Entre-S
Brookstone Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Entre-S Suspension
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- ENTRE-S DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- INDICATIONS
- ENTRE-S CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- ENTRE-S ADVERSE REACTIONS
- DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
- OVERDOSAGE
- ENTRE-S DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 473 mL Label
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Antitussive • Decongestant
• Antihistamine
Rx Only
ENTRE-S DESCRIPTION
Each teaspoonful (5 mL) of Entre-S Suspension contains:
| Dextromethorphan Hydrobromide | 30 mg |
| Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride | 30 mg |
| Chlorpheniramine Maleate | 4 mg |
Entre-S Suspension is used for oral administration only.
Entre-S Suspension contains the following inactive ingredients: Propylene Glycol, Glycerin, Tannic Acid, Magnesium Aluminum Silicate, Xanthan Gum, Saccharin Sodium, Bubblegum Flavor, Sodium Citrate, Citric Acid, Natural Masking Flavor, Grape Flavor, Red Dye, Benzoic Acid, Methyl Paraben, Propyl Paraben, and Purified Water.
Dextromethorphan Hydrobromide is a cough suppressant with the chemical name: Morphinan, 3-methoxy-17-methyl-(9α, 13α, 14α)-, hydrobromide, monohydrate. Its structure is as follows:
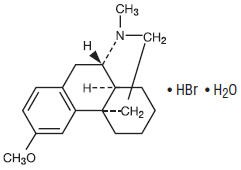
|
|
| C18H25NO • HBr • H2O | M.W. 370.32 |
Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride is a nasal decongestant with the chemical name: Benzenemethanol, α-[1-(methylamino)ethyl]-, [S-(R*,R*)-, hydrochloride. Its structure is as follows:
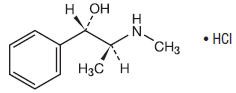
|
|
| C10H15NO • HCl | M.W. 201.69 |
Chlorpheniramine Maleate is an antihistamine having the chemical name: 2-Pyridinepropanamine, γ-(4-chlorphenyl)-N,N-dimethyl-, (Z)-2-butenedioate (1:1). , and has the following structural formula:
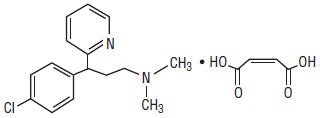
|
|
| C16H19ClN2 • C4H4O4 | M.W. 390.86 |
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Dextromethorphan is an antitussive agent which, unlike the isomeric levorphanol, has no analgesic or addictive properties. The drug acts centrally and elevates the threshold for coughing. It is about equal to codeine in depressing the cough reflex. In therapeutic dosage, dextromethorphan does not inhibit ciliary activity. Dextromethorphan is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, metabolized by the liver and excreted primarily in the urine.
Pseudoephedrine is an α-adrenergic receptor antagonist (sympathomimetic) which produces vasoconstriction by stimulating α-receptors within the mucosa of the respiratory tract. Clinically, pseudoephedrine shrinks swollen mucous membranes, reduces tissue hyperemia, edema, and nasal congestion, and increases nasal airway patency. The vasoconstriction action of pseudoephedrine is similar to that of ephedrine. In the usual dose it has minimal vasopressor effects. Pseudoephedrine is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Acidic urine is associated with faster elimination of the drug. The drug is distributed to body tissues and fluids, including the fetal tissue, breast milk and the central nervous system (CNS).
Chlorpheniramine is an alkylamine-type antihistamine. The antihistamine in Entre-S Suspension acts by competing with histamine for H1 histamine receptor sites, thereby preventing the action of histamine on the cell. Clinically, chlorpheniramine suppresses the histamine-mediated symptoms of allergic rhinitis, relieving sneezing, rhinorrhea, and itching of the eyes, nose, and throat.
