrointestinal Effects-Risk of Ulceration, Bleeding and Perforation ).
- IBUPROFEN tablets, like other NSAIDs, can cause serious skin side effects such as exfoliative dermatitis, SJS and TEN, which may result in hospitalization and even death. Although serious skin reactions may occur without warning, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of skin rash and blisters, fever, or other signs hypersensitivity such as itching, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative sign or symptoms. Patients should be advised to stop the drug immediately if they develop any type of rash and contact their physicians as soon as possible.
- Patients should promptly report signs or symptoms of unexplained weight gain or edema to their physicians.
- Patients should be informed of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pruritus, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness and “flu-like” symptoms). If these occur, patients should be instructed to stop therapy and seek immediate medical therapy.
- Patients should be informed of the signs of an anaphylactoid reaction (e.g. difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat). If these occur, patients should be instructed to seek immediate emergency help (see WARNINGS ).
- In late pregnancy, as with other NSAIDs, IBUPROFEN tablets should be avoided because it may cause premature closure of the ductus arteriosus.
Laboratory Tests
Drug Interactions
ACE-inhibitors:
Aspirin
Diuretics
WARNINGS, Renal Effects
Lithium
Methotrexate
Warfarin-type anticoagulants
H-2 Antagonists
Pregnancy
Teratogenic effects: Pregnancy Category C
Nonteratogenic effects
Labor and Delivery
Nursing Mothers
Pediatric Use
Geriatric Use
IBUPROFEN ADVERSE REACTIONS
|
Incidence Greater than 1%
(but less than 3%) Probable Causal Relationship |
Precise Incidence Unknown
(but less than 1%) Probable Causal Relationship** |
Precise Incidence Unknown
(but less than 1%) Causal Relationship Unknown** |
| GASTROINTESTINAL Nausea*, epigastric pain*, heartburn*, diarrhea, abdominal distress, nausea and vomiting, indigestion, constipation, abdominal cramps or pain, fullness of GI tract (bloating and flatulence) |
Gastric or duodenal ulcer with bleeding and/or perforation, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, melena, gastritis, hepatitis, jaundice, abnormal liver function tests; pancreatitis |
|
| CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Dizziness*, headache, nervousness |
Depression, insomnia, confusion, emotional lability, somnolence, aseptic meningitis with fever and coma (See PRECAUTIONS) |
Paresthesias, hallucinations, dream abnormalities, pseudo-tumor cerebri |
| DERMATOLOGIC Rash* (including maculopapular type), pruritus |
Vesiculobullous eruptions, urticaria, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, alopecia |
Toxic epidermal necrolysis, photoallergic skin reactions |
| SPECIAL SENSES Tinnitus |
Hearing loss, amblyopia (blurred and/or diminished vision, scotomata and/or changes in color vision) (see PRECAUTIONS) |
Conjunctivitis, diplopia, optic neuritis, cataracts |
| Conjunctivitis, diplopia, optic neuritis, cataracts |
Neutropenia, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, hemolytic anemia (sometimes Coombs positive), thrombocytopenia with or without purpura, eosinophilia, decreases in hemoglobin and hematocrit (see PRECAUTIONS) |
Bleeding episodes (eg epistaxis, menorrhagia) |
| METABOLIC/ENDOCRINE Decreased appetite |
|
Gynecomastia, hypoglycemic reaction, acidosis |
| CARDIOVASCULAR Edema, fluid retention (generally responds promptly to drug discontinuation) (see PRECAUTIONS) |
Congestive heart failure in patients with marginal cardiac function, elevated blood pressure, palpitations |
Arrhythmias (sinus tachycardia, sinus bradycardia) |
| ALLERGIC |
Syndrome of abdominal pain, fever, chills, nausea and vomiting; anaphylaxis; bronchospasm (see CONTRAINDICATIONS) |
Serum sickness, lupus erythematosus syndrome. Henoch-Schonlein vasculitis, angioedema |
| RENAL |
Acute renal failure (see PRECAUTIONS), decreased creatinine clearance, polyuria, azotemia, cystitis, Hematuria |
Renal papillary necrosis |
| MISCELLANEOUS |
Dry eyes and mouth, gingival ulcer, rhinitis |
|
| * Reactions occurring in 3% to 9% of patients treated with IBUPROFEN tablets. (Those reactions occurring in less than 3% of the patients are unmarked.) ** Reactions are classified under “Probable Causal Relationship (PCR)” if there has been one positive rechallenge or if three or more cases occur which might be causally related. Reactions are classified under “Causal Relationship Unknown” if seven or more events have been reported but the criteria for PCR have not been met. |
|
|
OVERDOSAGE
IBUPROFEN DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
WARNINGSRheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, including flare-ups of chronic disease:
Suggested Dosage:
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
In chronic conditions
Mild to moderate pain:
Dysmenorrhea:
HOW SUPPLIED

