Amlodipine Besylate
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use amlodipine besylate tablets, USP safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for amlodipine besylate tablets, USP. Amlodipine besylate tablets, USP for oral administrationInitial U.S. Approval: 1987 INDICATIONS AND USAGEAmlodipine besylate tablets,USP is a calcium channel blocker and may be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive and antianginal agents for the treatment of:•Hypertension (1.1) Amlodipine besylate tablets,USP is indicated for the treatment of hypertension, to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions. • Coronary Artery Disease (1.2) Chronic Stable Angina Vasospastic Angina (Prinzmetal’s or Variant Angina) Angiographically Documented Coronary Artery Disease in patients without heart failure or an ejection fraction < 40% DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Adult recommended starting dose: 5 mg once daily with maximum dose 10 mg once daily. (2.1) Small, fragile, or elderly patients, or patients with hepatic insufficiency may be started on 2.5 mg once daily. (2.1) Pediatric starting dose: 2.5 mg to 5 mg once daily. (2.2) Important Limitation: 2.2DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS 2.5 mg, 5 mg, and 10 mg Tablets (3) CONTRAINDICATIONS Known sensitivity to amlodipine (4) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS• Symptomatic hypotension is possible, particularly in patients with severe aortic stenosis. However, acute hypotension is unlikely. (5.1) • Worsening angina and acute myocardial infarction can develop after starting or increasing the dose of Amlodipine besylate tablets,USP, particularly in patients with severe obstructive coronary artery disease. (5.2) • Titrate slowly in patients with severe hepatic impairment. (5.3) Side EffectsMost common adverse reaction to amlodipine is edema which occurred in a dose related manner. Other adverse experiences not dose related but reported with an incidence >1.0% are fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, and somnolence. (6) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Ascend Laboratories, LLC at 1-877-ASC-RX01 (877-272-7901) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch DRUG INTERACTIONS Do not exceed doses greater than 20 mg daily of simvastatin. (7.7) USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Pregnancy: Use only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk. (8.1) Nursing: Discontinue when administering amlodipine besylate. (8.3) Pediatric: Effect on patients less than 6 years old is not known. (8.4) Geriatric: Start dosing at the low end of the dose range. (8.5)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- 1 INDICATIONS & USAGE
- 2 DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS
- 4 AMLODIPINE BESYLATE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 6 AMLODIPINE BESYLATE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 AMLODIPINE BESYLATE DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 2.5 mg Tablets
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5 mg Tablets
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg Tablets
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS & USAGE
1.1 Hypertension
Amlodipine besylate tablets,USP is indicated for the treatment of hypertension, to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions. These benefits have been seen in controlled trials of antihypertensive drugs from a wide variety of pharmacologic classes including Amlodipine besylate tablets,USP .
Control of high blood pressure should be part of comprehensive cardiovascular risk management, including, as appropriate, lipid control, diabetes management, antithrombotic therapy, smoking cessation, exercise, and limited sodium intake. Many patients will require more than one drug to achieve blood pressure goals. For specific advice on goals and management, see published guidelines, such as those of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program’s Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC).
Numerous antihypertensive drugs, from a variety of pharmacologic classes and with different mechanisms of action, have been shown in randomized controlled trials to reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, and it can be concluded that it is blood pressure reduction, and not some other pharmacologic property of the drugs, that is largely responsible for those benefits. The largest and most consistent cardiovascular outcome benefit has been a reduction in the risk of stroke, but reductions in myocardial infarction and cardiovascular mortality also have been seen regularly.
Elevated systolic or diastolic pressure causes increased cardiovascular risk, and the absolute risk increase per mmHg is greater at higher blood pressures, so that even modest reductions of severe hypertension can provide substantial benefit. Relative risk reduction from blood pressure reduction is similar across populations with varying absolute risk, so the absolute benefit is greater in patients who are at higher risk independent of their hypertension (for example, patients with diabetes or hyperlipidemia), and such patients would be expected to benefit from more aggressive treatment to a lower blood pressure goal.