INDICATIONS
Entre-S Suspension is indicated for temporary relief of nasal congestion and cough associated with respiratory tract infections and related conditions such as sinusitis, pharyngitis, bronchitis, and asthma, when these conditions are complicated by tenacious mucus and/or mucous plugs and congestion. Entre-S Suspension is effective in a productive as well as a nonproductive cough, but is of particular value in a dry nonproductive cough which tends to injure the mucous membrane of the air passages.
ENTRE-S CONTRAINDICATIONS
Entre-S Suspension is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to chlorpheniramine, dextromethorphan, or with hypersensitivity or idiosyncrasy to sympathomimetic amines which may be manifested by insomnia, dizziness, weakness, tremor or arrhythmias. Sympathomimetic amines are contraindicated in patients with severe hypertension, severe coronary artery disease, and patients that are now taking a prescription monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) (certain drugs for depression, psychiatric, or emotional conditions, or Parkinson's disease), or for two weeks after stopping the MAOI drug. This product is contraindicated in women who are pregnant or nursing.
WARNINGS
Do not take this product for persistent or chronic cough such as occurs with smoking, asthma, chronic bronchitis, or emphysema, or where cough is accompanied by excessive phlegm (mucus) unless directed by a doctor. Sympathomimetic amines should be used with caution in patients with hypertension, ischemic heart disease, diabetes mellitus, increased intraocular pressure, hyperthyroidism, or prostatic hypertrophy. Sympathomimetics may produce central nervous system stimulation with convulsions or cardiovascular collapse with accompanying hypotension. Nervousness, dizziness or sleeplessness may occur at higher doses.
Hypertensive crises can occur with concurrent use of pseudoephedrine and MAOI, indomethacin, or with beta blockers and methyldopa. If a hypertensive crisis occurs, these drugs should be discontinued immediately and therapy to lower blood pressure should be instituted. Fever should be managed by means of external cooling. Do not exceed recommended dosage.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Before prescribing medication to suppress or modify cough, it is important that the underlying cause of cough is identified, that modification of cough does not increase the risk of clinical or physiologic complications, and that appropriate therapy for the primary disease is instituted. Check with physician if cough persists after medication has been used for seven days or if high fever, skin rash, or continued headache, or sore throat is present with cough. Caution should be exercised in patients with high blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes mellitus, or thyroid disease. Dextromethorphan should be used with caution in sedated or debilitated patients, and in patients confined to the supine position. Administration of dextromethorphan may be accompanied by histamine release and should be used with caution in atopic children. The antihistamine in Entre-S Suspension may exhibit additive effects with CNS depressants, including alcohol.
Information for Patients
Patient consultation should include the following information regarding proper use of Entre-S Suspension:
- Entre-S Suspension may be taken with food to minimize gastric irritation.
- Do not take MAOI while taking Entre-S Suspension.
- Keep all medications out of the reach of children. In case of accidental overdose, seek professional assistance or contact a poison control center immediately.
- Antihistamines may impair mental and physical abilities required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks, such as driving a vehicle or operating machinery.
Drug Interactions
- MAOI and tricyclic antidepressants may prolong and intensify the anticholinergic (drying) effects of antihistamines.
- Beta-adrenergic blockers and MAOI may potentiate the pressor effect of pseudoephedrine.
- Concurrent use of digitalis glycosides may increase the possibility of cardiac arrhythmias.
- Sympathomimetics may reduce the hypotensive effects of guanethidine, mecamylamine, methyldopa, reserpine and veratrum alkaloids.
- Concurrent use of tricyclic antidepressants may antagonize the effects of pseudoephedrine.
- Concomitant use of antihistamines with alcohol, tricyclic antidepressants, barbiturates, and other CNS depressants may have an additive effect.
Laboratory Test Interactions
The in vitro addition of pseudoephedrine to sera containing the cardiac isoenzyme MB of serum creatine phosphokinase progressively inhibits the activity of the enzyme. The inhibition becomes complete over six hours.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No data is available on the long-term potential of the components of Entre-S Suspension for carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, or impairment of fertility in animals or humans.