Medication Guide
for
What is the most important information I should know about medicines called Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
NSAID medicines may increase the chance of a heart attack or stroke that can lead to death.
NSAID medicines should never be used right before or after a heart surgery called a
NSAID medicines can cause ulcers and bleeding in the stomach and intestines at any time during treatment.
Ulcers and bleeding:
The chance of a person getting an ulcer or bleeding increases with:
NSAID medicines should only be used:
What are Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
Who should not take a Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug (NSAID)?
Do not take an NSAID medicine:
Tell your healthcare provider:
What are the possible side effects of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
|
Serious side effects include:
|
Other side effects include: |
| • heart attack • stroke • high blood pressure • heart failure from body swelling (fluid retention) • kidney problems including kidney failure • bleeding and ulcers in the stomach and intestine • low red blood cells (anemia) • life-threatening skin reactions • life-threatening allergic reactions • liver problems including liver failure • asthma attacks in people who have asthma |
• stomach pain • constipation • diarrhea • gas • heartburn • nausea • vomiting • dizziness |
Stop your NSAID medicine and call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
Other information about Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAID medicines that need a prescription
|
Generic Name |
Tradename |
| Celecoxib |
Celebrex |
| Diclofenac |
Cataflam, Voltaren, Arthrotec (combined with misoprostol) |
| Diflunisal |
Dolobid |
| Etodolac |
Lodine, Lodine XL |
| Fenoprofen |
Nalfon, Nalfon 200 |
| Flurbirofen |
Ansaid |
| Ibuprofen |
Motrin, Tab-Profen, *Vicoprofen (combined with hydrocodone), Combunox (combined with oxycodone) |
| Indomethacin |
Indocin, Indocin SR, Indo-Lemmon, Indomethagan |
| Ketoprofen |
Oruvail |
| Ketorolac |
Toradol |
| Mefenamic Acid |
Ponstel |
| Meloxicam |
Mobic |
| Nabumetone |
Relafen |
| Naproxen |
Naprosyn, Anaprox, Anaprox DS, EC-Naproxyn, Naprelan, Naprapac (copackaged with lansoprazole) |
| Oxaprozin |
Daypro |
| Piroxicam |
Feldene |
| Sulindac |
Clinoril |
| Tolmetin |
Tolectin, Tolectin DS, Tolectin 600 |
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
ASCEND
Laboratories, LLC
NDC 67877-119-05
IBUPROFEN
TABLETS, USP
400 mg
Rx Only
500 Tablets

ASCEND
Laboratories, LLC
NDC 67877-120-05
IBUPROFEN
TABLETS, USP
600 mg
Rx Only
500 Tablets

ASCEND
Laboratories, LLC
NDC 67877-121-05
IBUPROFEN
TABLETS, USP
800 mg
Rx Only
500 Tablets

ibuprofenibuprofen TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ibuprofenibuprofen TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ibuprofenibuprofen TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||