Some antihypertensive drugs have smaller blood pressure effects (as monotherapy) in black patients, and many antihypertensive drugs have additional approved indications and effects (e.g., on angina, heart failure, or diabetic kidney disease). These considerations may guide selection of therapy.
Amlodipine besylate tablets,USP may be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents.
1.2 Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Chronic Stable Angina
Vasospastic Angina (Prinzmetal’s or Variant Angina)
Angiographically Documented CAD
2 DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Adults
The usual initial antihypertensive oral dose of Amlodipine besylate tablets,USP is 5 mg once daily, and the maximum dose is 10 mg once daily.
Small, fragile, or elderly patients, or patients with hepatic insufficiency may be started on 2.5 mg once daily and this dose may be used when adding Amlodipine besylate tablets,USP to other antihypertensive therapy.
Adjust dosage according to blood pressure goals. In general, wait 7 to 14 days between titration steps. Titrate more rapidly, however, if clinically warranted, provided the patient is assessed frequently.
Angina: The recommended dose for chronic stable or vasospastic angina is 5 to 10 mg, with the lower dose suggested in the elderly and in patients with hepatic insufficiency. Most patients will require 10 mg for adequate effect.
Coronary artery disease: The recommended dose range for patients with coronary artery disease is 5 to 10 mg once daily. In clinical studies, the majority of patients required 10 mg [see Clinical Studies (14.4)].
2.2 Children
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4), Clinical Studies (14.1)]
3 DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypotension
Symptomatic hypotension is possible, particularly in patients with severe aortic stenosis. Because of the gradual onset of action, acute hypotension is unlikely.
5.2 Increased Angina or Myocardial Infarction
Worsening angina and acute myocardial infarction can develop after starting or increasing the dose of Amlodipine besylate tablets, particularly in patients with severe obstructive coronary artery disease.
5.3 Patients with Hepatic Failure
Because amlodipine is extensively metabolized by the liver and the plasma elimination half-life (t 1/2) is 56 hours in patients with impaired hepatic function, titrate slowly when administering amlodipine to patients with severe hepatic impairment.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
| 2.5mg N=275 |
Amlodipine 5mg N=296 |
10mg N=268 |
Placebo N=520 |
|
| Edema |
1.8 |
3.0 |
10.8 |
0.6 |
| Dizziness |
1.1 |
3.4 |
3.4 |
1.5 |
| Flushing |
0.7 |
1.4 |
2.6 |
0.0 |
| Palpitation |
0.7 |
1.4 |
4.5 |
0.6 |
Other adverse reactions that were not clearly dose related but were reported with an incidence greater than 1.0% in placebo-controlled clinical trials include the following:
| |
Amlodipine (%) (N=1730) |
Placebo (%) (N=1250) |
| Fatigue |
4.5 |
2.8 |
| Nausea |
2.9 |
1.9 |
| Abdominal pain |
1.6 |
0.3 |
| Somnolence |
1.4 |
0.6 |
For several adverse experiences that appear to be drug and dose related, there was a greater incidence in women than men associated with amlodipine treatment as shown in the following table:
| |
Amlodipine |
Placebo |
||
| |
Male=% (N=1218) |
Female=% (N=512) |
Male=% (N=914) |
Female=% (N=336) |
| Edema |
5.6 |
14.6 |
1.4 |
5.1 |
| Flushing |
1.5 |
4.5 |
0.3 |
0.9 |
| Palpitations |
1.4 |
3.3 |
0.9 |
0.9 |
| Somnolence |
1.3 |
1.6 |
0.8 |
0.3 |
The following events occurred in <1% but >0.1% of patients in controlled clinical trials or under conditions of open trials or marketing experience where a causal relationship is uncertain; they are listed to alert the physician to a possible relationship:
Cardiovascular: arrhythmia (including ventricular tachycardia and atrial fibrillation), bradycardia, chest pain, peripheral ischemia, syncope, tachycardia, vasculitis.