Pregnancy
Category C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Entre-S Suspension. It is also not known if Entre-S Suspension can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity.
Nursing Mothers
Pseudoephedrine is excreted in breast milk. Use of Entre-S Suspension by nursing mothers is not recommended because of the higher-than-usual risk for infants from sympathomimetic amines.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of Entre-S Suspension in pediatric patients under the age of two years have not been established. Pseudoephedrine may be more likely to cause side effects in infants, especially newborn and premature infants, than in older children and adults. No age specific problems related to dextromethorphan or chlorpheniramine have been documented in the pediatric population to date.
Geriatric Use
(Ages 65 and older) Geriatric patients taking sympathomimetics may be more likely to experience confusion, hallucinations, seizures, and central nervous system CNS depression. Geriatric patients may also be more sensitive to the effects, especially to the vasopressor effects, of sympathomimetic amines.
ENTRE-S ADVERSE REACTIONS
Pseudoephedrine may cause mild central nervous system stimulation, especially in those patients who are hypersensitive to sympathomimetic drugs. Nervousness, excitability, restlessness, dizziness, weakness and insomnia may also occur. Headache and drowsiness have also been reported. Large doses may cause lightheadedness, nausea and/or vomiting. Sympathomimetics have been associated with certain untoward reactions including fear, anxiety, nervousness, restlessness, tremor, weakness, pallor, respiratory difficulty, dysuria, insomnia, hallucinations, convulsions, CNS depression, arrhythmias, and cardiovascular collapse with hypotension. Adverse effects associated with dextromethorphan are generally infrequent and mild. Products containing dextromethorphan have been associated with nausea, dizziness, fatigue, gastrointestinal disturbances, and skin eruptions.
Chlorpheniramine may cause slight to moderate drowsiness and is the most frequent side effect. Other possible side effects of antihistamines include:
General: Urticaria, drug rash, anaphylactic shock, photosensitivity, excessive perspiration, chills, dryness of mouth, nose and throat;
Cardiovascular: Hypotension, headache, palpitation, tachycardia, extra systoles;
Hematological: Hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis;
CNS: Sedation, dizziness, disturbed coordination, fatigue, confusion, restlessness, excitation, nervousness, tremor, irritability, insomnia, euphoria, paresthesia, blurred vision, diplopia, vertigo, tinnitus, hysteria, neuritis, convulsion;
Gastrointestinal: Epigastric distress, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation;
Genitourinary: Urinary frequency, difficult urination, urinary retention, early menses;
Respiratory: Thickening of bronchial secretions, tightness of chest, wheezing and nasal stuffiness.
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
Pseudoephedrine, like other CNS stimulants, has been abused. At high doses, subjects commonly experience an elevation of mood, a sense of increased energy and alertness, and decreased appetite. Some individuals become anxious, irritable, and loquacious. In addition to the marked euphoria, the user experiences a sense of markedly enhanced physical strength and mental capacity. With continued use, tolerance develops, the user increases the dose and toxic signs and symptoms appear. Depression may follow rapid withdrawal. Narcotic antitussives and stimulants, such as pseudoephedrine, are banned and tested for by the U.S. Olympic Committee (USOC) and the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA).
OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage with pseudoephedrine may manifest itself as excessive CNS stimulation resulting in excitement, tremor, restlessness, and insomnia. Other effects may include tachycardia, hypertension, pallor, mydriasis, hyperglycemia and urinary retention. Severe overdosage may cause tachypnea or hyperpnea, hallucinations, convulsions or delirium, but in some individuals there may be CNS depression with somnolence, stupor or respiratory depression. Arrhythmias (including ventricular fibrillation) may lead to hypotension and circulatory collapse. Severe hypokalemia can occur, probably due to a compartmental shift rather than a depletion of potassium. No organ damage or significant metabolic derangement is associated with pseudoephedrine overdosage. Overdose with dextromethorphan include CNS effects as most prevalent, such as psychosis, hallucinations, mania, seizures, ataxia, dizziness, and psychological dependence. Urinary retention and tachycardia have also been reported. Very high doses may lead to respiratory depression coma/unconsciousness, and cyanosis. Manifestations of antihistamine overdosage may vary from CNS depression (sedation, apnea, cardiovascular collapse) to stimulation (insomnia, hallucinations, tremors or convulsions). Other signs and symptoms may be dizziness, tinnitus, ataxia, blurred vision, and hypotension. Stimulation is particularly likely in children, as are atropine-like signs and symptoms (dry mouth; fixed, dilated pupils; flushing; hyperthermia and gastrointestinal symptoms).
Treatment
In the event of overdosage, emergency treatment should be started immediately. Treatment of overdosage should be directed toward reducing further absorption and supporting the patient for at least that length of time. Gastric emptying (Syrup of Ipecac) and/or lavage is recommended as soon as possible after ingestion, even if the patient has vomited spontaneously. Either isotonic or half-isotonic saline may be used for lavage. Administration of an activated charcoal slurry is beneficial after lavage and/or emesis if less than four hours have passed since ingestion. Saline cathartics, such as Milk of Magnesia, are useful for hastening the evacuation of unreleased medication. Adrenergic receptor blocking agents are antidotes to pseudoephedrine. In practice, the most useful is the beta-blocker propanolol, which is indicated when there are signs of cardiac toxicity.
In severe cases of overdosage, it is essential to monitor both the heart (by electrocardiograph) and plasma electrolytes, and to give intravenous potassium as indicated. Vasopressors may be used to treat hypotension. Excessive CNS stimulation may be counteracted with parenteral diazepam. Stimulants should not be used. Hyperpyrexia, especially in children, may require treatment with tepid water sponge baths or a hyperthermic blanket. Apnea is treated with ventilatory support.
ENTRE-S DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Adults and children over age 12
1 – 2 teaspoonsful every 6 to 8 hours.
Children ages 6 to 12
1/2 teaspoonful every 6 to 8 hours.
Children ages 6 and under
As directed by a physician.
HOW SUPPLIED
Entre-S Suspension is a red, grape bubblegum flavored suspension. Available in 16 fl. oz. (473 mL) NDC 42192-514-16.
Dispense in a well closed, light-resistant container. Store at controlled room temperature, 20°–25°C (68°– 77°F).
All prescription substitutions and/or recommendations using this product shall be made subject to state and federal statutes as applicable. Please note: this is not an Orange Book product and has not been subjected to FDA therapeutic equivalency or other equivalency testing. Each person recommending a prescription substitution using this product shall make such recommendations based on each such person's professional opinion and knowledge, upon evaluating the active ingredients, excipients, inactive ingredients and chemical information provided herein.
Shake well before use.
WARNING
KEEP THIS AND ALL MEDICATIONS OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN. IN CASE OF ACCIDENTAL OVERDOSE, SEEK PROFESSIONAL ASSISTANCE OR CONTACT A POISON CONTROL CENTER IMMEDIATELY.
Manufactured for:
Acella Pharmaceuticals, LLC.
9005 Westside Parkway
Alpharetta, GA 30009
Utilizing Neuvosyn ™ Technology
PI389
Rev. 10/09
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 473 mL Label
NDC 42192-514-16
Entre-S
Suspension
16 fl oz. (473 mL)
Rx Only
Antitussive • Decongestant • Antihistamine
Grape Bubblegum Flavor
| Each teaspoonful (5 mL) Contains: | |
| Dextromethorphan Hydrobromide | 30 mg |
| Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride | 30 mg |
| Chlorpheniramine Maleate | 4 mg |
SHAKE WELL
Acella
PHARMACEUTICALS, LLC

Entre-SDextromethorphan Hydrobromide, Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride and Chlorpheniramine Maleate SYRUP
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||