Central and Peripheral Nervous System: hypoesthesia, neuropathy peripheral, paresthesia, tremor, vertigo.
Gastrointestinal: anorexia, constipation, dysphagia, diarrhea, flatulence, pancreatitis, vomiting, gingival hyperplasia.
General: allergic reaction, asthenia,1 back pain, hot flushes, malaise, pain, rigors, weight gain, weight decrease.
Musculoskeletal System: arthralgia, arthrosis, muscle cramps,1 myalgia.
Psychiatric: sexual dysfunction (male1 and female), insomnia, nervousness, depression, abnormal dreams, anxiety, depersonalization.
Respiratory System: dyspnea,1 epistaxis.
Skin and Appendages: angioedema, erythema multiforme, pruritus,1 rash,1 rash erythematous, rash maculopapular.
Special Senses: abnormal vision, conjunctivitis, diplopia, eye pain, tinnitus.
Urinary System: micturition frequency, micturition disorder, nocturia.
Autonomic Nervous System: dry mouth, sweating increased.
Metabolic and Nutritional: hyperglycemia, thirst.
Hemopoietic: leukopenia, purpura, thrombocytopenia.
1 These events occurred in less than 1% in placebo-controlled trials, but the incidence of these side effects was between 1% and 2% in all multiple dose studies.
Amlodipine besylate tablets,USP therapy has not been associated with clinically significant changes in routine laboratory tests. No clinically relevant changes were noted in serum potassium, serum glucose, total triglycerides, total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, uric acid, blood urea nitrogen, or creatinine.
In the CAMELOT and PREVENT studies [see Clinical Studies (14.4)], the adverse event profile was similar to that reported previously (see above), with the most common adverse event being peripheral edema.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The following postmarketing event has been reported infrequently where a causal relationship is uncertain: gynecomastia. In postmarketing experience, jaundice and hepatic enzyme elevations (mostly consistent with cholestasis or hepatitis), in some cases severe enough to require hospitalization, have been reported in association with use of amlodipine.
Amlodipine has been used safely in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, well-compensated congestive heart failure, coronary artery disease, peripheral vascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and abnormal lipid profiles.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 In Vitro Data
In vitro
7.2 Cimetidine
Co-administration of amlodipine with cimetidine did not alter the pharmacokinetics of amlodipine .
7.3 Grapefruit Juice
Co-administration of 240 mL of grapefruit juice with a single oral dose of amlodipine 10 mg in 20 healthy volunteers had no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of amlodipine.
7.4 Magnesium and Aluminum Hydroxide Antacid
Co-administration of a magnesium and aluminum hydroxide antacid with a single dose of amlodipine had no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of amlodipine .
7.5 Sildenafil
A single 100 mg dose of sildenafil in subjects with essential hypertension had no effect on the pharmacokinetic parameters of amlodipine . When amlodipine and sildenafil were used in combination, each agent independently exerted its own blood pressure lowering effect.
7.6 Atorvastatin
Co-administration of multiple 10 mg doses of amlodipine with 80 mg of atorvastatin resulted in no significant change in the steady-state pharmacokinetic parameters of atorvastatin.
7.7 Simvastatin
Co-administration of multiple doses of 10 mg of amlodipine with 80 mg simvastatin resulted in a 77% increase in exposure to simvastatin compared to simvastatin alone. Limit the dose of simvastatin in patients on amlodipine to 20 mg daily.
7.8 digoxin
Co-administration of amlodipine with digoxin did not change serum digoxin levels or digoxin renal clearance in normal volunteers.
7.9 Ethanol (Alcohol)
Single and multiple 10 mg doses of amlodipine had no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of ethanol.
7.10 Warfarin
Co-administration of amlodipine with warfarin did not change the warfarin prothrombin response time.
7.11 CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Co-administration of a 180 mg daily dose of diltiazem with 5 mg amlodipine in elderly hypertensive patients resulted in a 60% increase in amlodipine systemic exposure. Erythromycin co-administration in healthy volunteers did not significantly change amlodipine systemic exposure. However, strong inhibitors of CYP3A4 (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, ritonavir) may increase the plasma concentrations of amlodipine to a greater extent. Monitor for symptoms of hypotension and edema when amlodipine is co-administered with CYP3A4 inhibitors.
7.12 CYP3A4 Inducers
No information is available on the quantitative effects of CYP3A4 inducers on amlodipine. Blood pressure should be closely monitored when amlodipine is co-administered with CYP3A4 inducers.
7.13 Cyclosporine
A prospective study in renal transplant patients (N=11) showed on an average of 40% increase in trough cyclosporine levels when concomitantly treated with amlodipine.
7.14 Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Amlodipine should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the risk to the fetus.
No evidence of teratogenicity or other embryo/fetal toxicity was found when pregnant rats and rabbits were treated orally with amlodipine maleate at doses up to 10 mg amlodipine/kg/day (respectively, 8 times2 and 23 times2 the maximum recommended human dose of 10 mg on a mg/m2 basis) during their respective periods of major organogenesis. However, litter size was significantly decreased (by about 50%) and the number of intrauterine deaths was significantly increased (about 5-fold) in rats receiving amlodipine maleate at a dose equivalent to 10 mg amlodipine/kg/day for 14 days before
mating and throughout mating and gestation. Amlodipine maleate has been shown to prolong both the gestation period and the duration of labor in rats at this dose.
2
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
Amlodipine besylate tablets,USP (2.5 to 5 mg daily) is effective in lowering blood pressure in patients 6 to 17 years [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Effect of amlodipine on blood pressure in patients less than 6 years of age is not known.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of amlodipine did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy. Elderly patients have decreased clearance of amlodipine with a resulting increase of AUC of approximately 40 to 60%, and a lower initial dose may be required [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
2
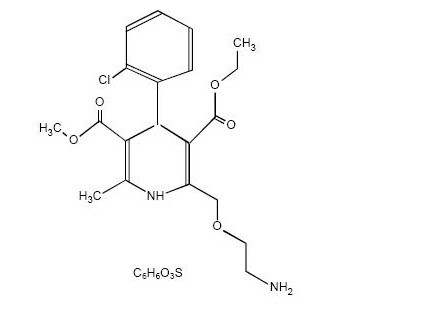
11 DESCRIPTION
202525663
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
in vitro
in vitro
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism
Ex vivo
12.4 Pediatric Patients
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
2 3 2 3
32
3
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Effects in Hypertension
Adult Patients
Pediatric Patients
14.2 Effects in Chronic Stable Angina
14.3 Effects in Vasospastic Angina
14.4 Effects in Documented Coronary Artery Disease
Figure 1 -Kaplan-Meier Analysis of Composite Clinical Outcomes for Amlodipine versus Placebo
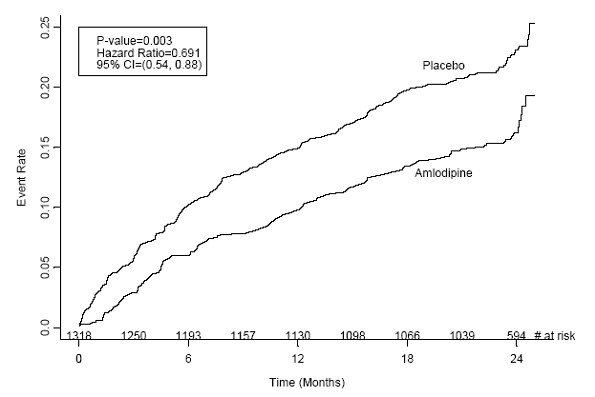
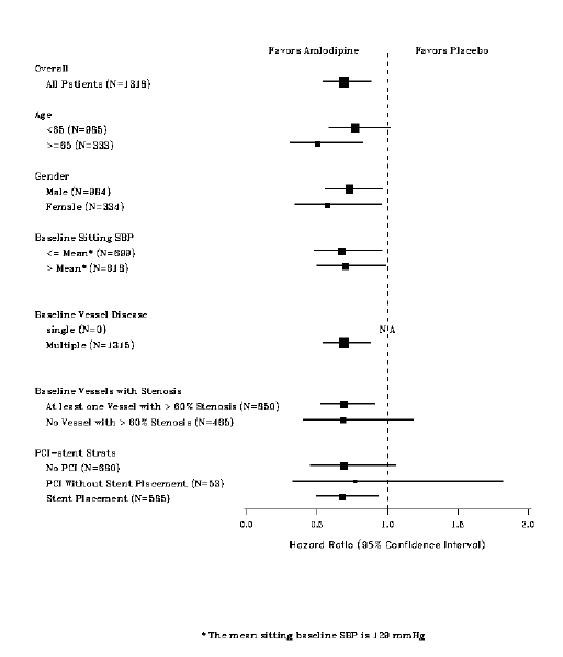
Figure 2 – Effects on Primary Endpoint of Amlodipine versus Placebo across Sub-Groups
| Clinical Outcomes N (%) |
Amlodipine (N=663) |
Placebo (N=655) |
Risk Reduction (p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Composite CV Endpoint |
110 (16.6) |
151 (23.1) |
31% (0.003) |
| Hospitalization for Angina* |
51 (7.7) |
84 (12.8) |
42% (0.002) |
| Coronary Revascularization* |
78 (11.8) |
103 (15.7) |
27% (0.033) |
| *Total patients with these events |
|||
14.5 Studies in Patients with Heart Failure
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 2.5 mg Tablets
16.2 5 mg Tablets
16.3 10 mg Tablets
16.4 Storage
ALKEM LABORATORIES LTD.
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
AMLODIPINE BESYLATE TABLETS, USP 2.5 mg, 5 mg, and 10 mg
What is amlodipine besylate?
High Blood Pressure (hypertension)
Angina
Who should not use amlodipine besylate?
What should I tell my doctor before taking amlodipine besylate?
- ever had heart disease
- ever had liver problems
- are pregnant, or plan to become pregnant. Your doctor will decide if amlodipine besylate is the best treatment for you.
- are breastfeeding. Do not breastfeed while taking amlodipine besylate. You can stop breastfeeding or take a different medicine.
How should I take amlodipine besylate tablets, USP?
- Take amlodipine besylate tablets, USP once a day, with or without food.
- It may be easier to take your dose if you do it at the same time every day, such as with breakfast or dinner, or at bedtime. Do not take more than one dose of amlodipine besylate at a time.
- If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. Do not take amlodipine besylate if it has been more than 12 hours since you missed your last dose. Wait and take the next dose at your regular time.
- Other medicines: You can use nitroglycerin and amlodipine besylate together. If you take nitroglycerin for angina, don't stop taking it while you are taking amlodipine besylate.
- While you are taking amlodipine besylate, do not stop taking your other prescription medicines, including any other blood pressure medicines, without talking to your doctor.
- If you took too much amlodipine besylate, call your doctor or Poison Control Center, or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What should I avoid while taking amlodipine besylate?
- Do not breastfeed. It is not known if amlodipine besylate will pass through your milk.
- Do not start any new prescription or non-prescription medicines or supplements, unless you check with your doctor first.
What are the possible side effects of amlodipine besylate?
- swelling of your legs or ankles
- tiredness, extreme sleepiness
- stomach pain, nausea
- dizziness
- flushing (hot or warm feeling in your face)
- arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat)
- heart palpitations (very fast heartbeat)
How do I store amlodipine besylate tablets, USP?
General advice about amlodipine besylate tablets, USP
ALKEM LABORATORIES LTD.
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 2.5 mg Tablets

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5 mg Tablets

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg Tablets

Amlodipine BesylateAmlodipine besylate TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amlodipine BesylateAmlodipine besylate TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amlodipine BesylateAmlodipine besylate TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||